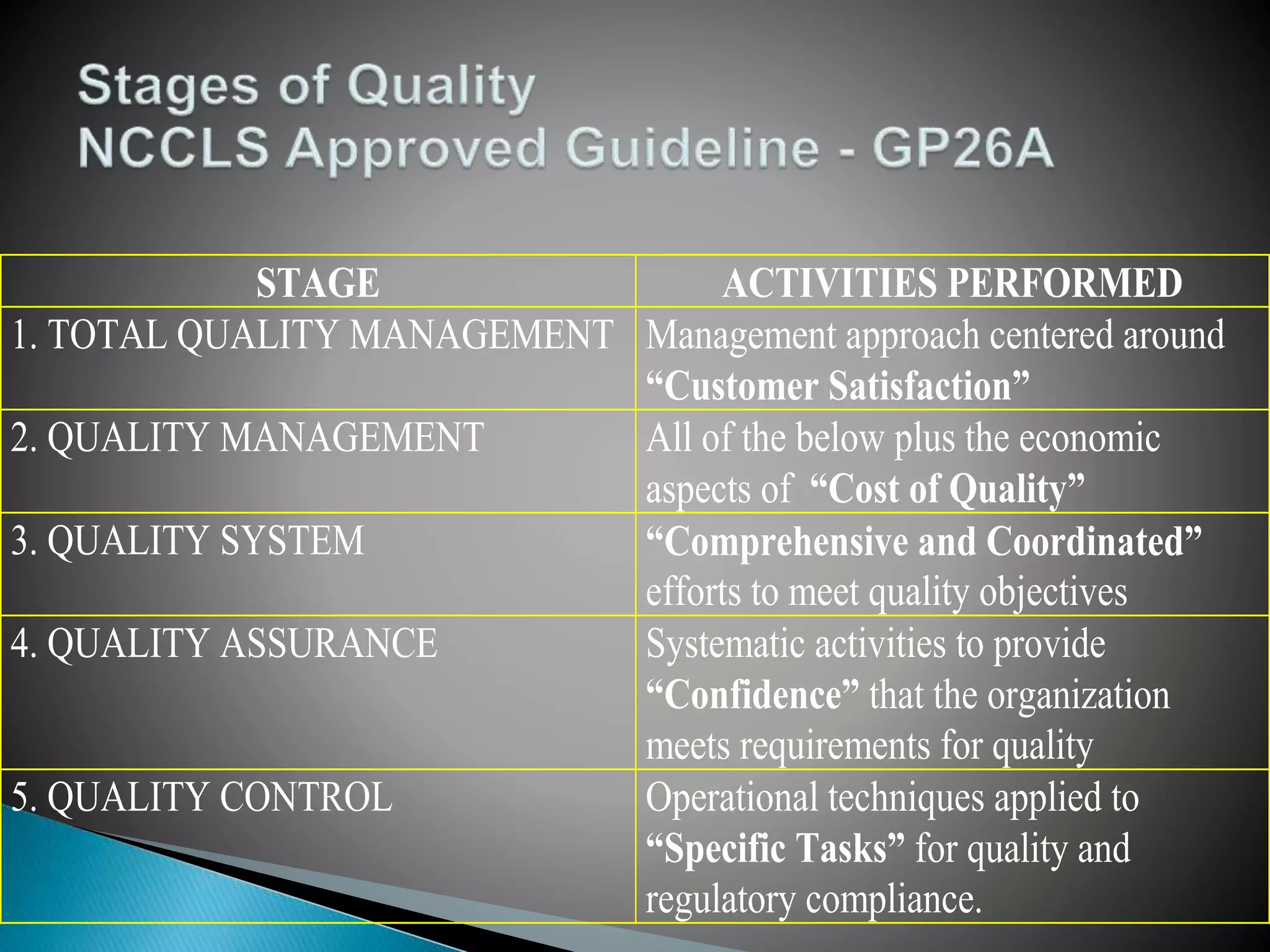
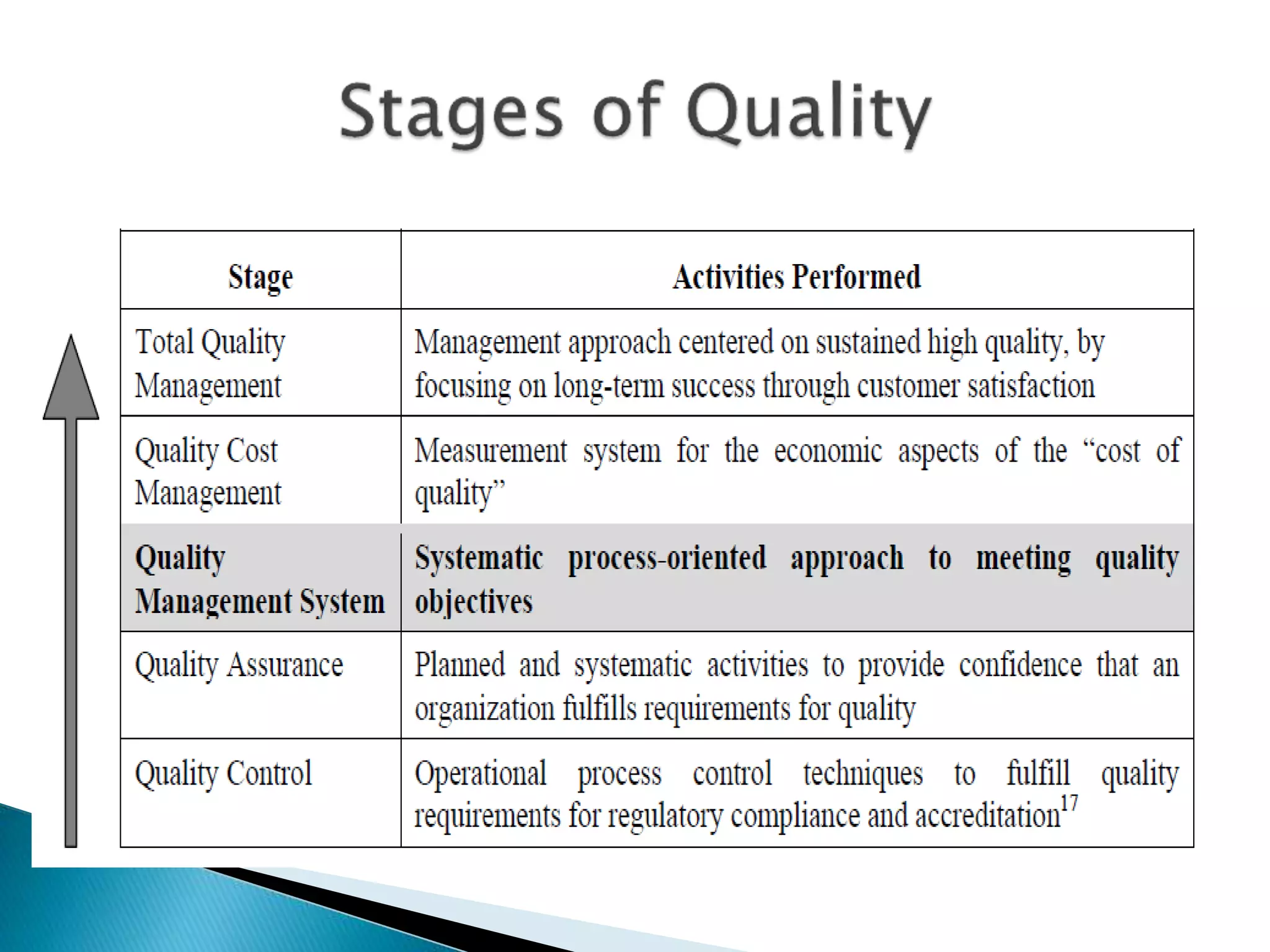
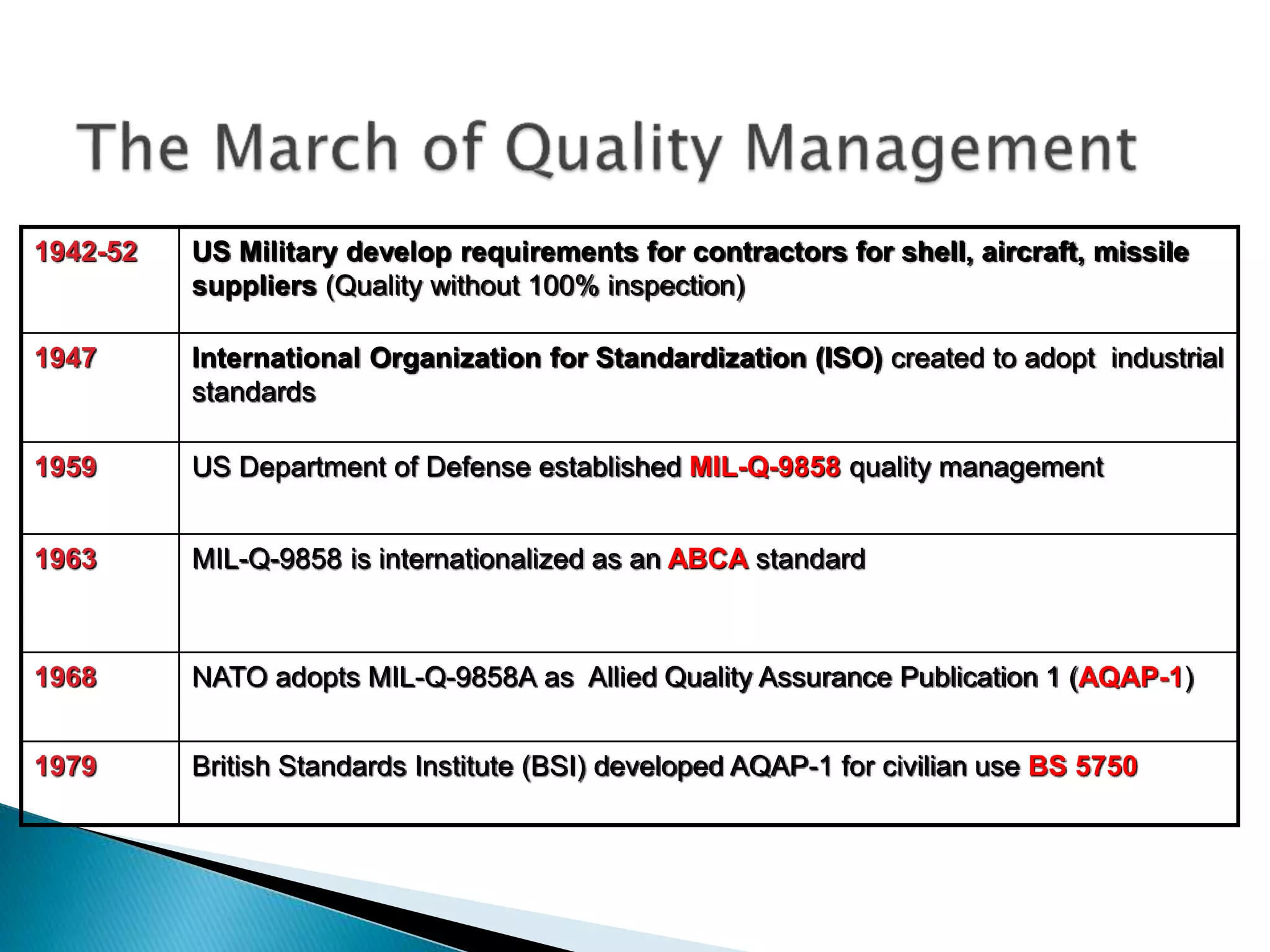
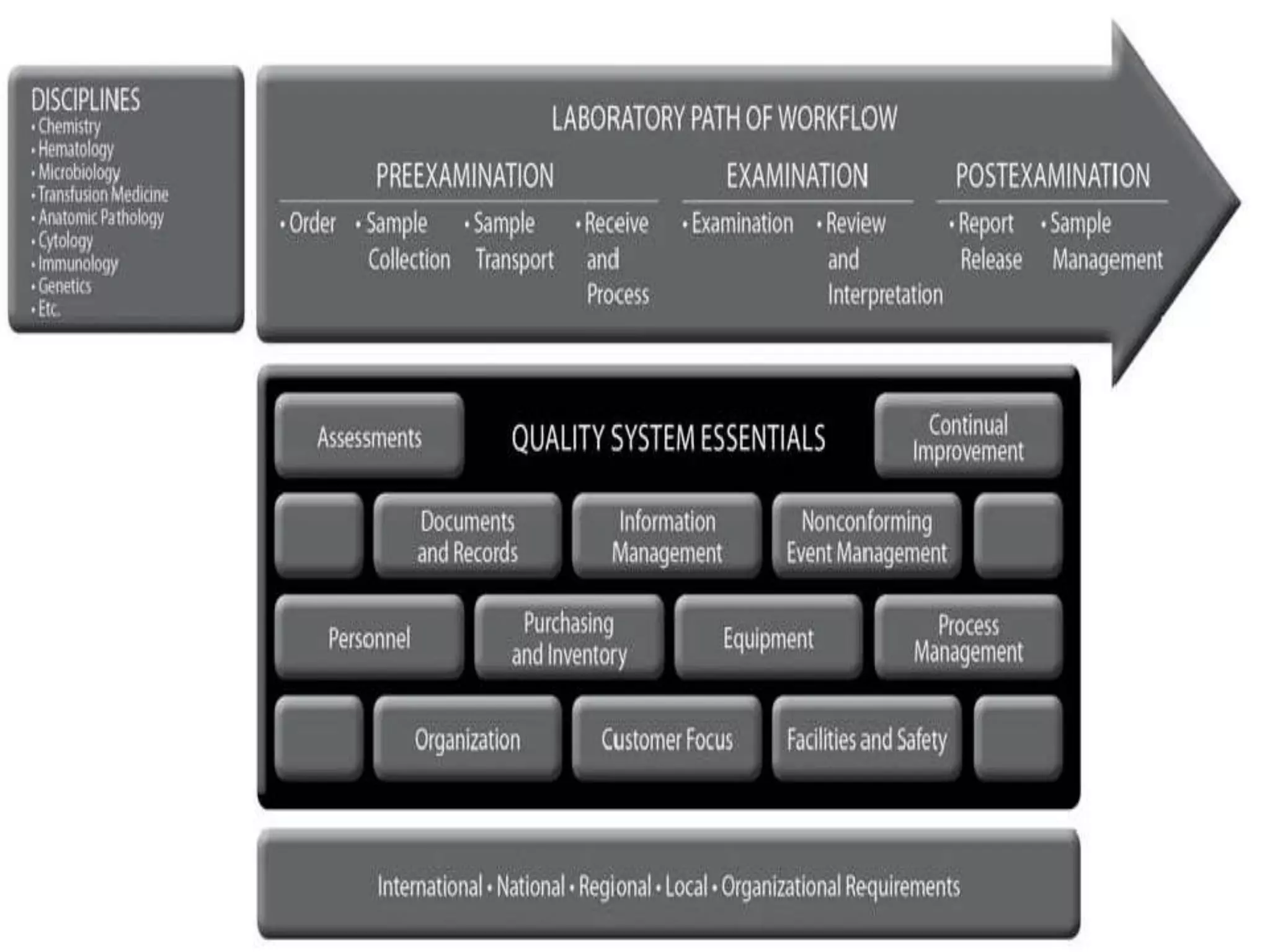
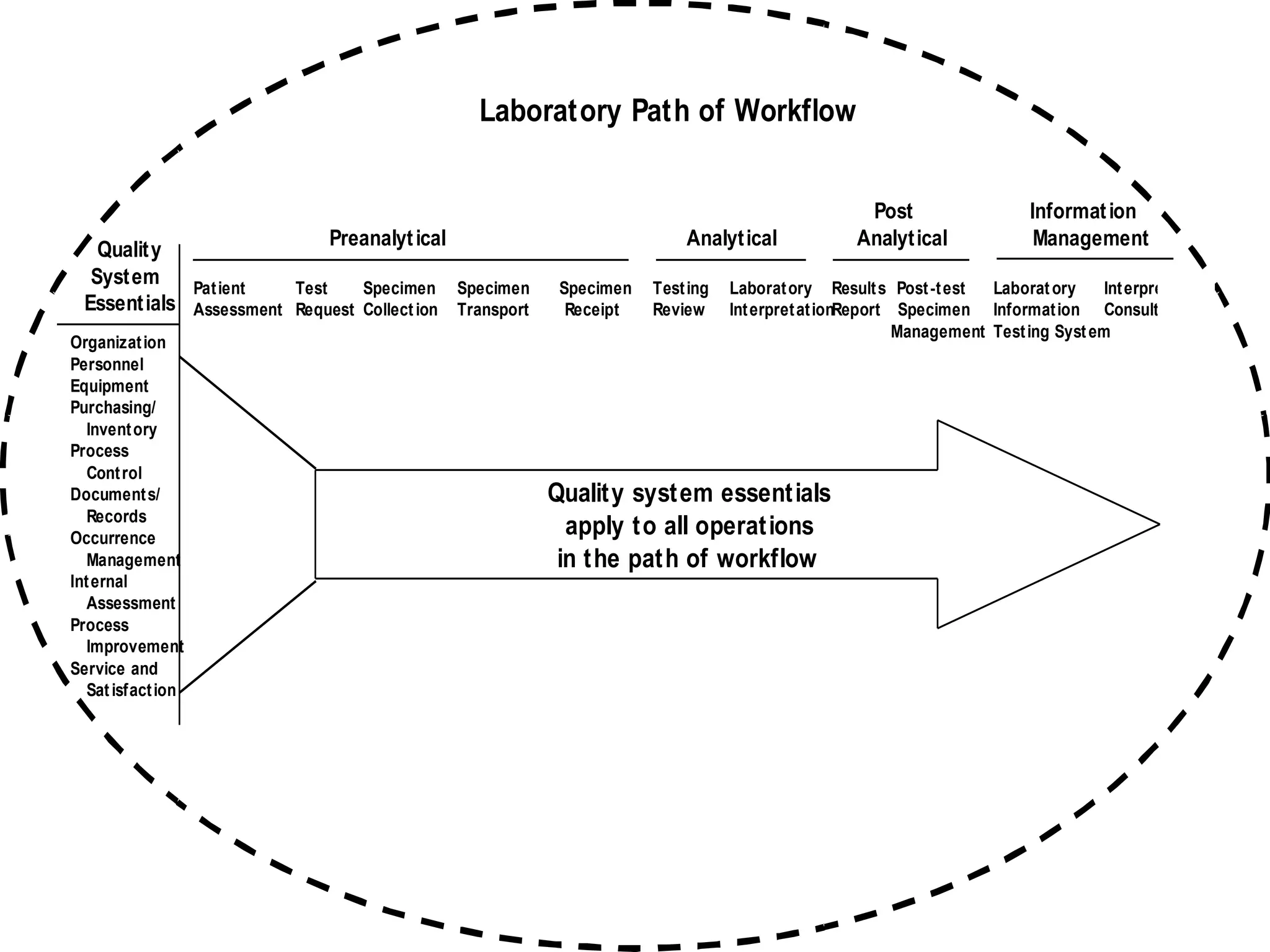
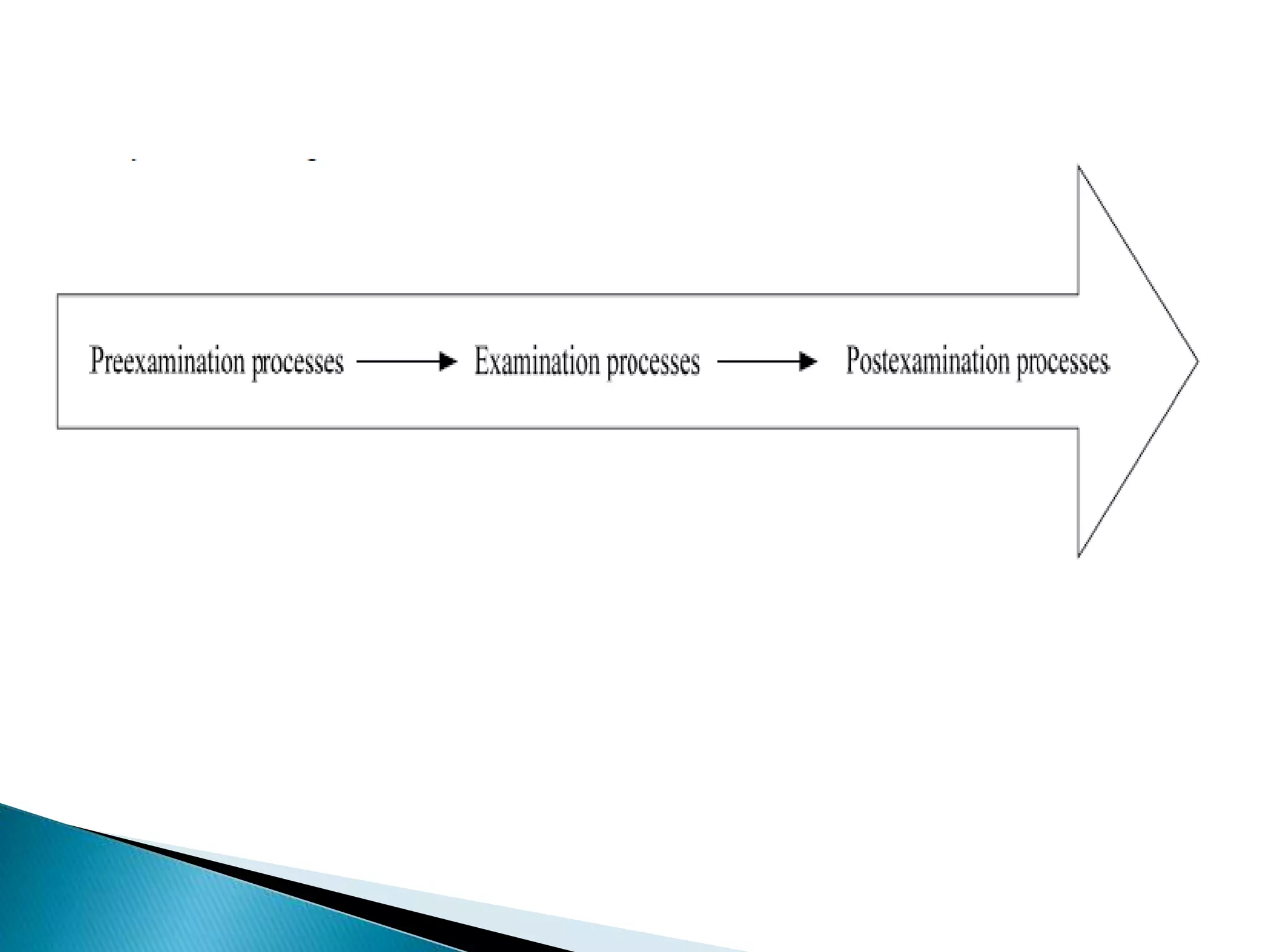
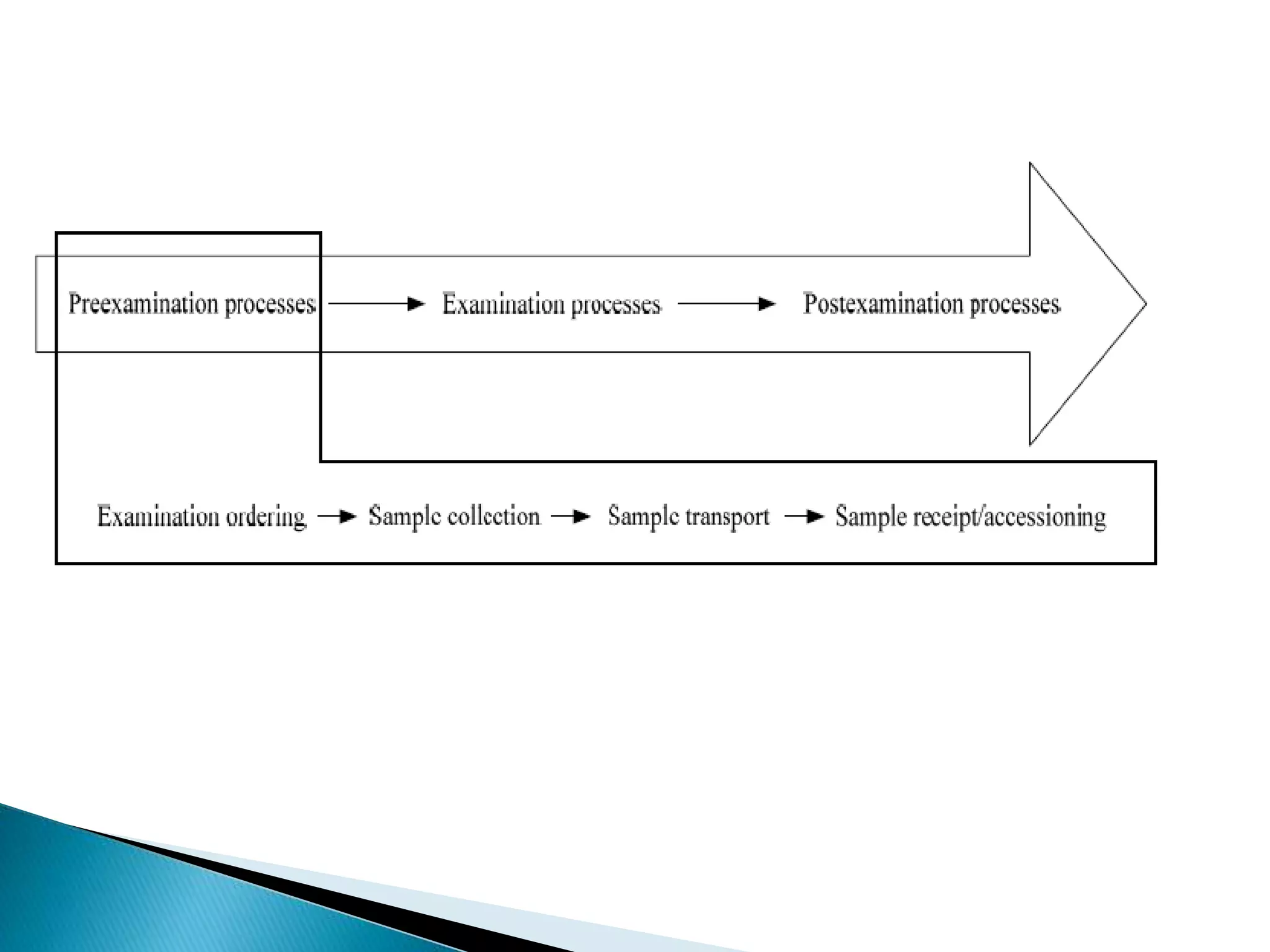
