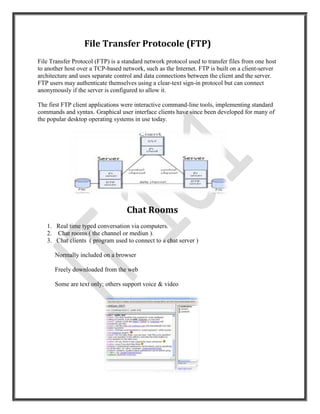
The document discusses the history and services provided by the internet. It describes how the internet began as a research project called ARPANET in the 1960s and expanded to include private networks, leading to the development of common network protocols. Today, over 2 billion people worldwide use internet services. The key services discussed include electronic mail, the World Wide Web, file transfer protocol, chat rooms, mailing lists, instant messaging, online chat, and newsgroups. Each service is briefly described.