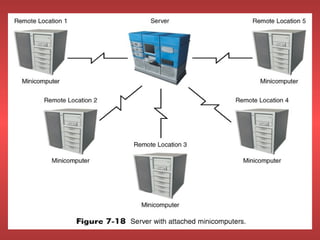
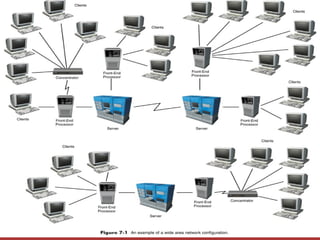
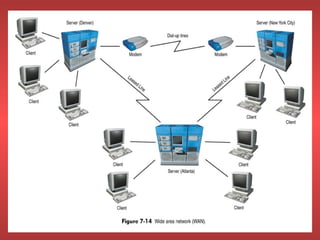
Networks connect two or more computers using various mediums like cables or wireless signals. They allow for sharing of files, data, and applications between systems without needing to physically transfer anything. Networks can be configured in a client-server model where some computers act as servers providing resources and other computers act as clients accessing those resources. Alternatively, networks can use a peer-to-peer model where each computer both acts as a client and server, allowing all systems to share directly. Networks can operate within a single location or span multiple geographic areas. Hardware like network interface cards and cables form the physical infrastructure while networking software manages communication and resource sharing.