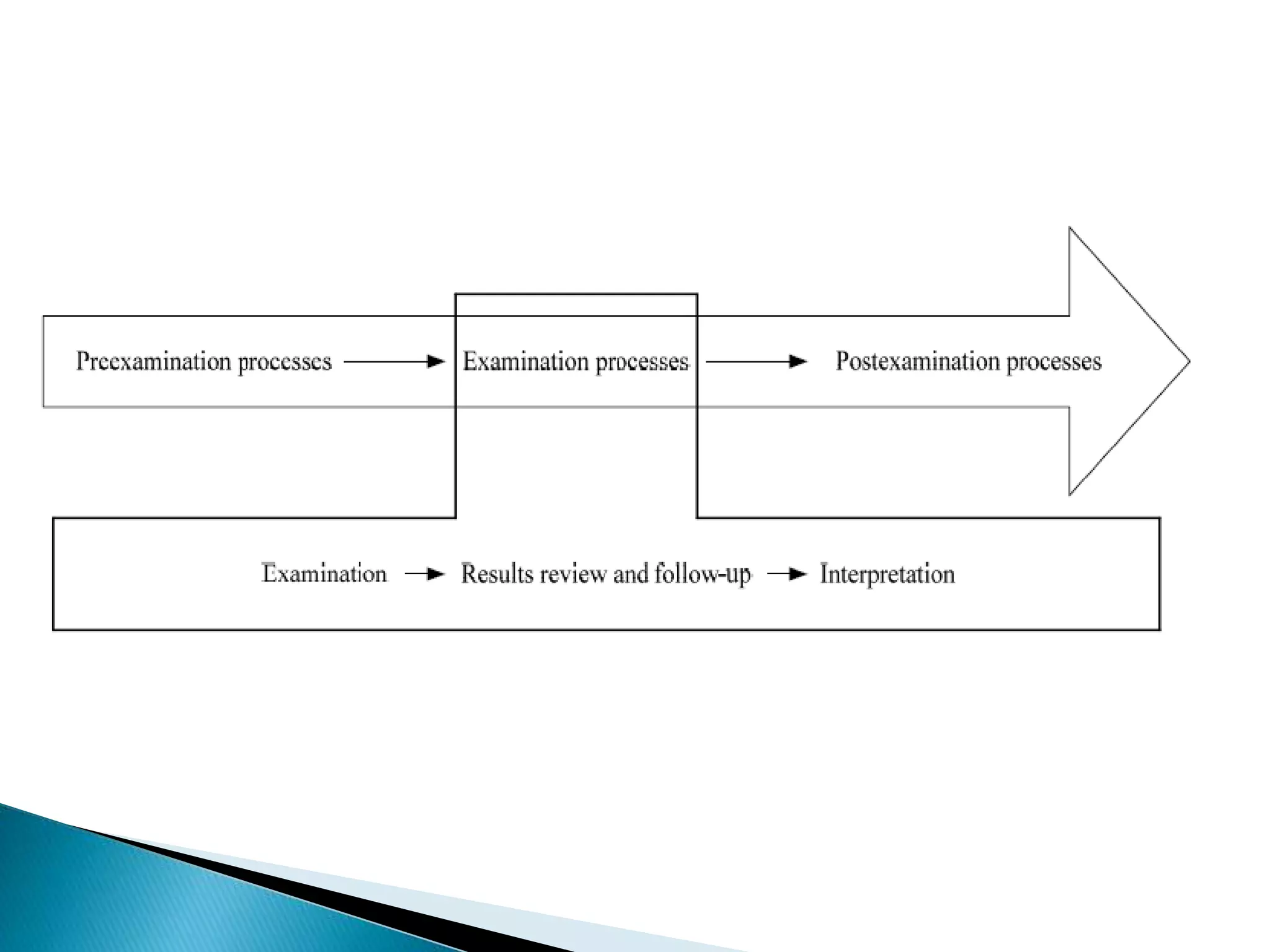
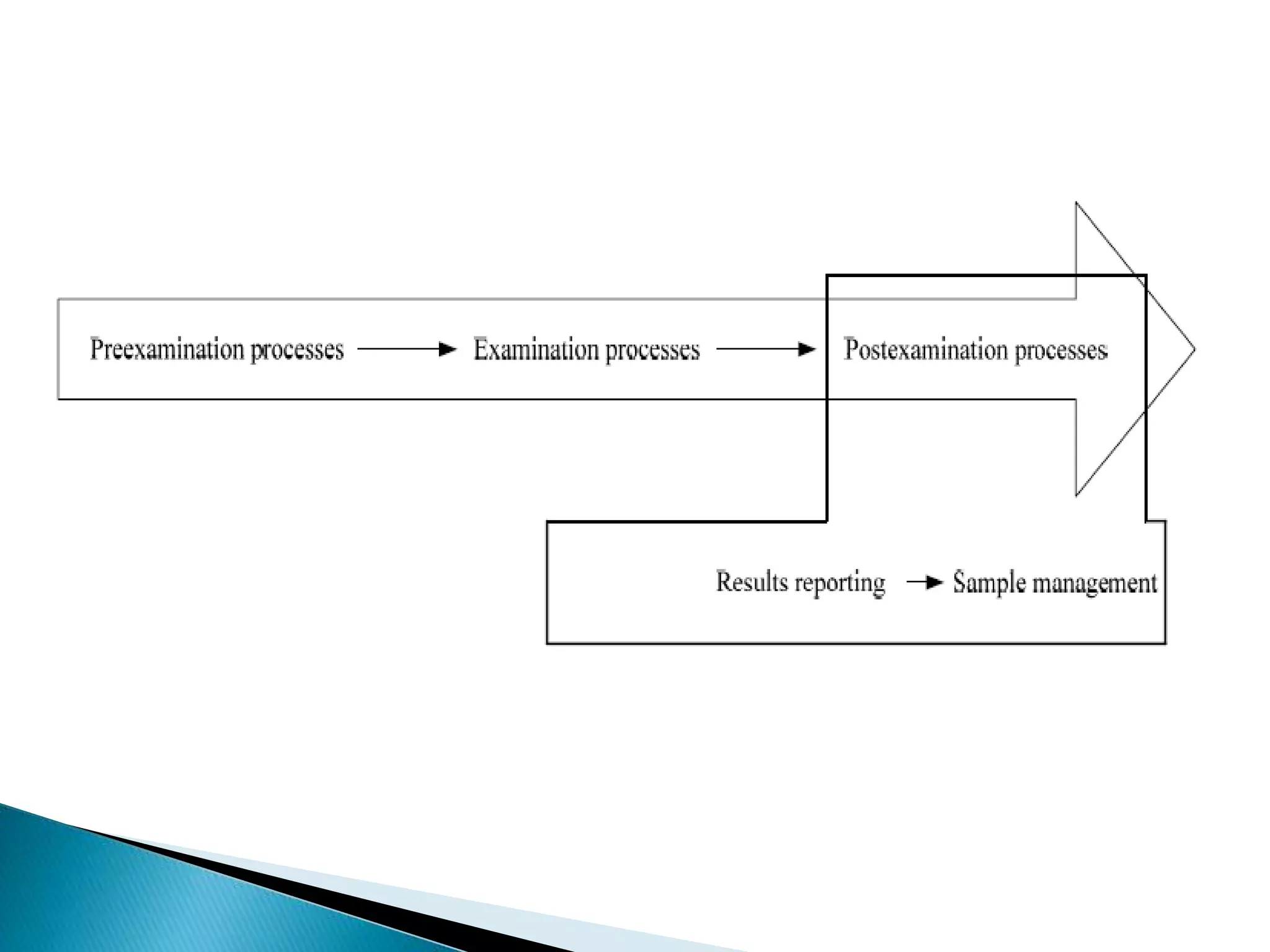
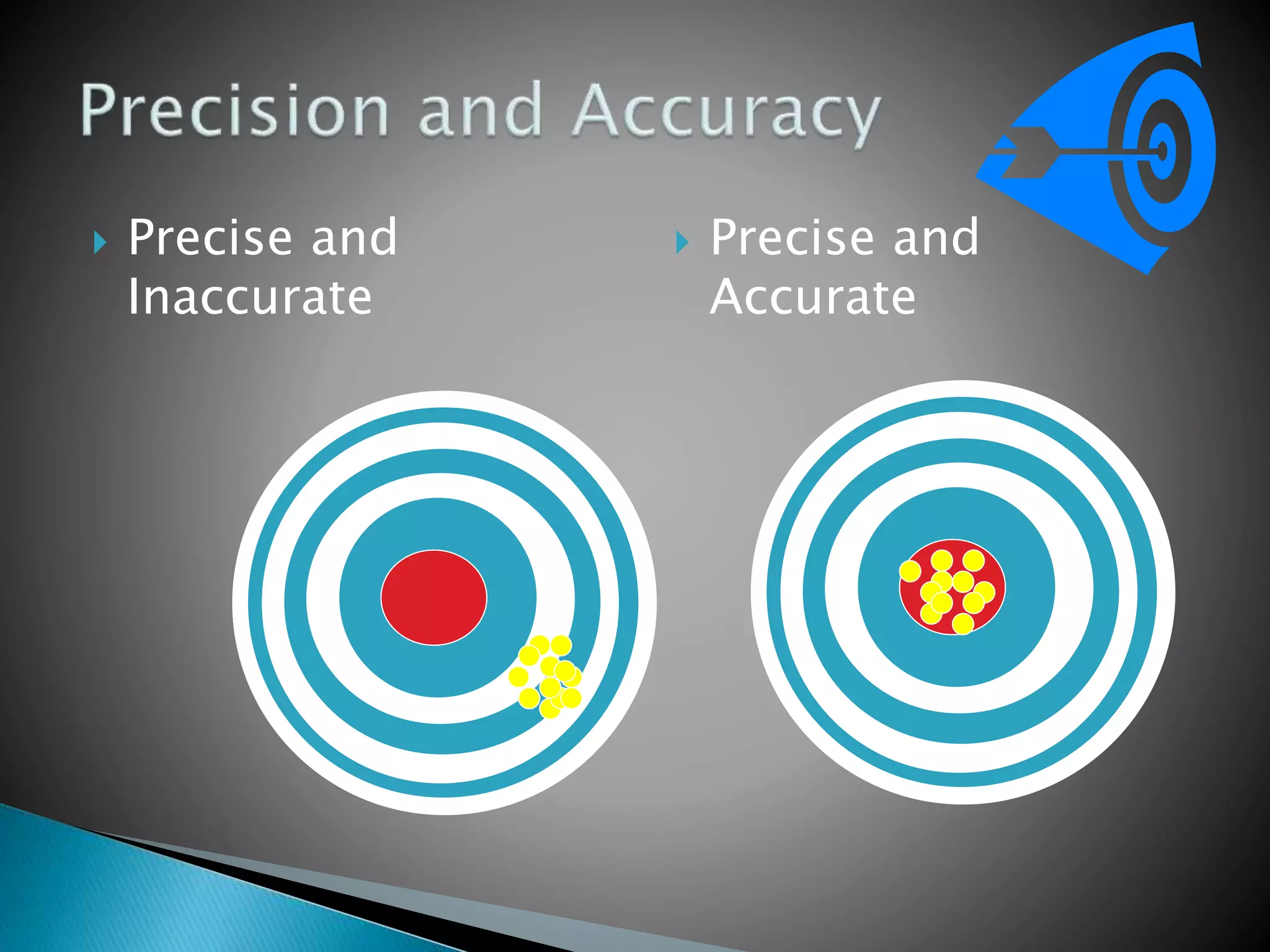
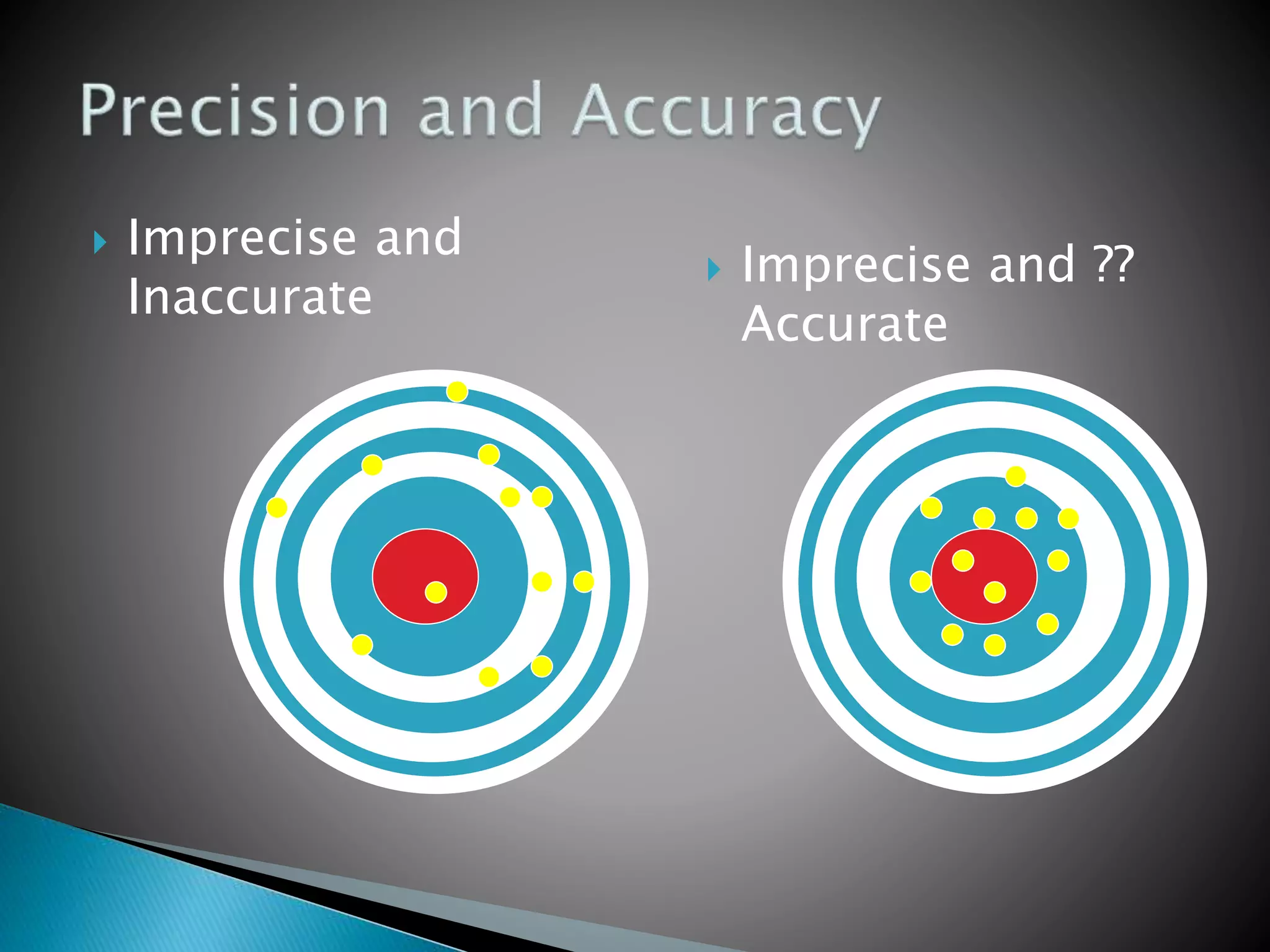
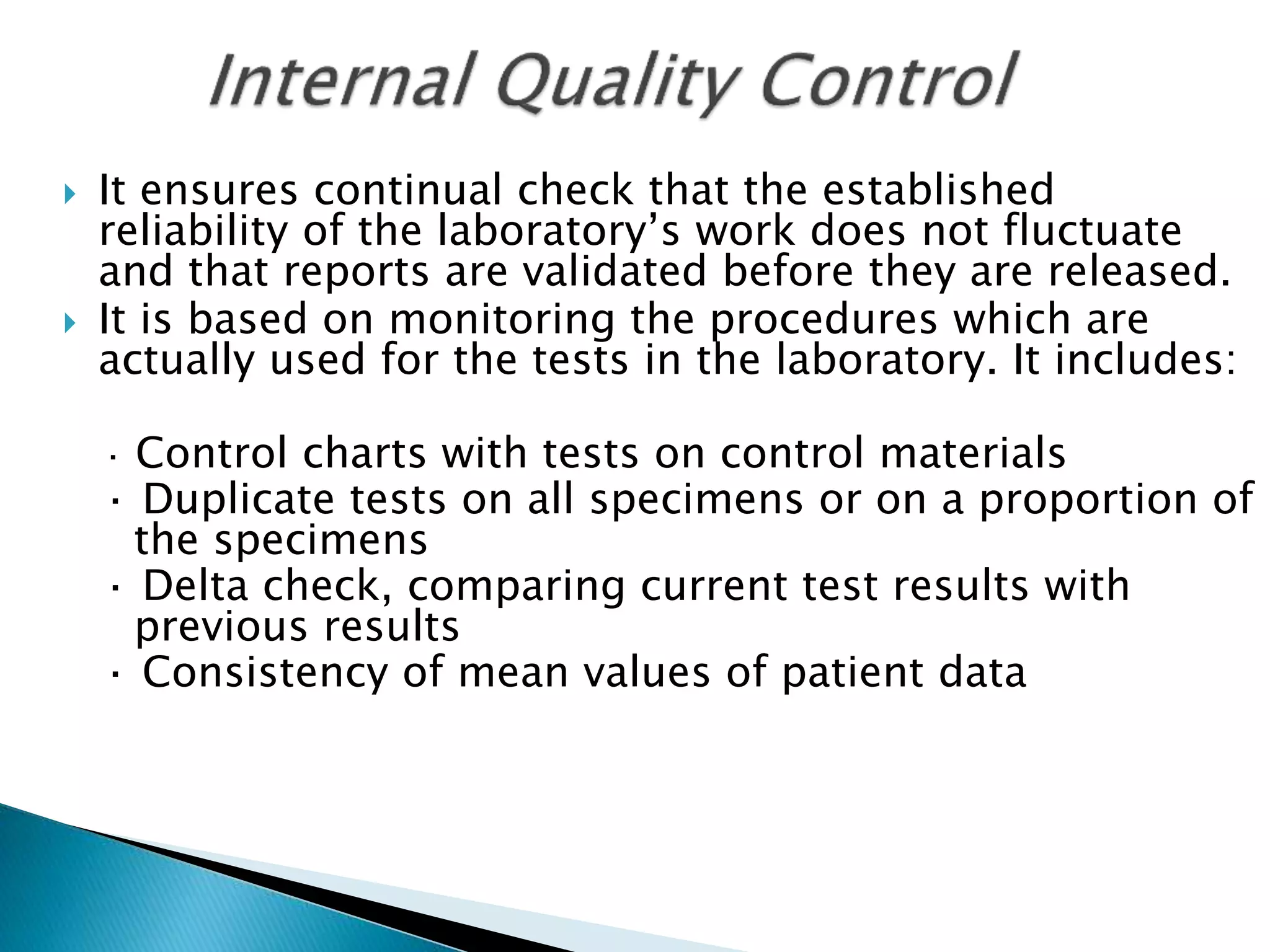
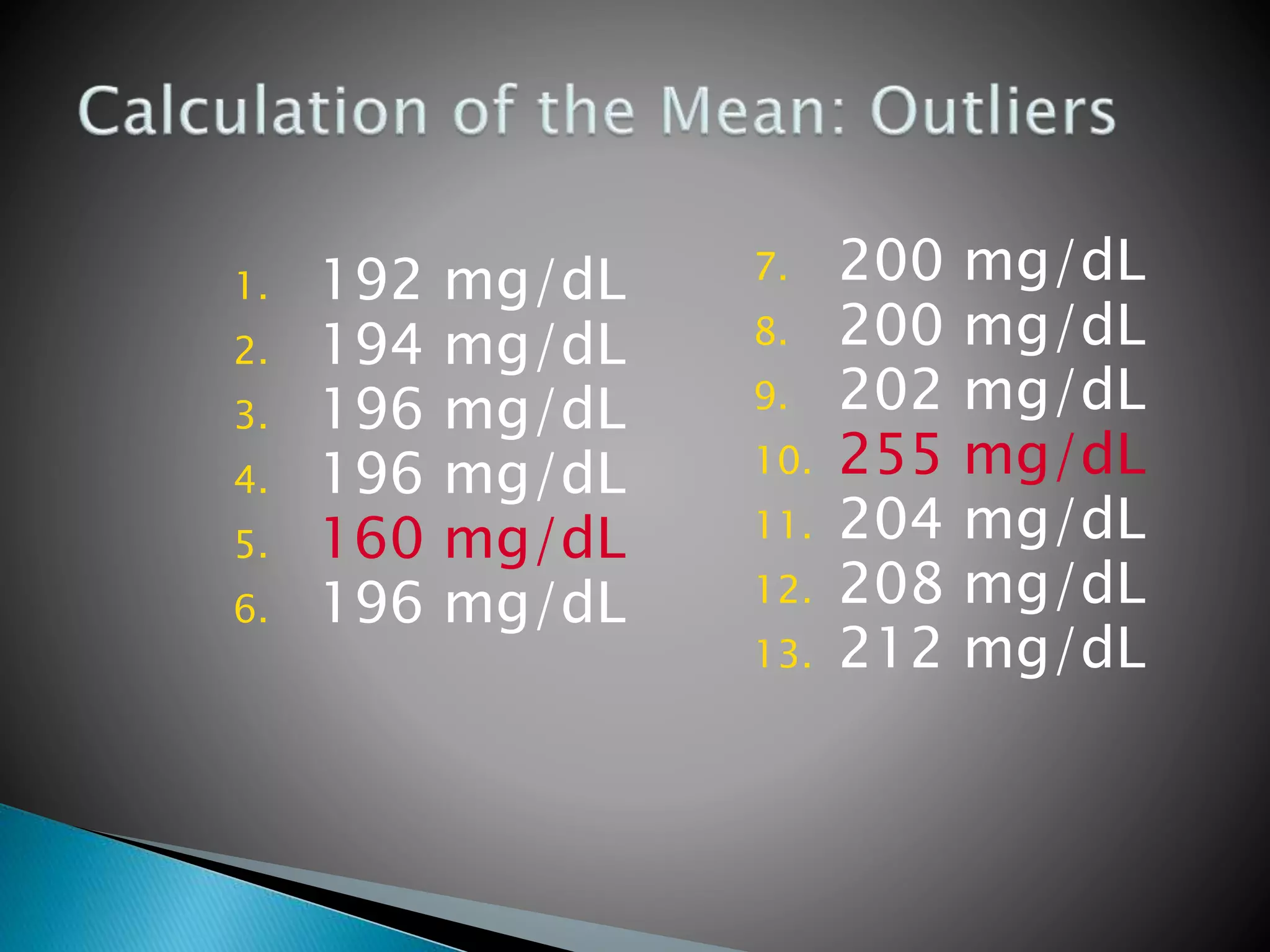
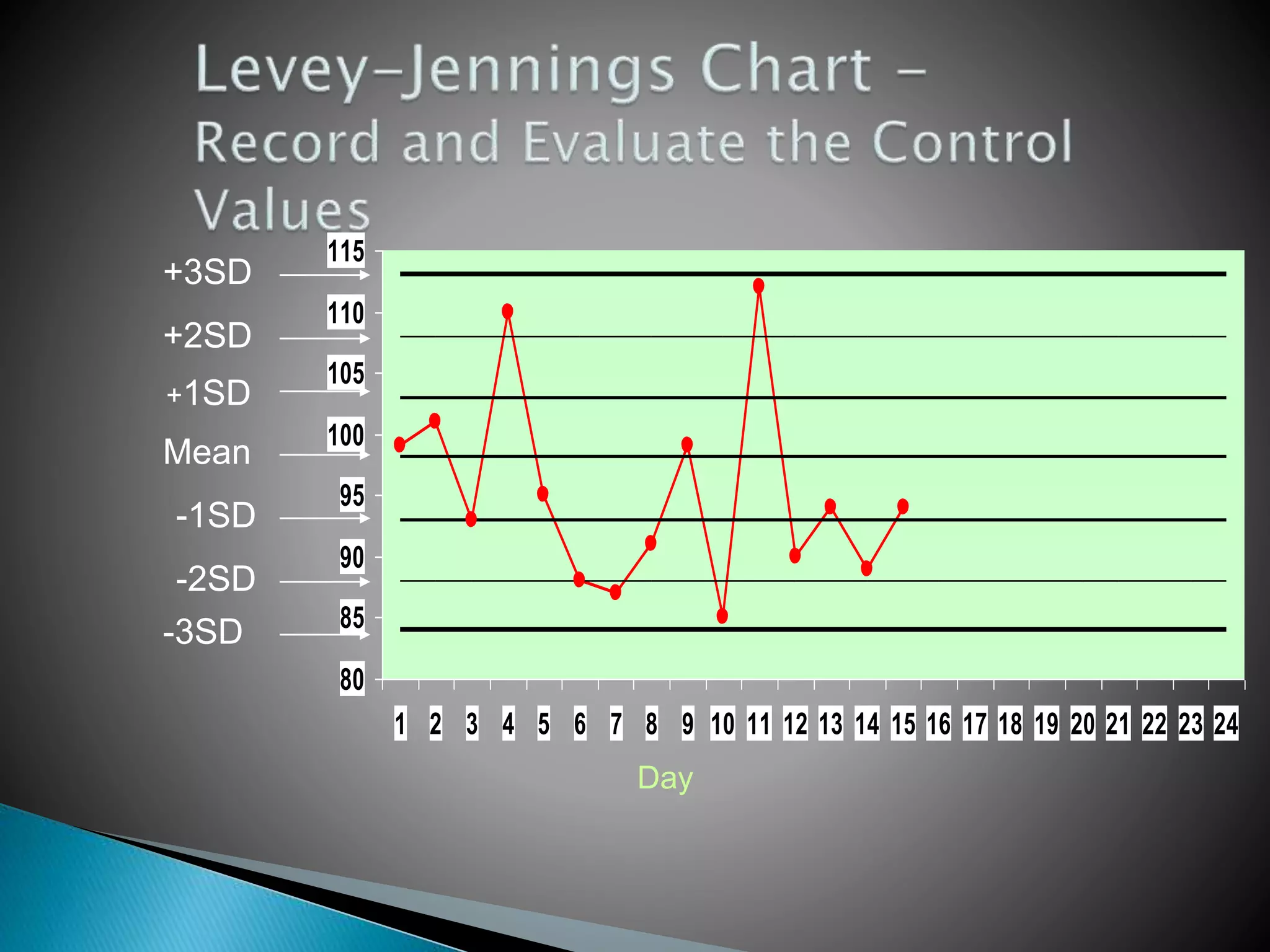
