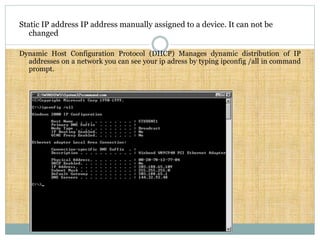
A protocol is a set of rules for exchanging data between two or more computers. Common internet protocols include SMTP for email, FTP for file transfers. The TCP/IP model uses protocols like IP and TCP. IP is an unreliable connectionless protocol that does not guarantee delivery. TCP provides reliable data delivery through a connection-oriented approach requiring a connection be established before transmitting data. Common TCP/IP application layer protocols are Telnet, FTP, SMTP, and SNMP for network management. Devices on a TCP/IP network are assigned unique 32-bit IP addresses divided into four octets separated by periods, which can be static or dynamically assigned by DHCP.