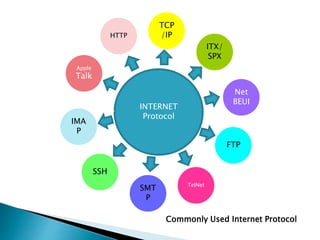
1. A protocol is a set of rules that govern communication between computers on a network. Internet protocols specify how data is addressed, transmitted, and acknowledged.
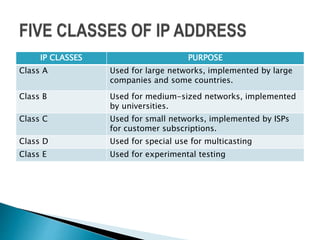
2. An IP address is a unique number assigned to each device on a network to identify it. An IP address consists of 32 binary bits grouped into four octets for human readability.
3. Common internet protocols include TCP/IP for exchanging data packets, HTTP for web content, SMTP for sending email, and FTP for file transfer.