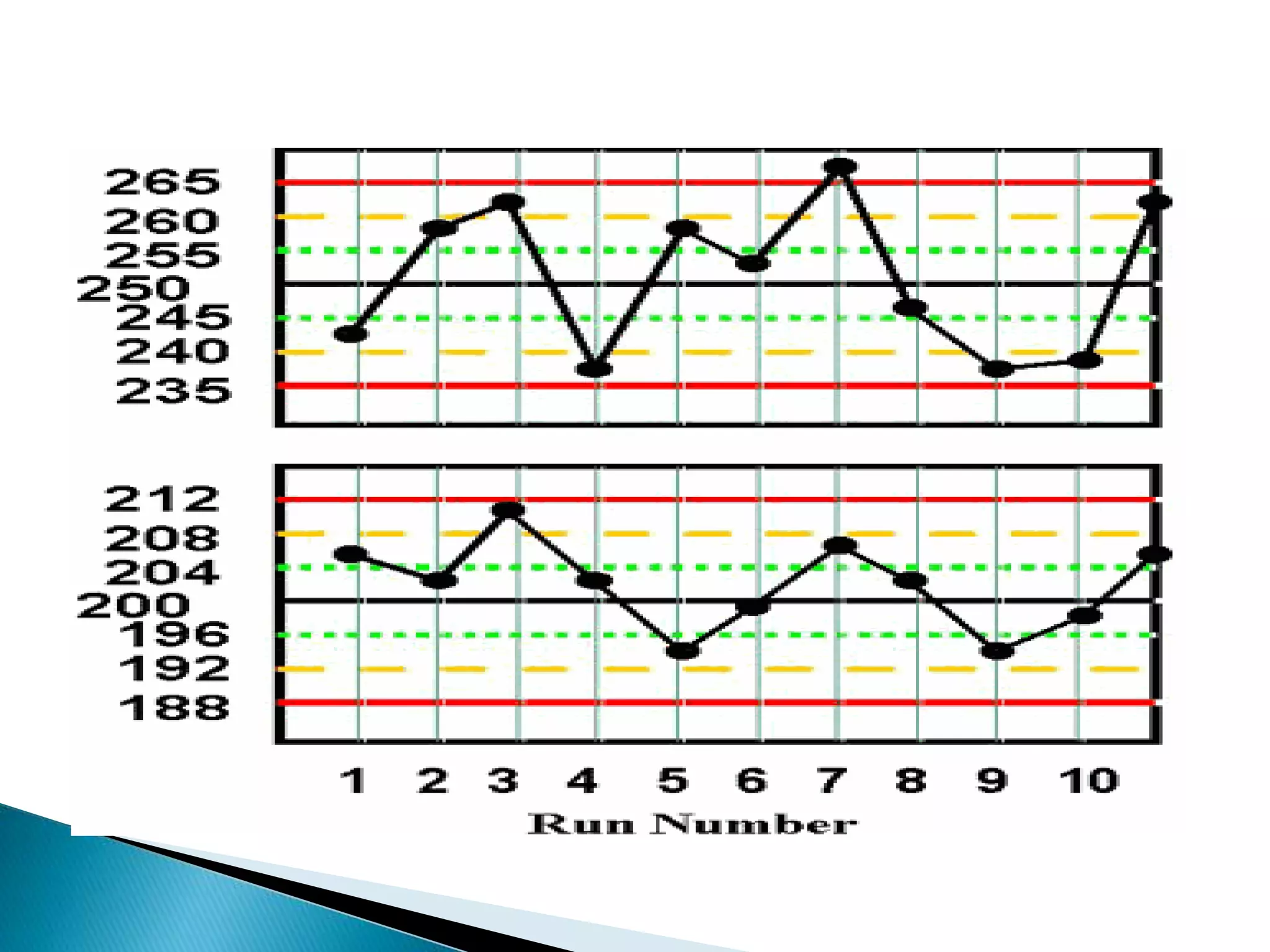
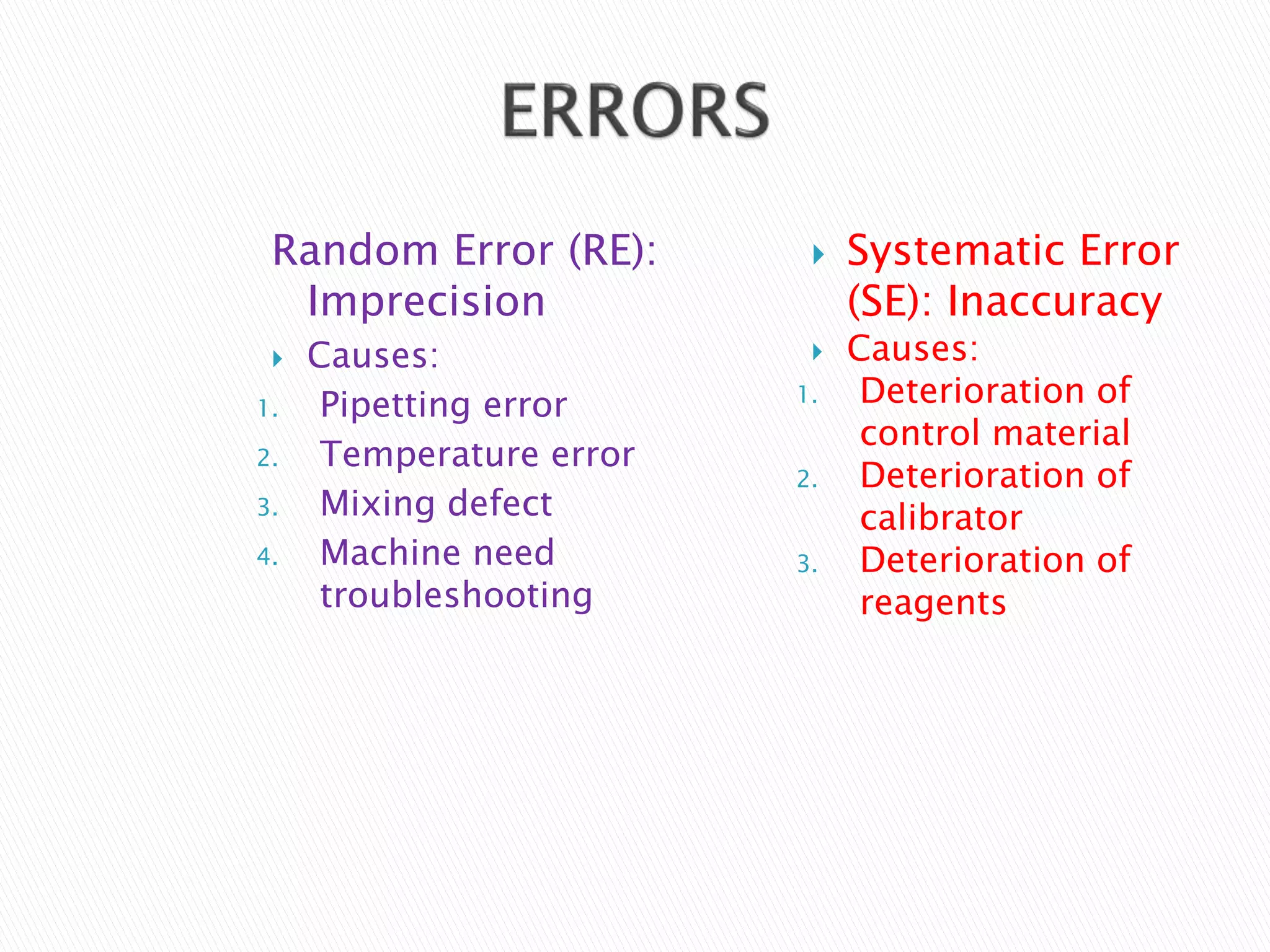
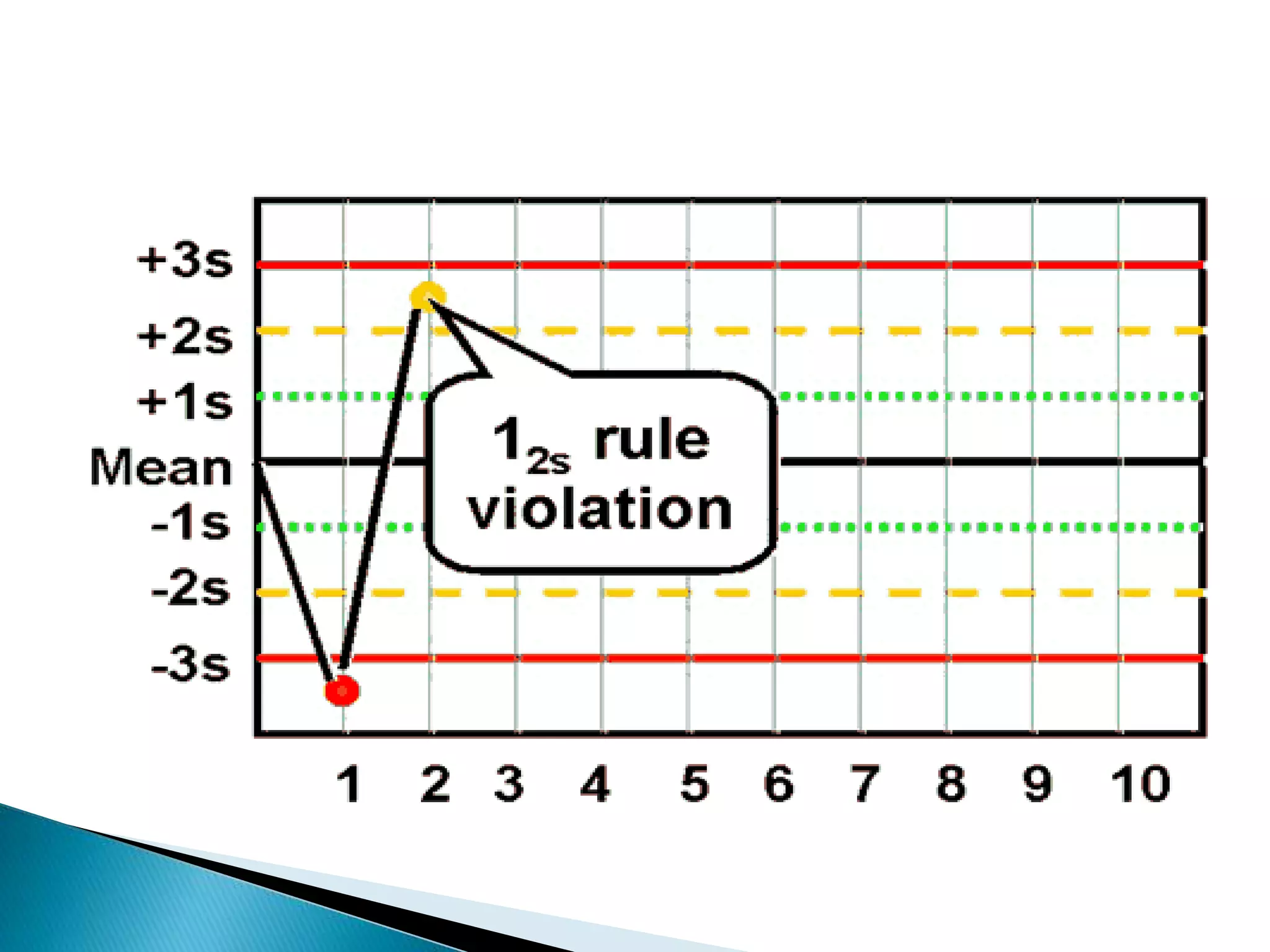
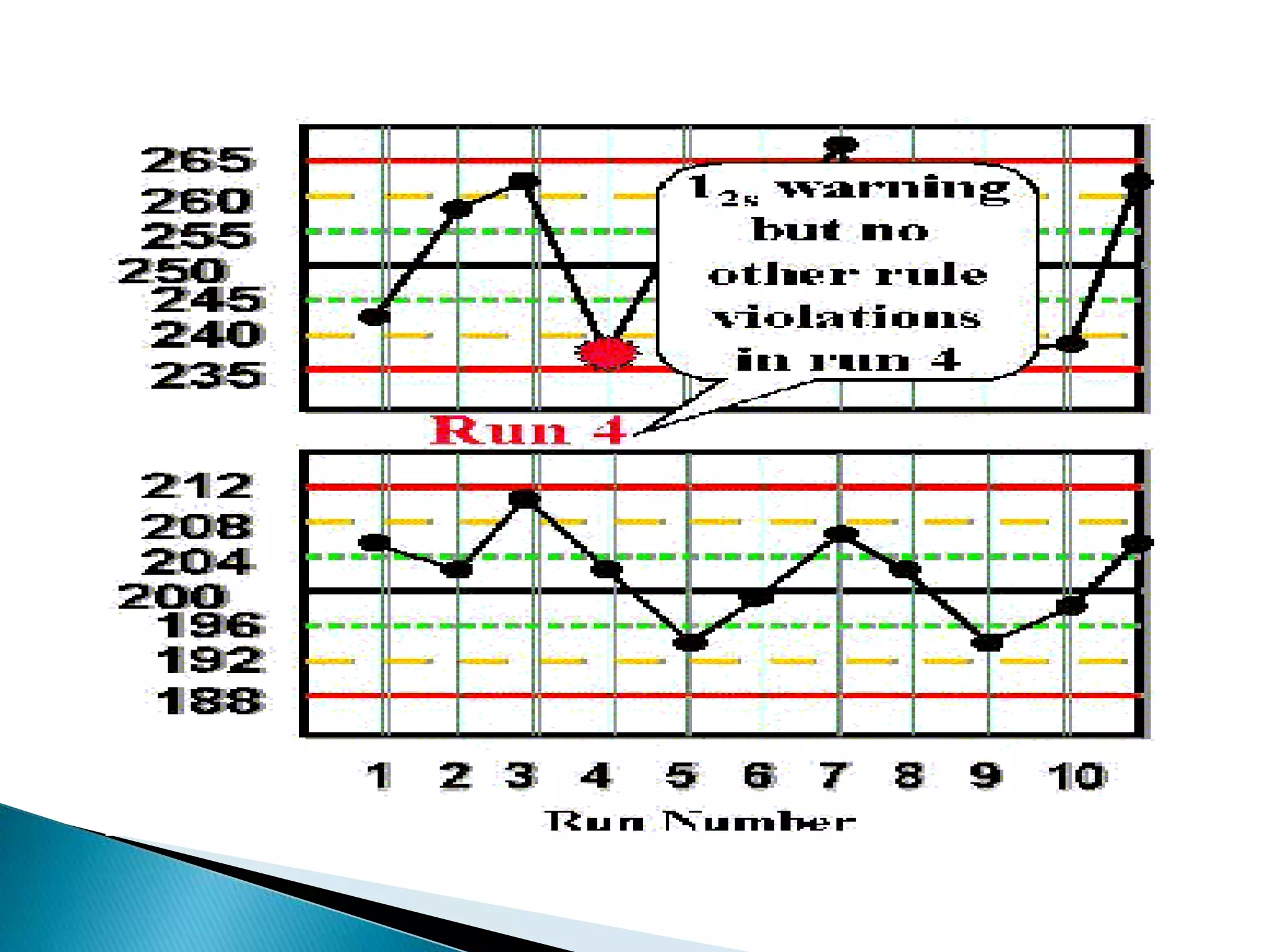
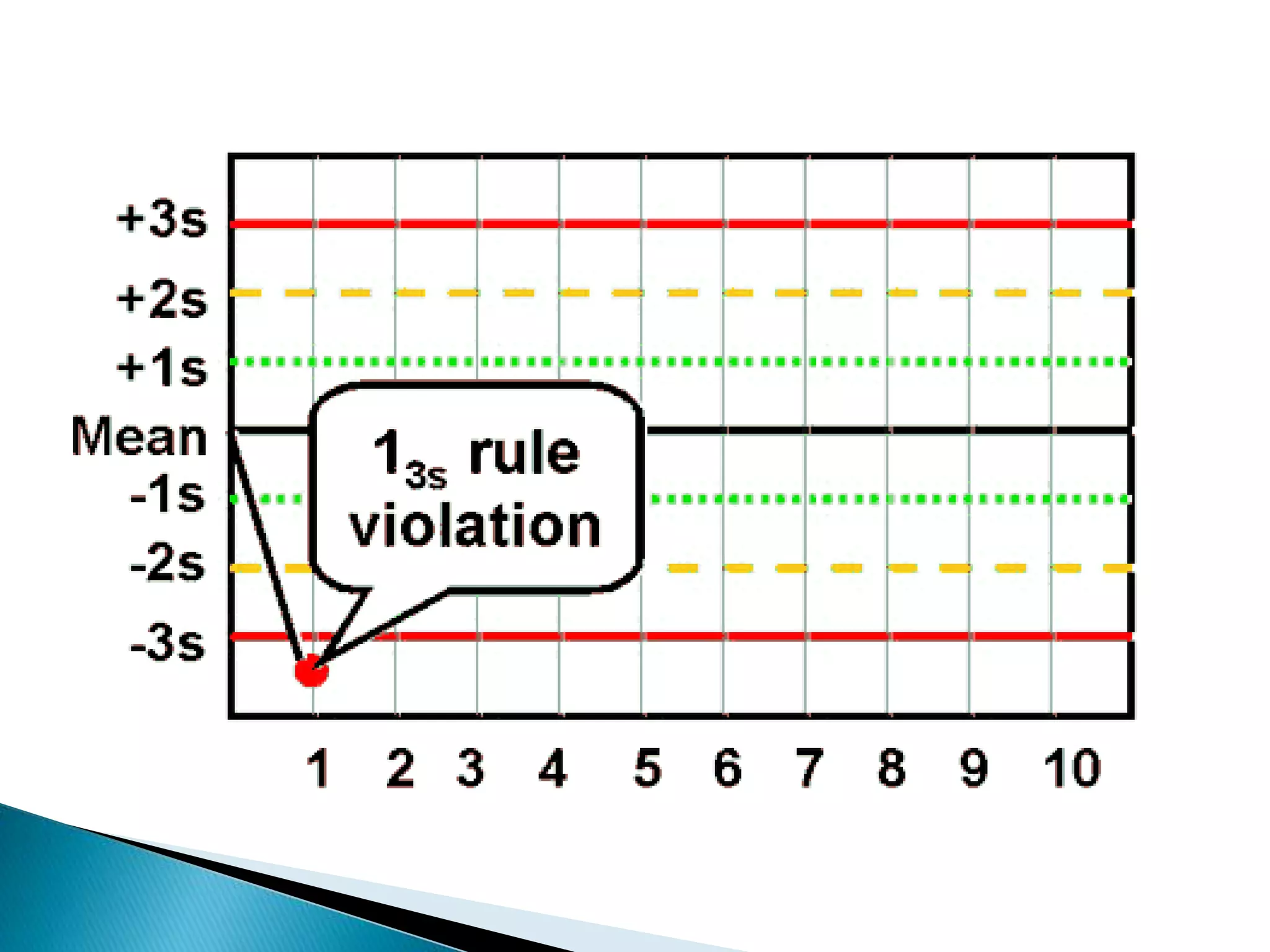
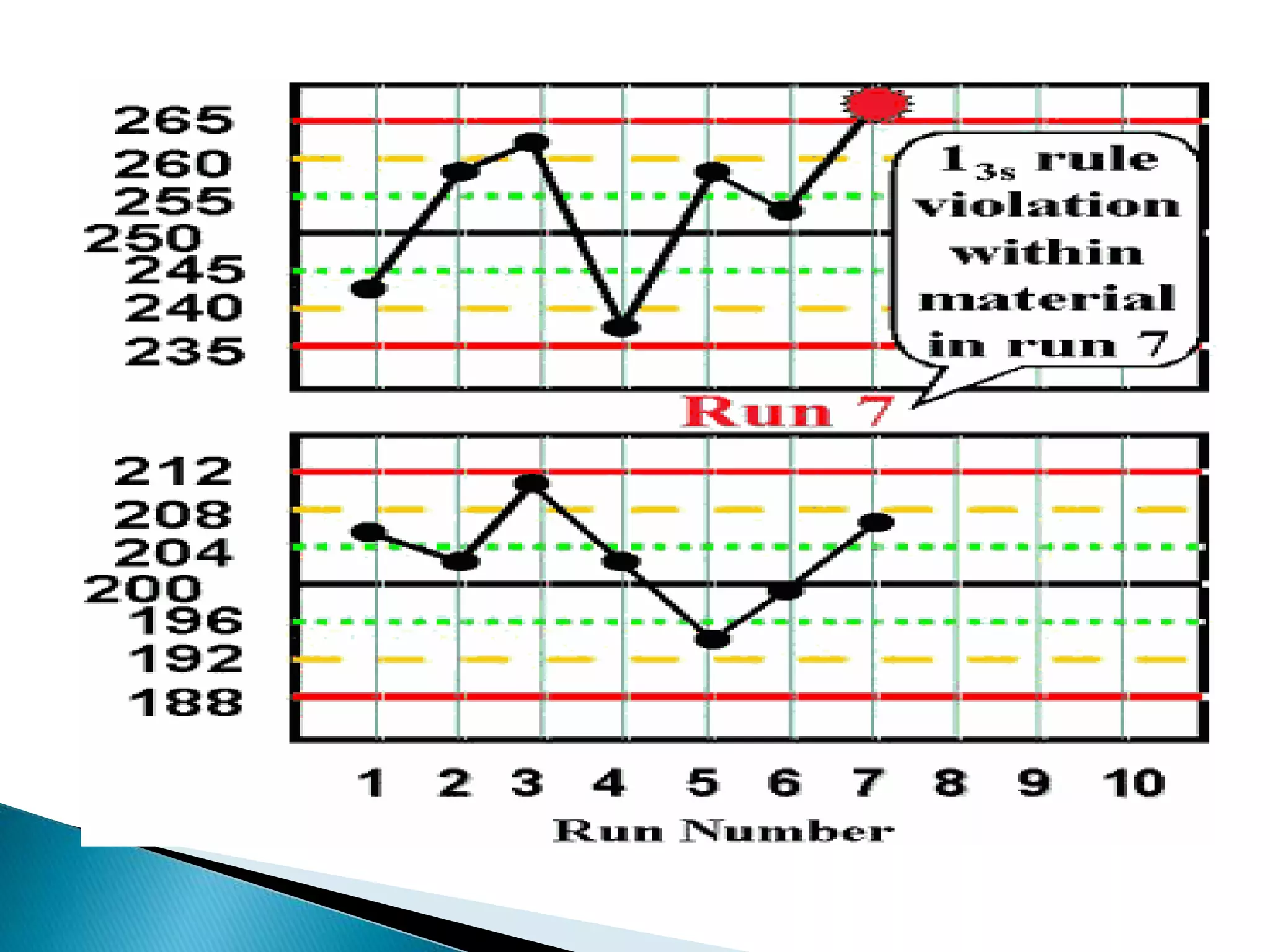
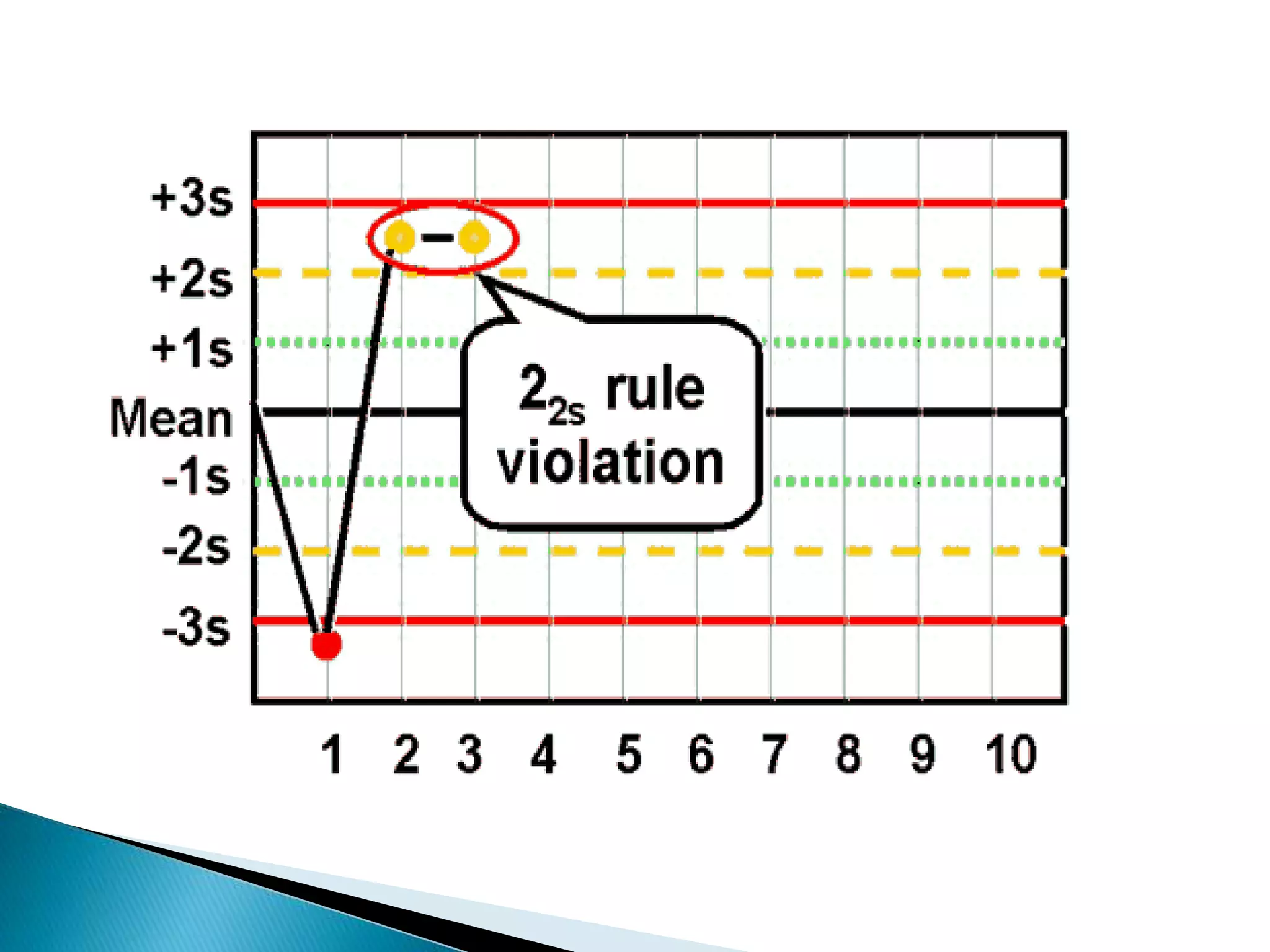
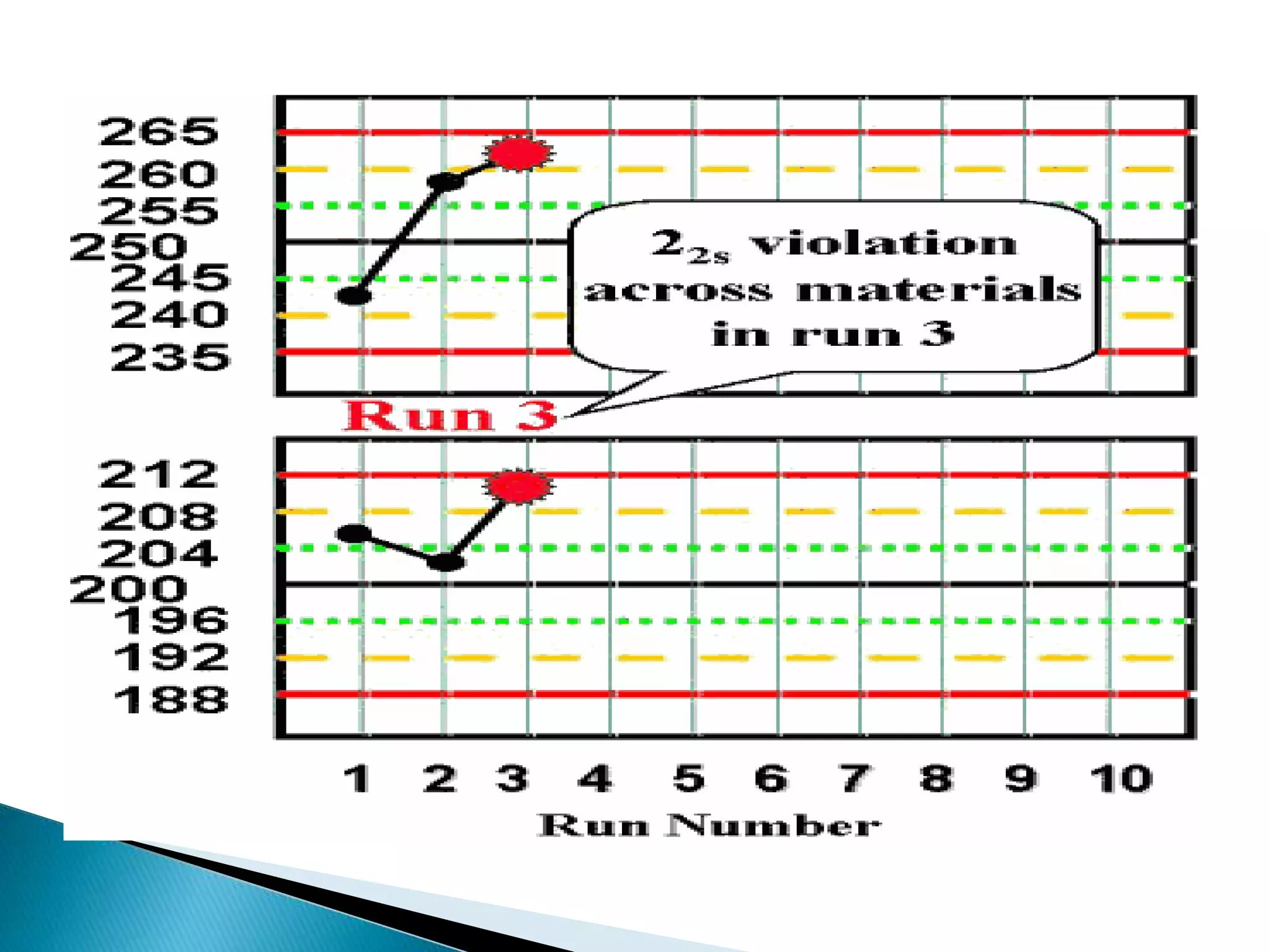
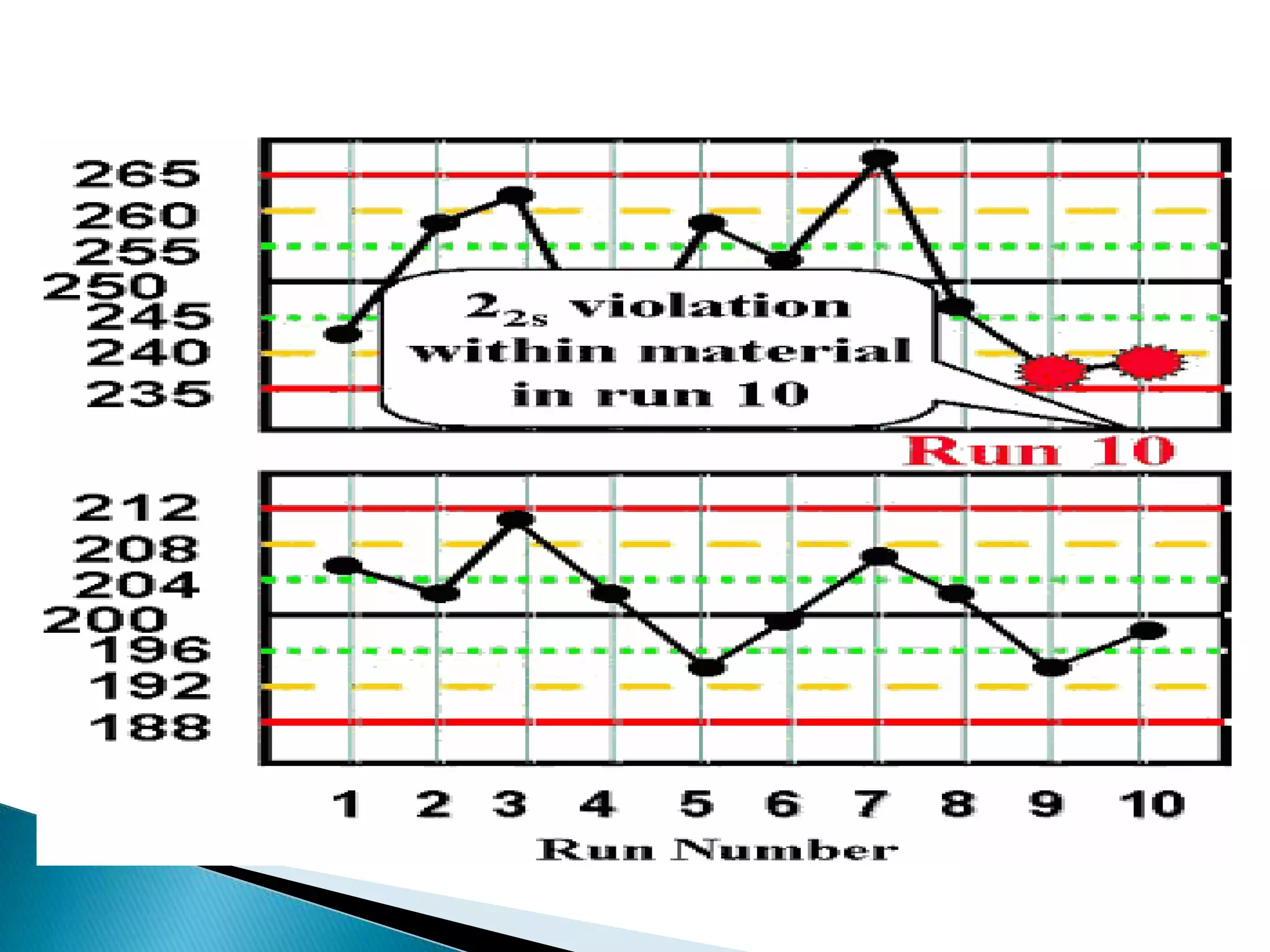
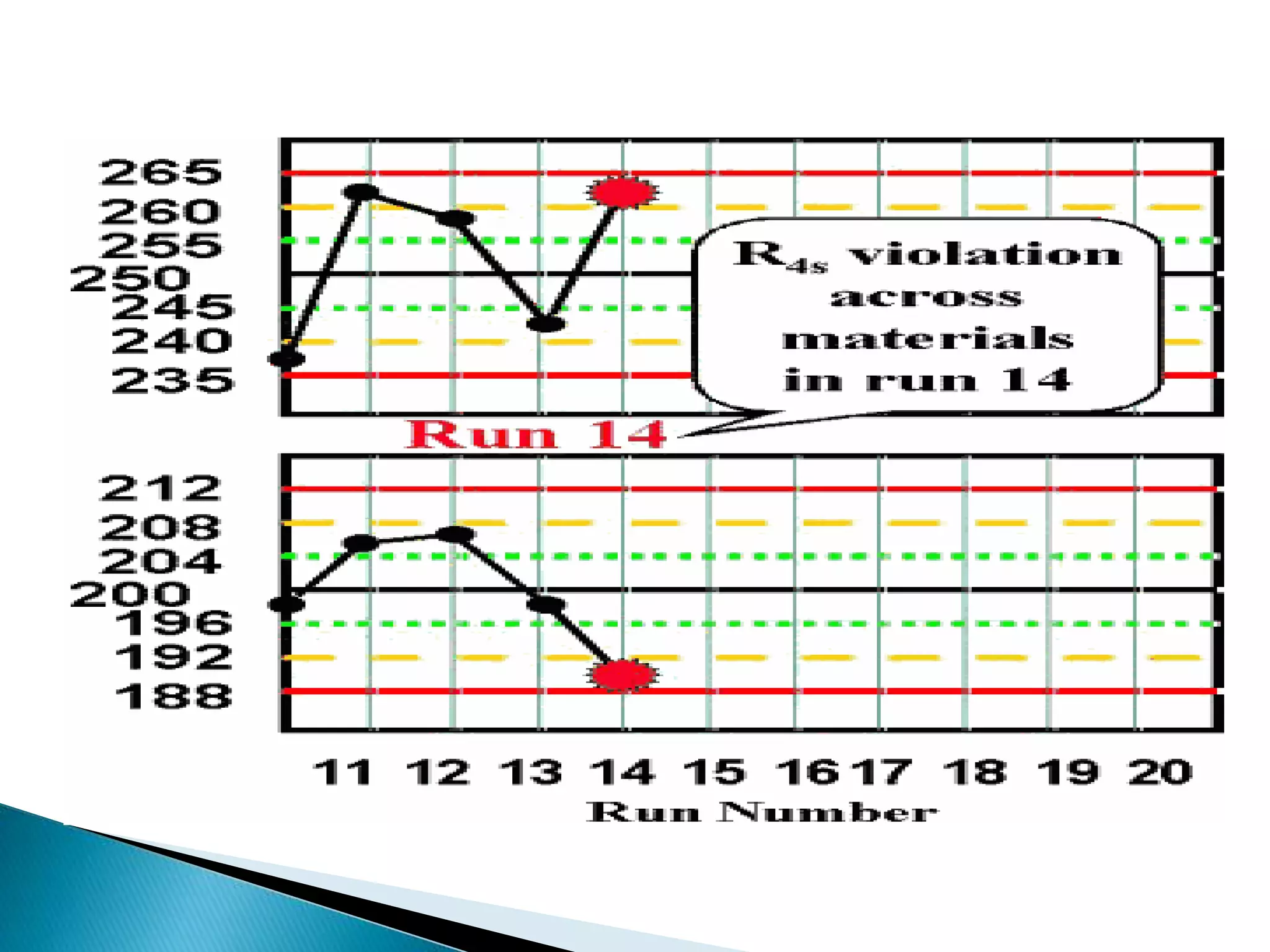
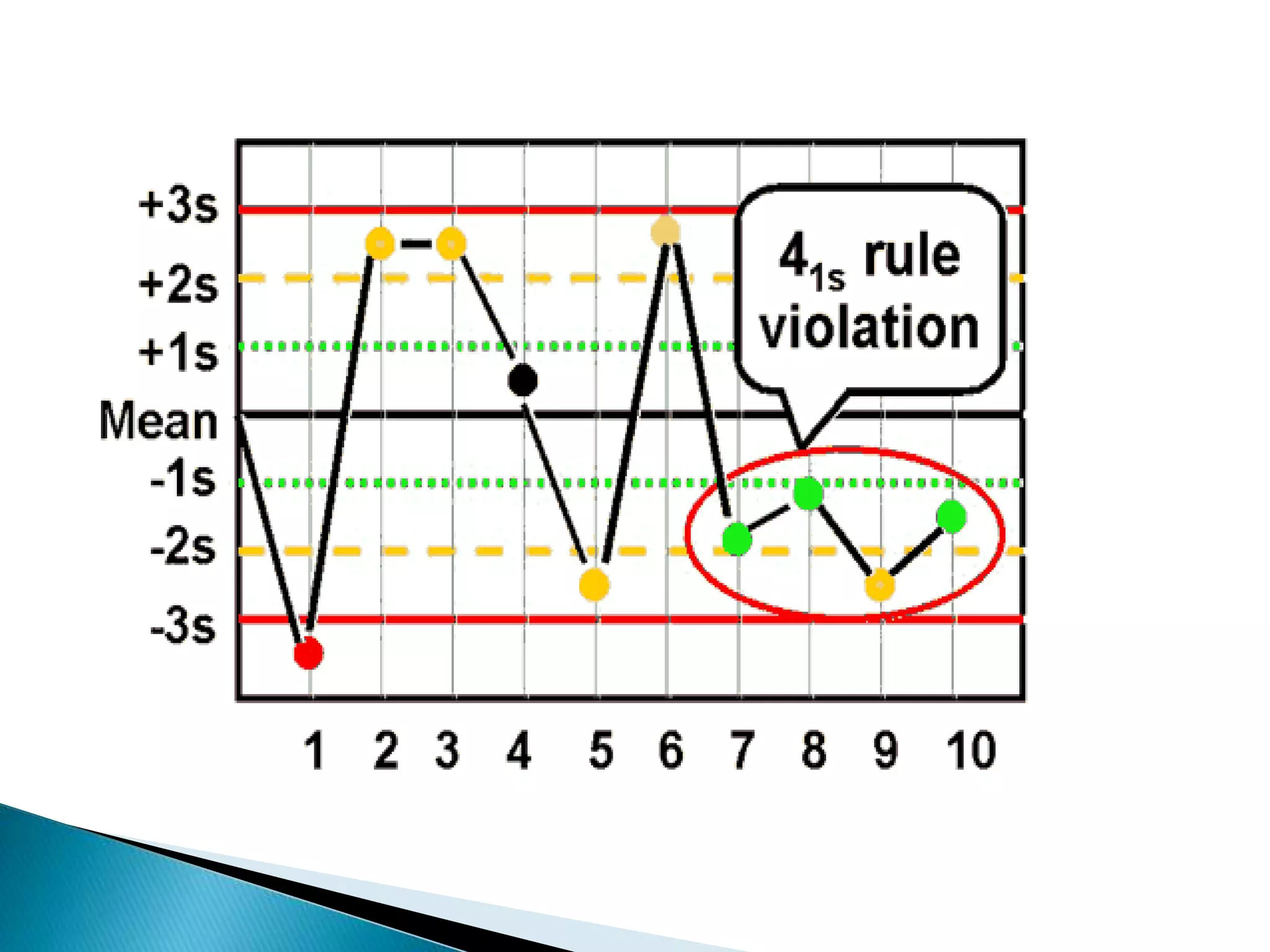
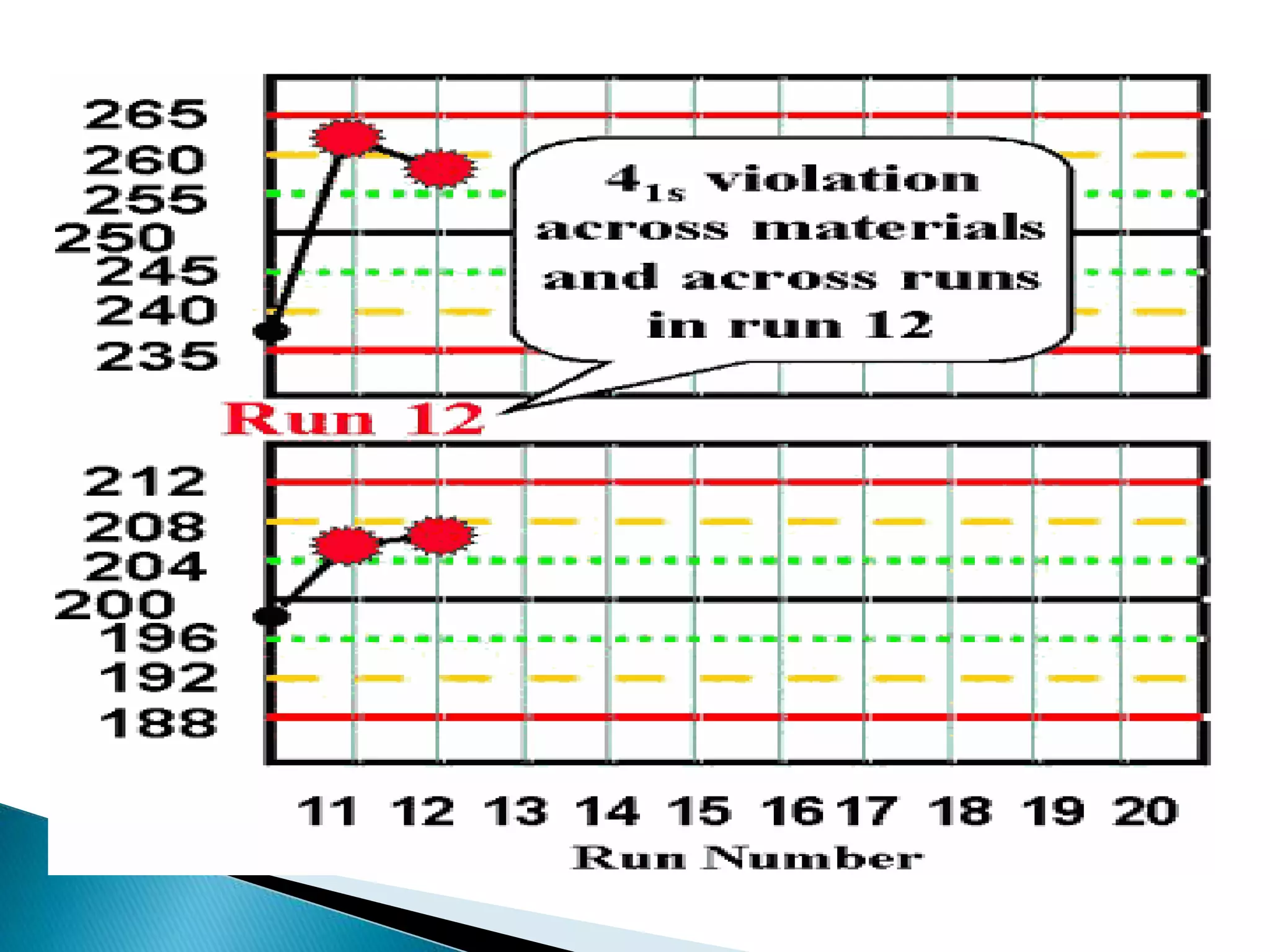
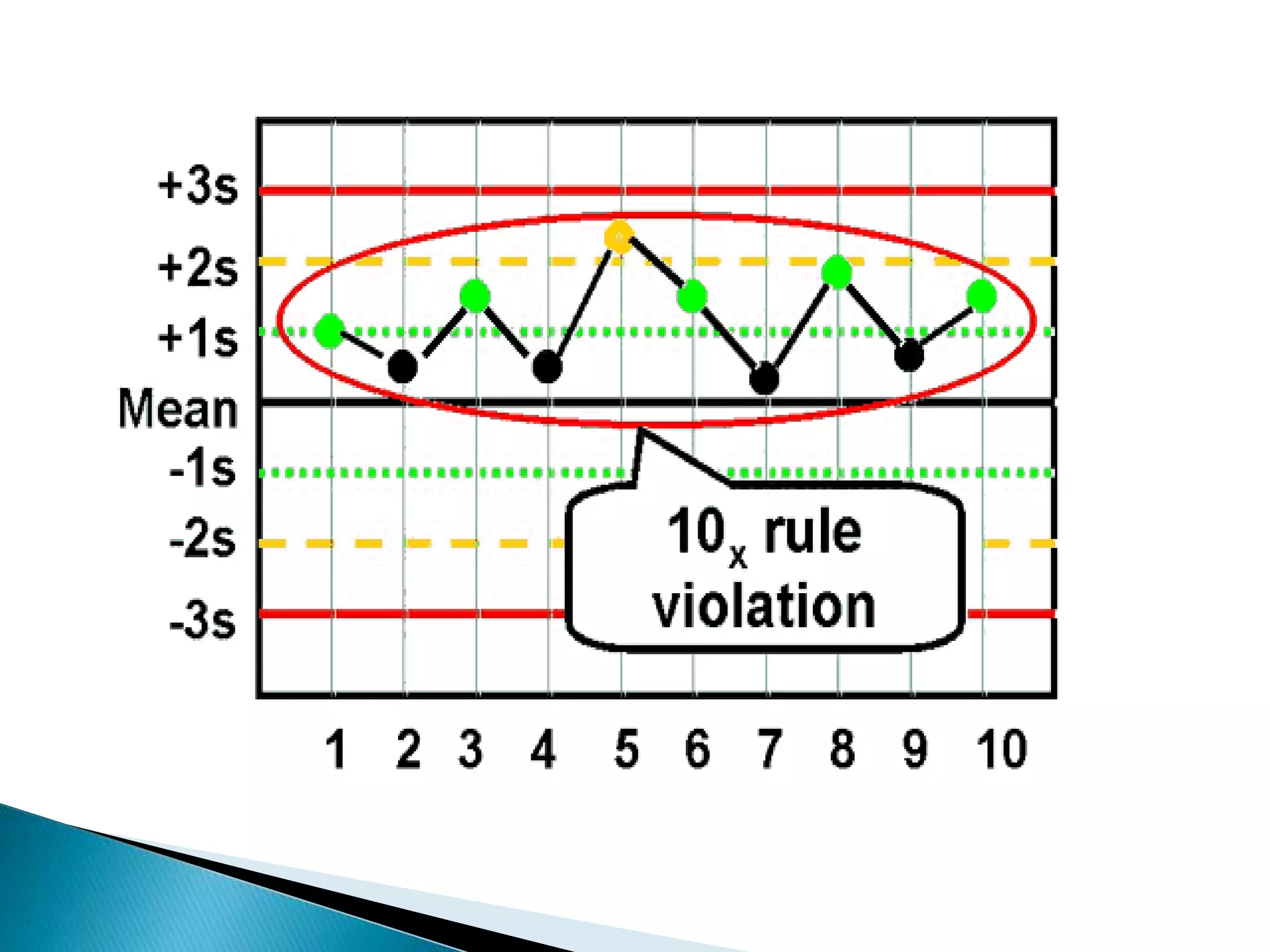
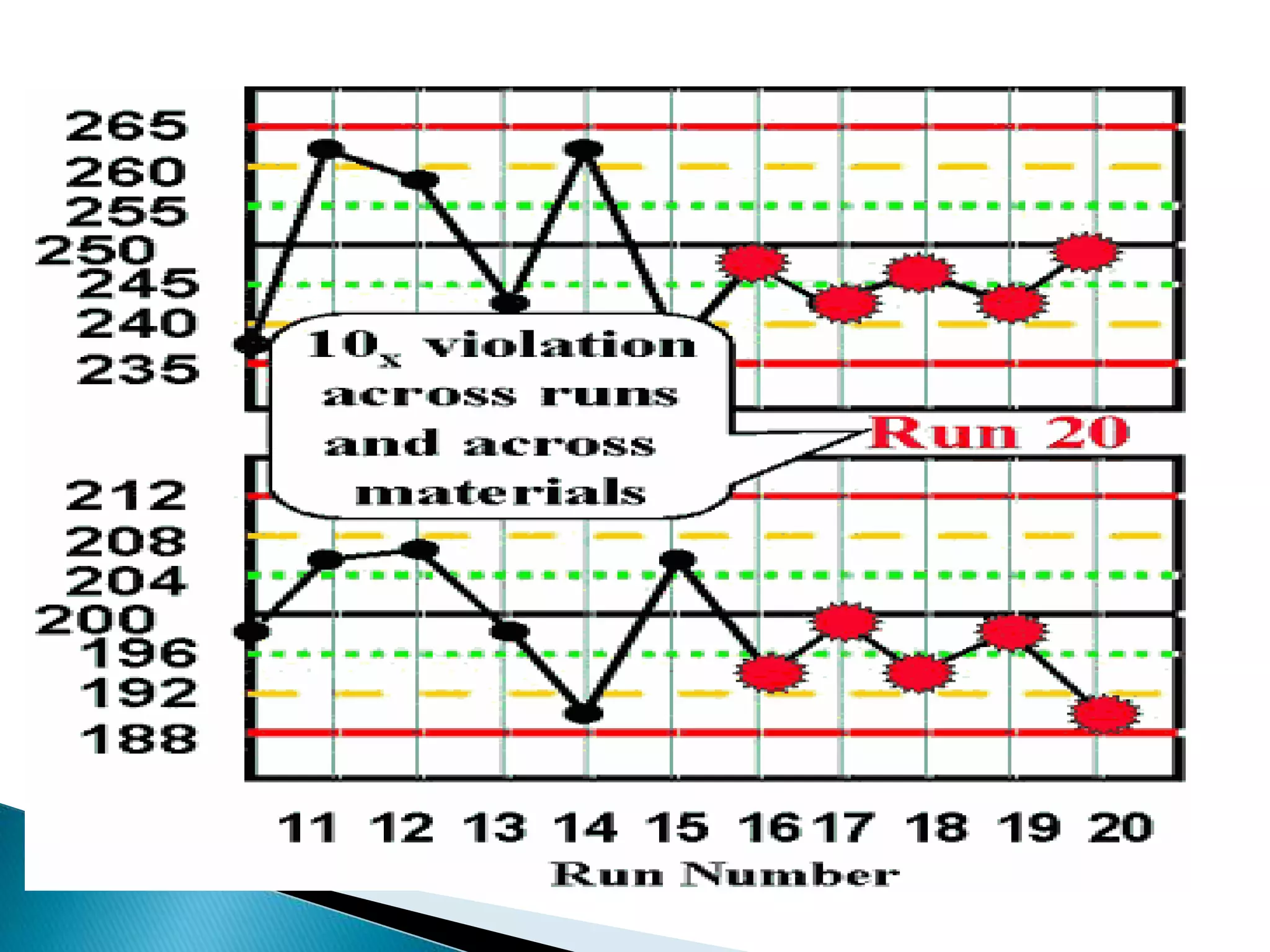
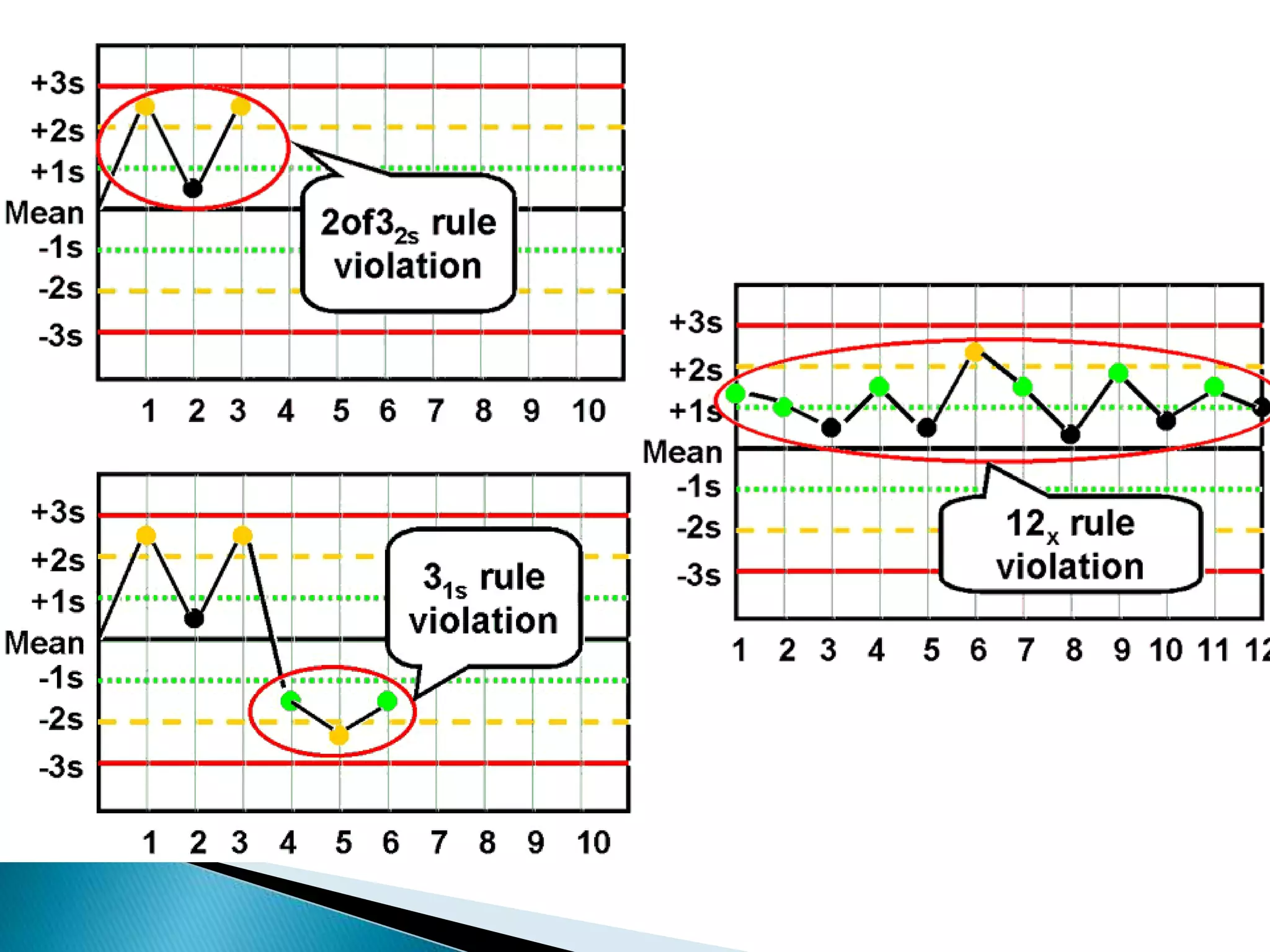
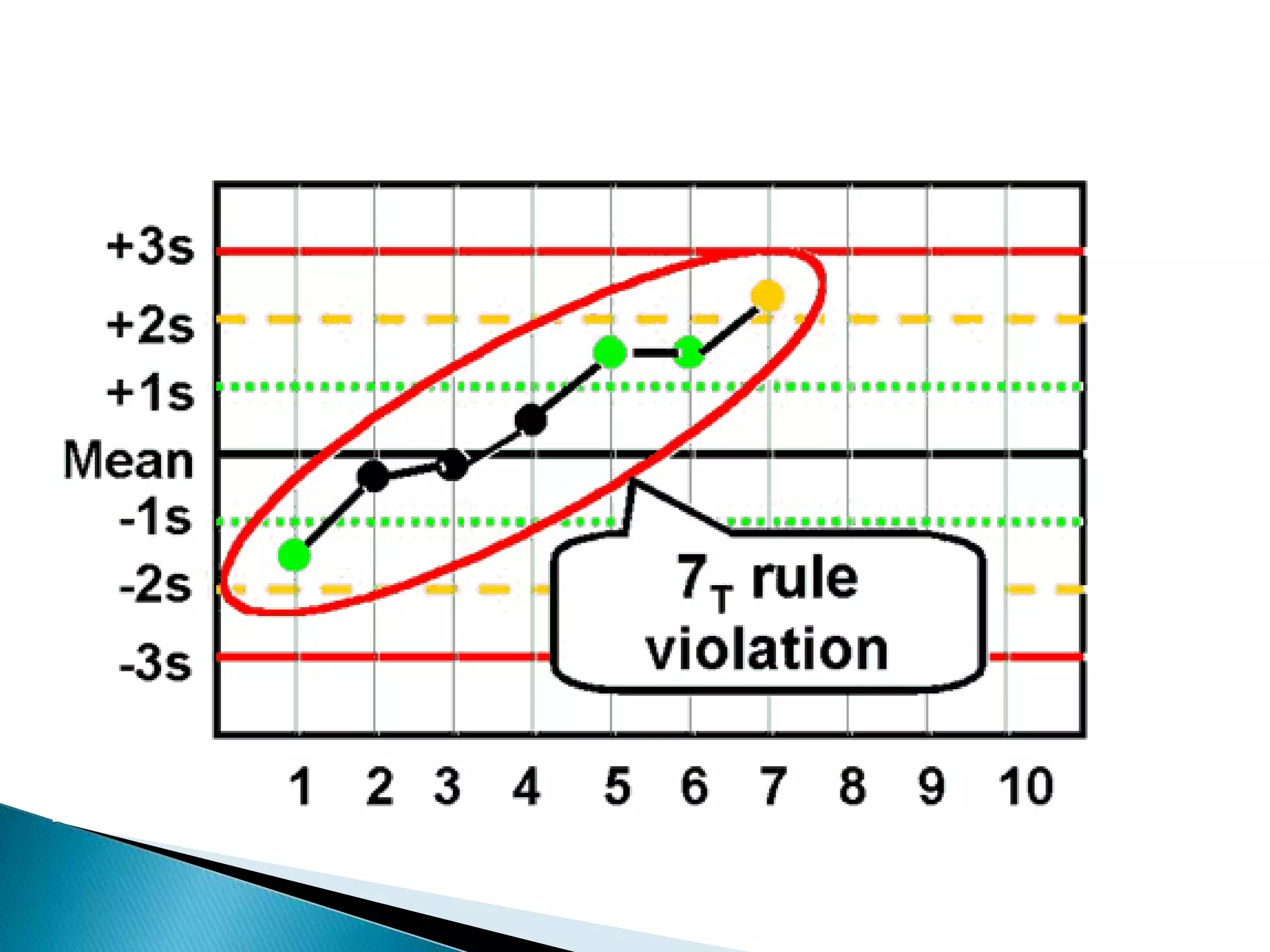
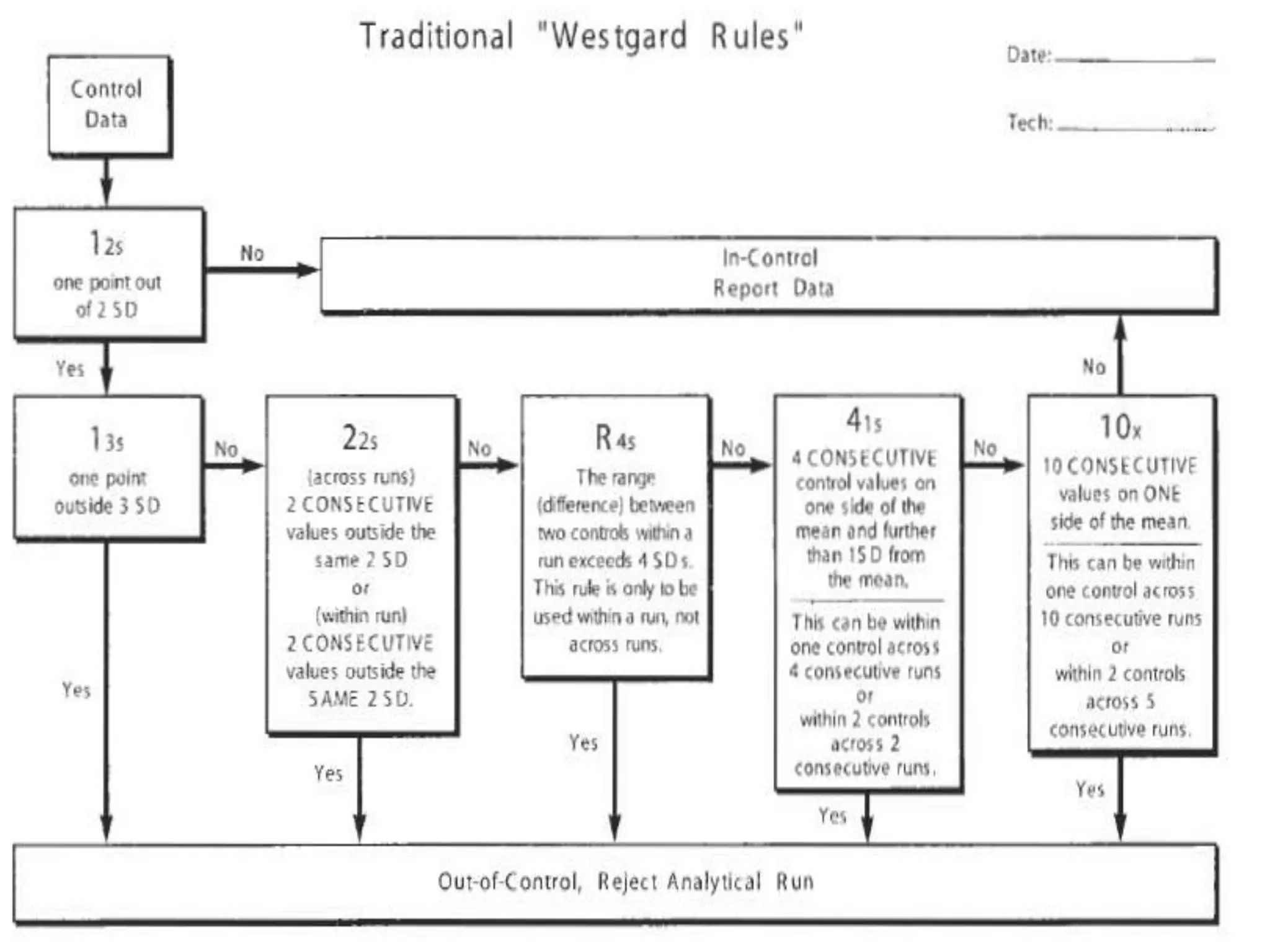
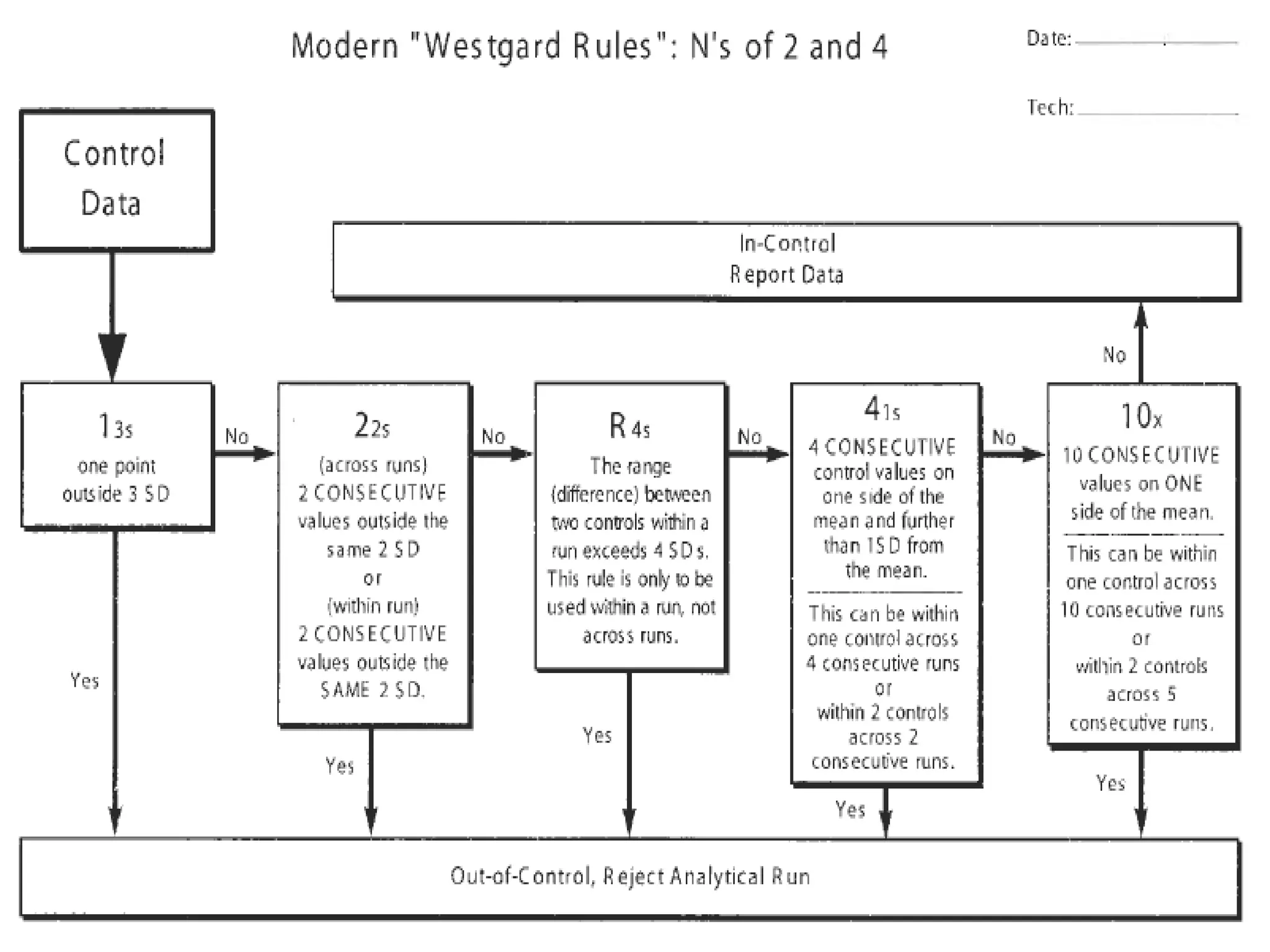
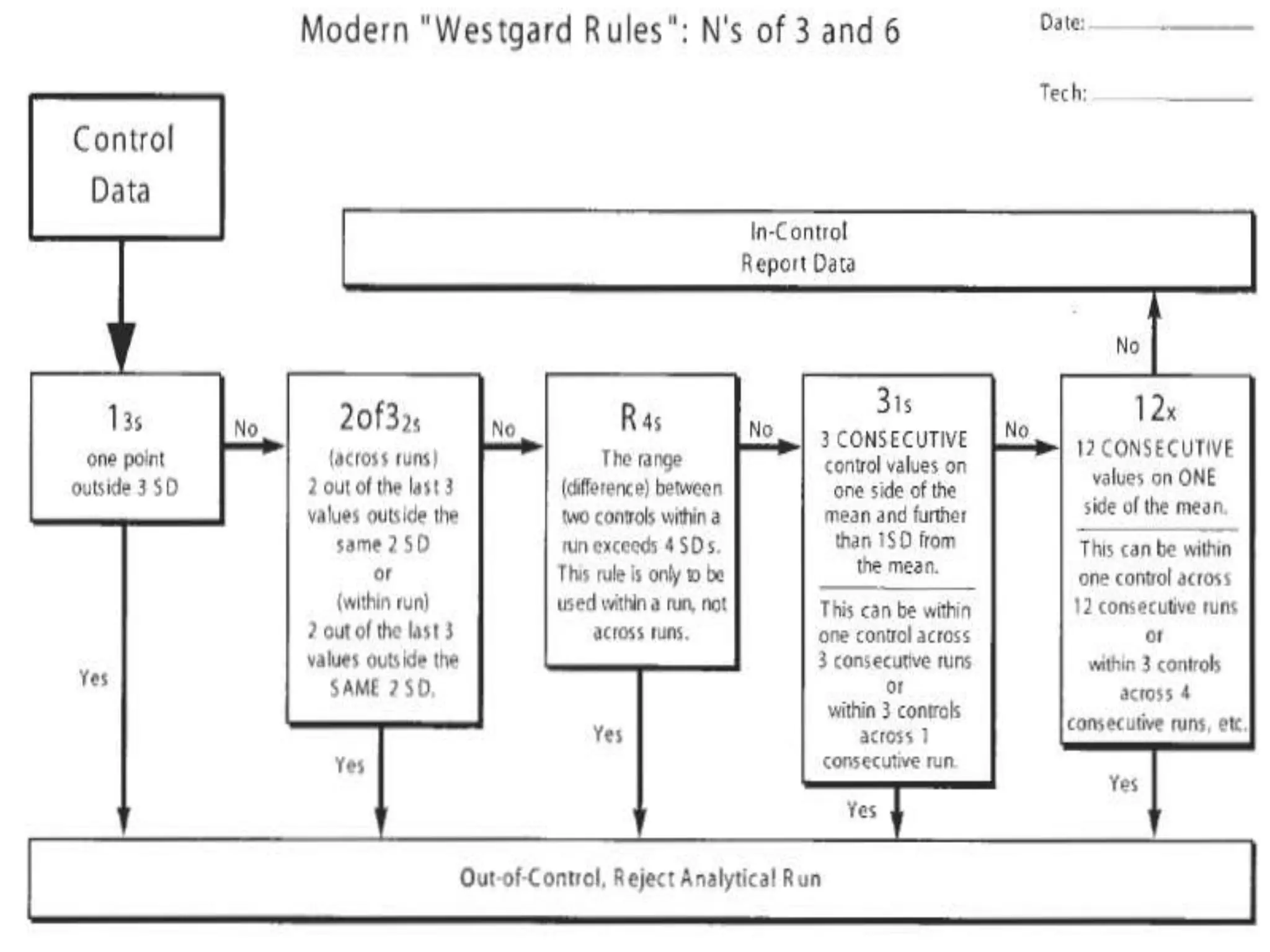
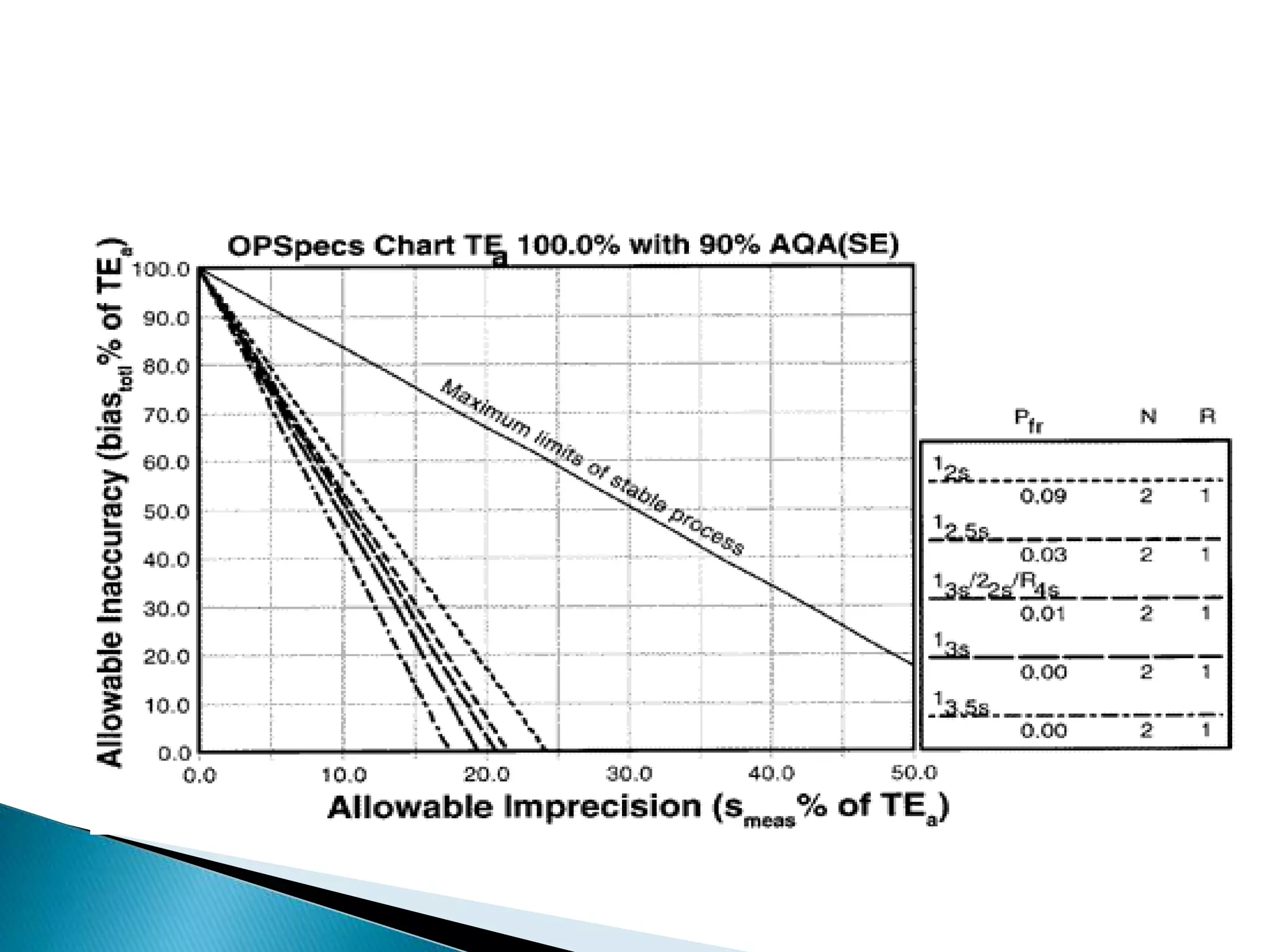
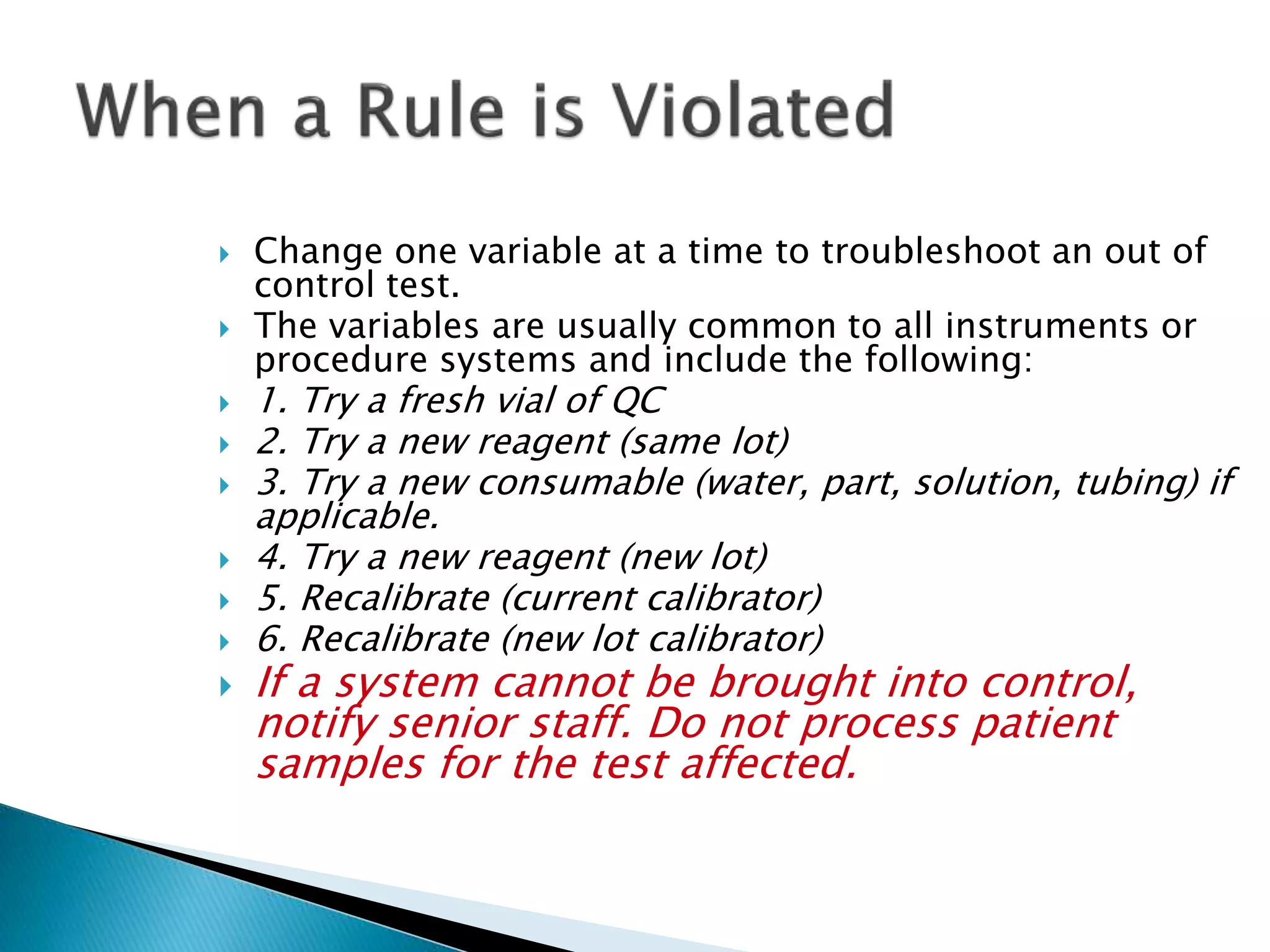
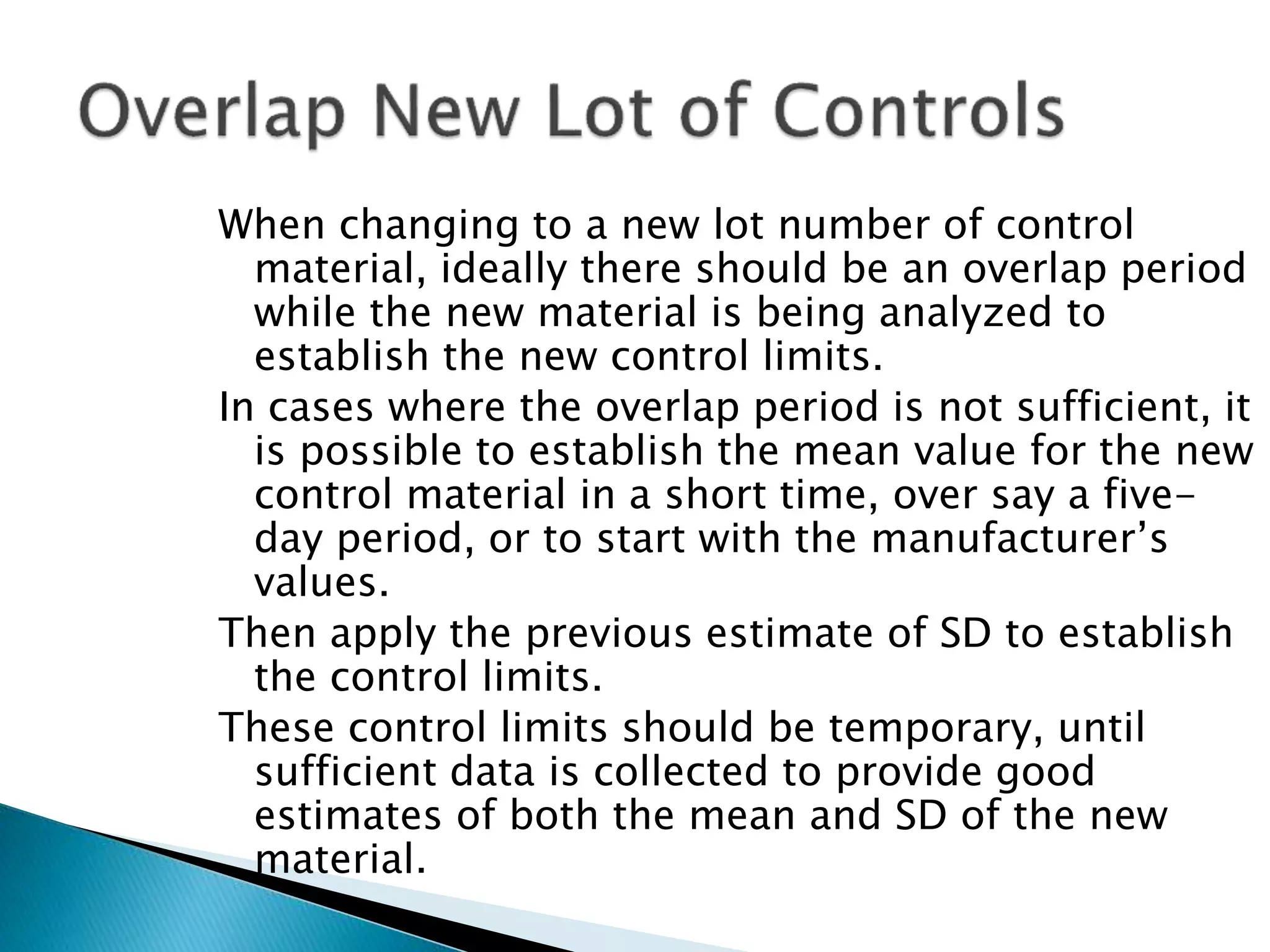
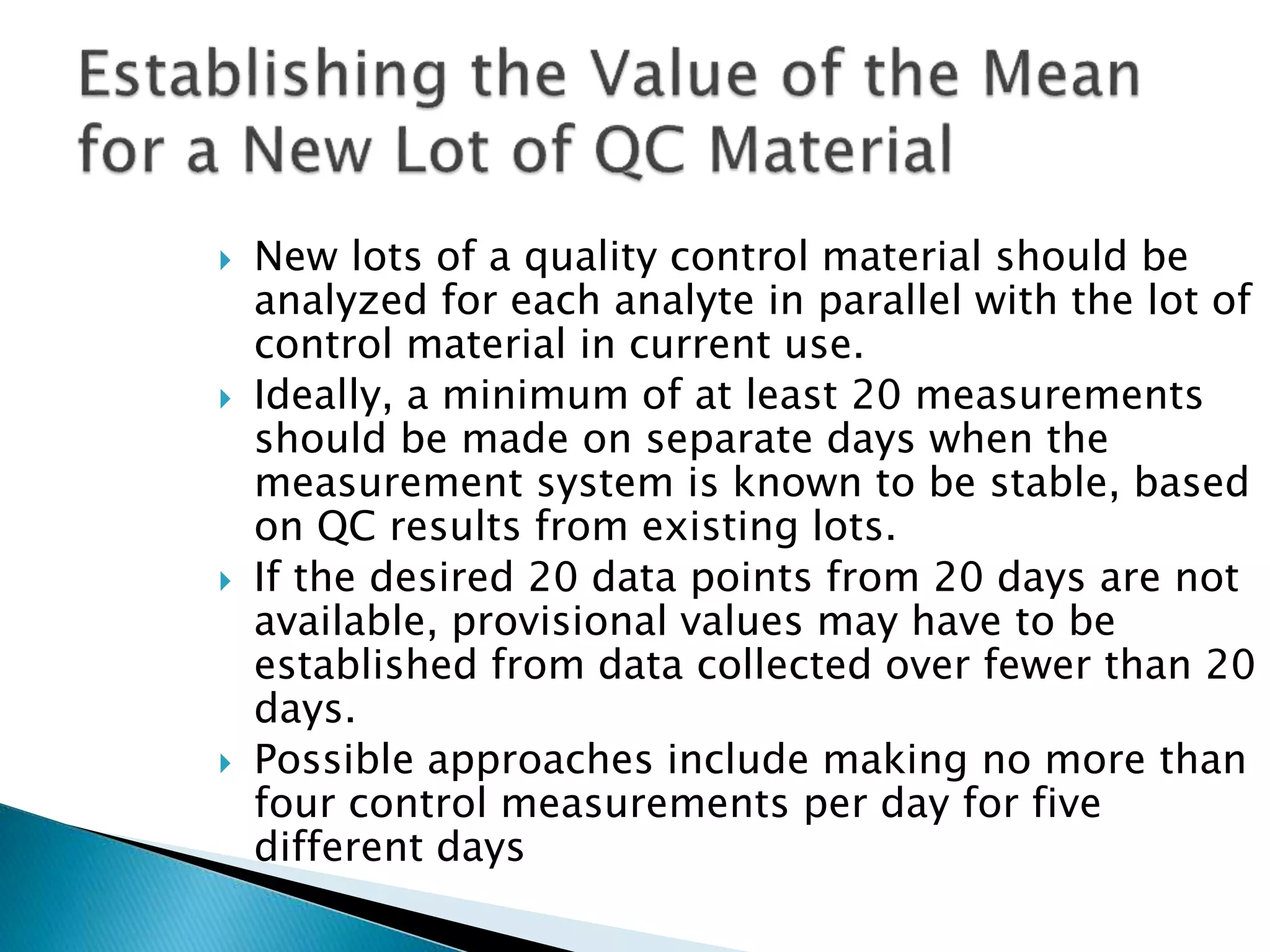
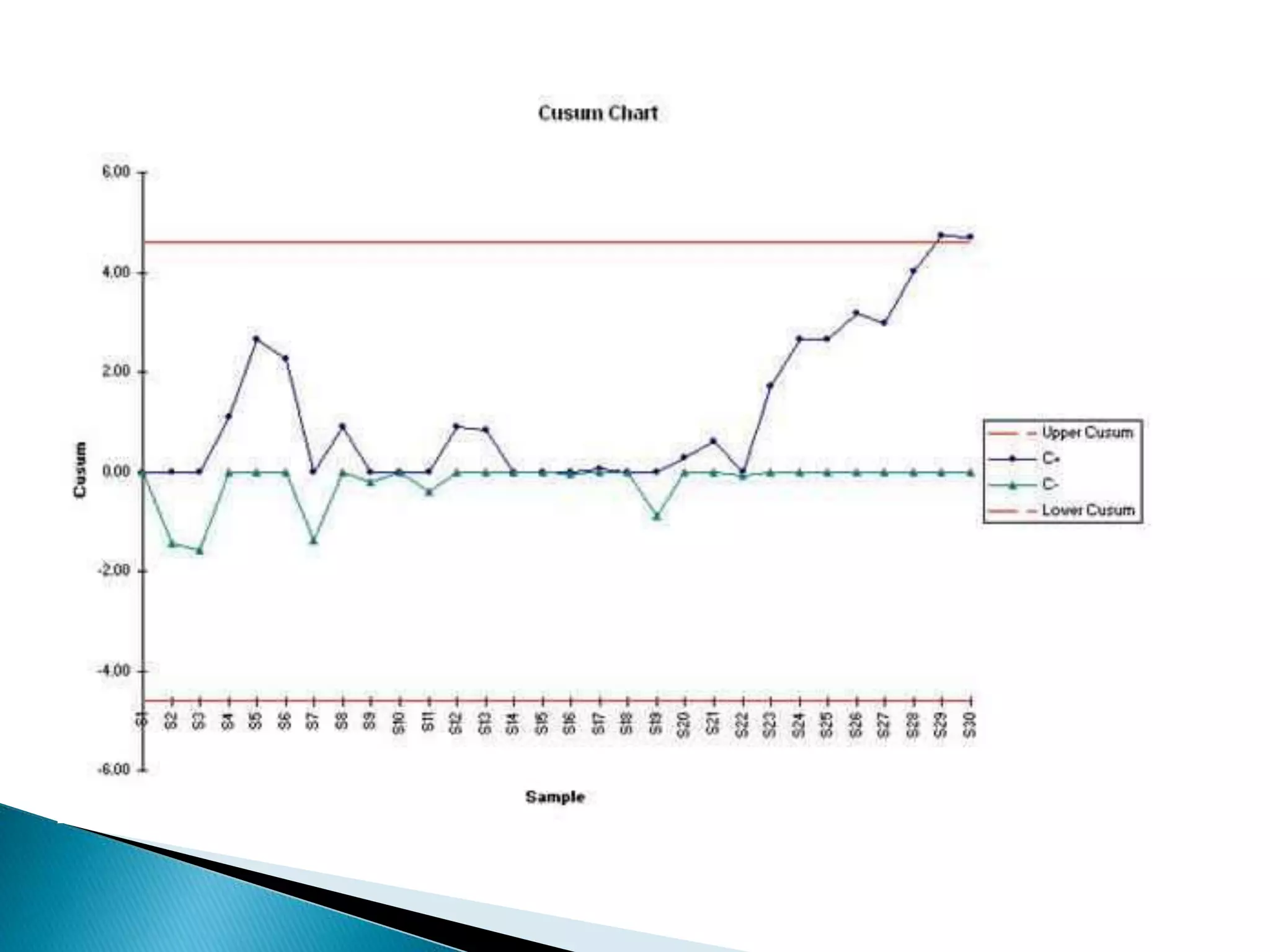
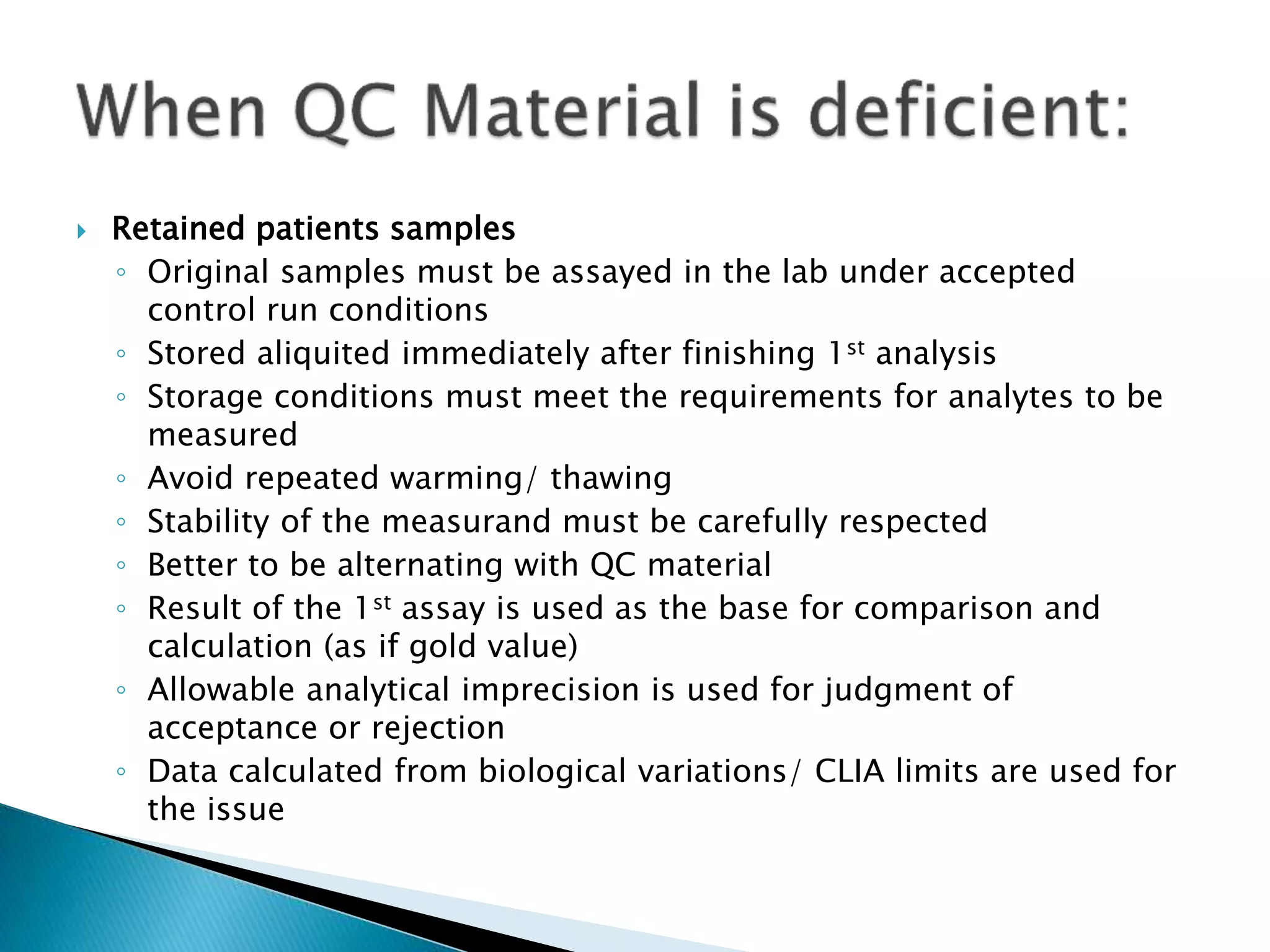
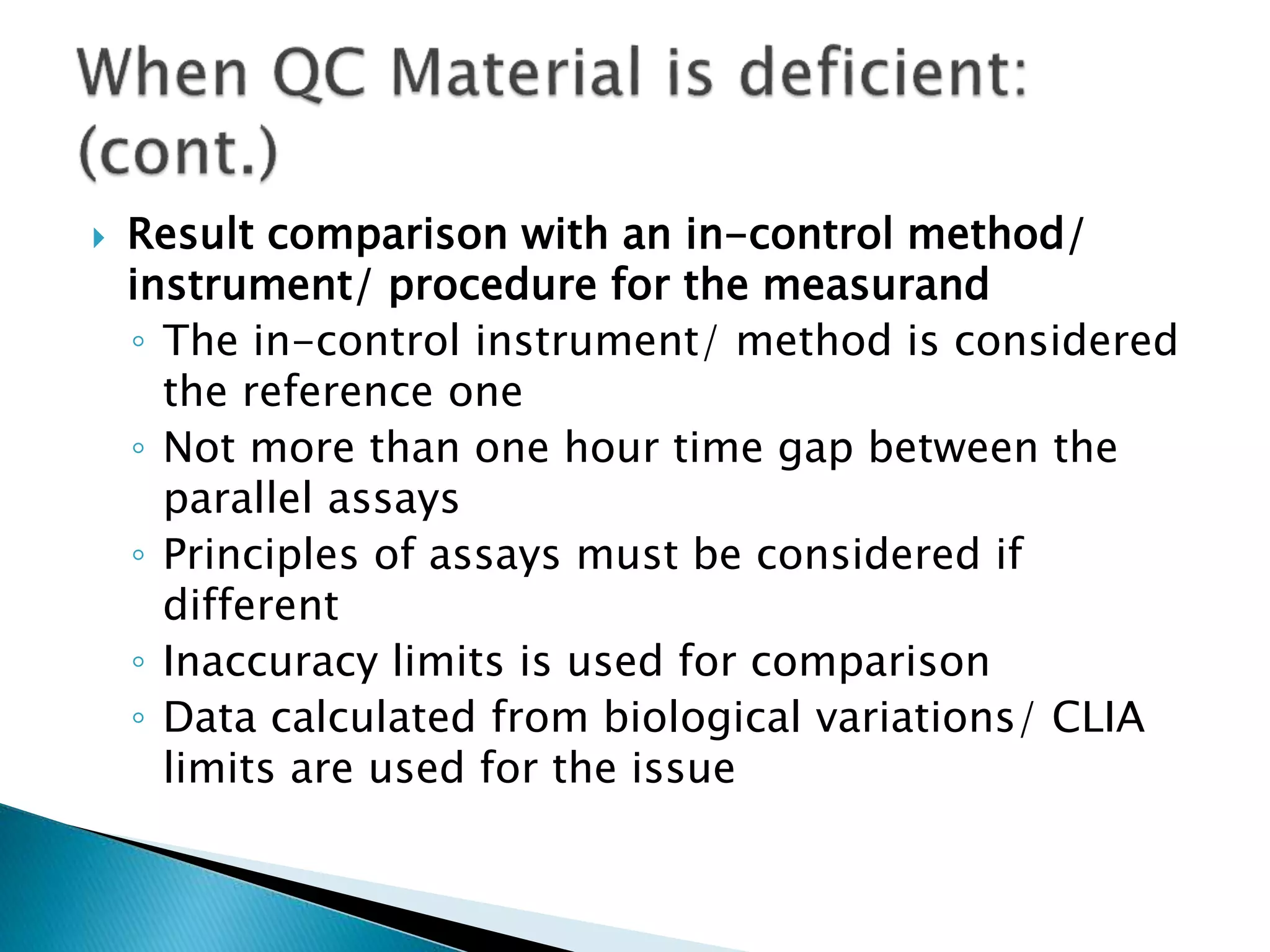
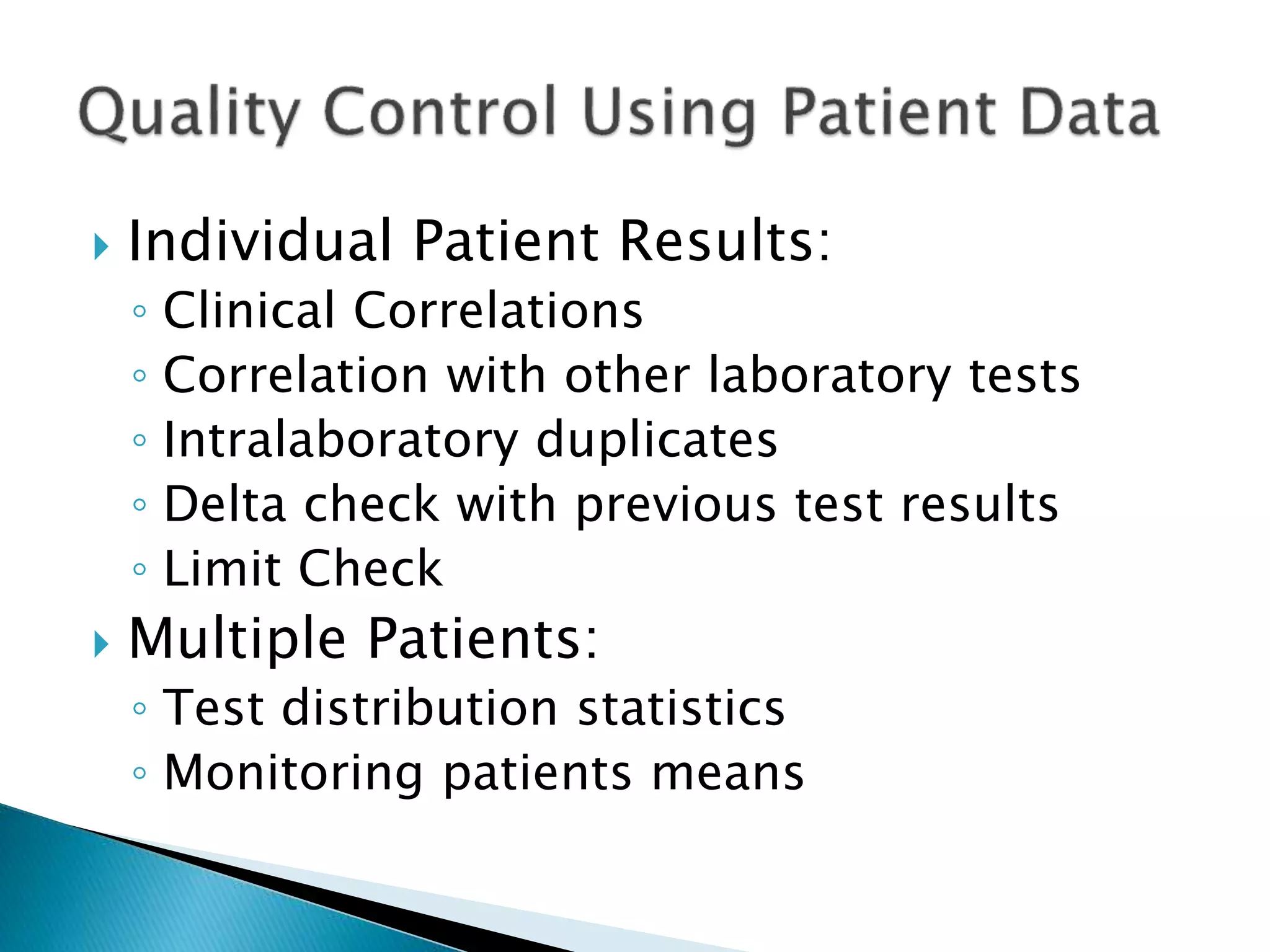
The document discusses internal quality control in clinical laboratories. It defines key terms like quality control, quality assurance, and quality management. It explains the importance of internal quality control in ensuring accurate and reliable test results. Quality control involves running control samples alongside patient samples and using statistical tools like control charts and Westgard rules to monitor the analytical process and ensure it is in control. Factors that could indicate the process is out of control are also summarized.