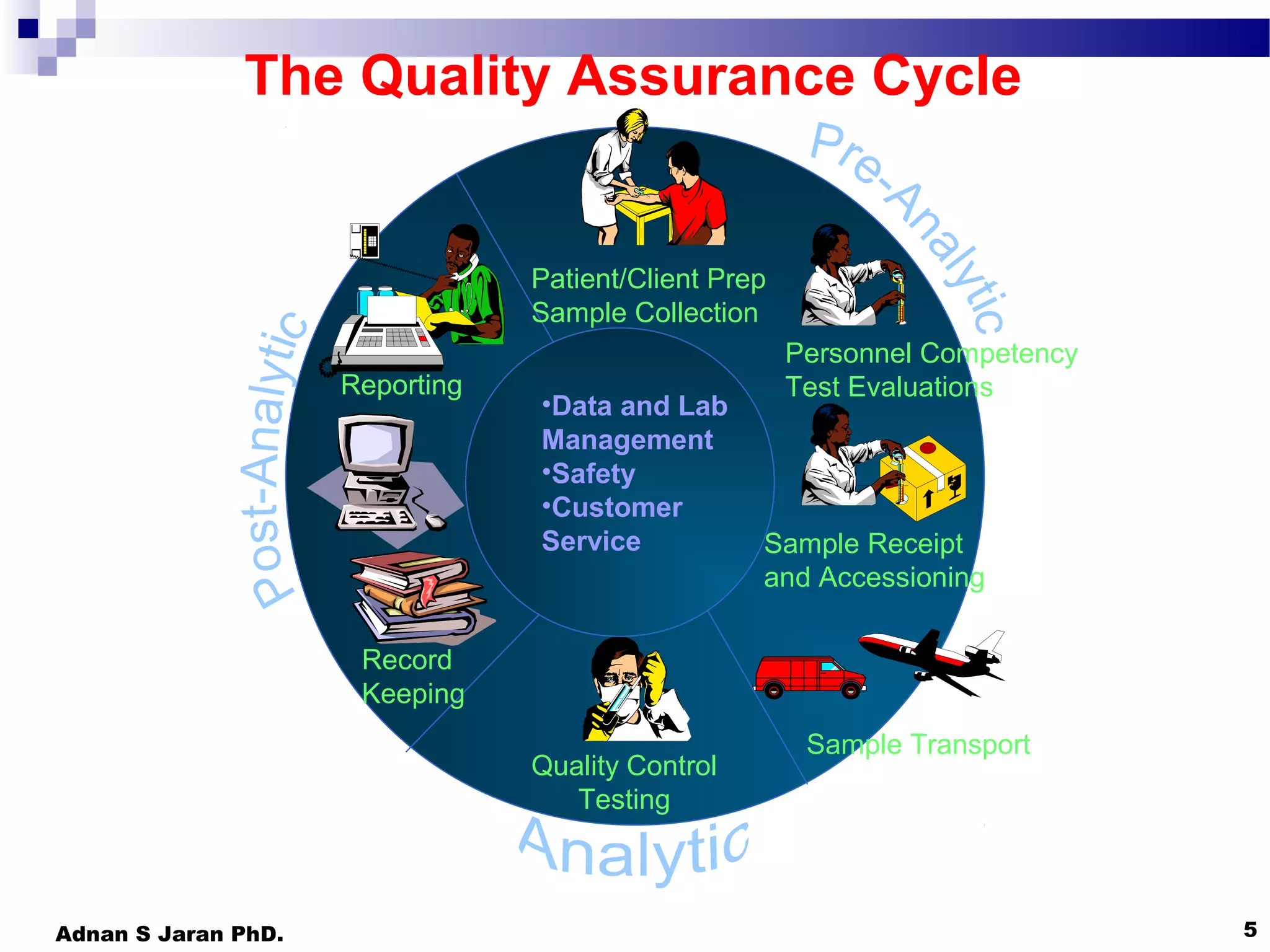
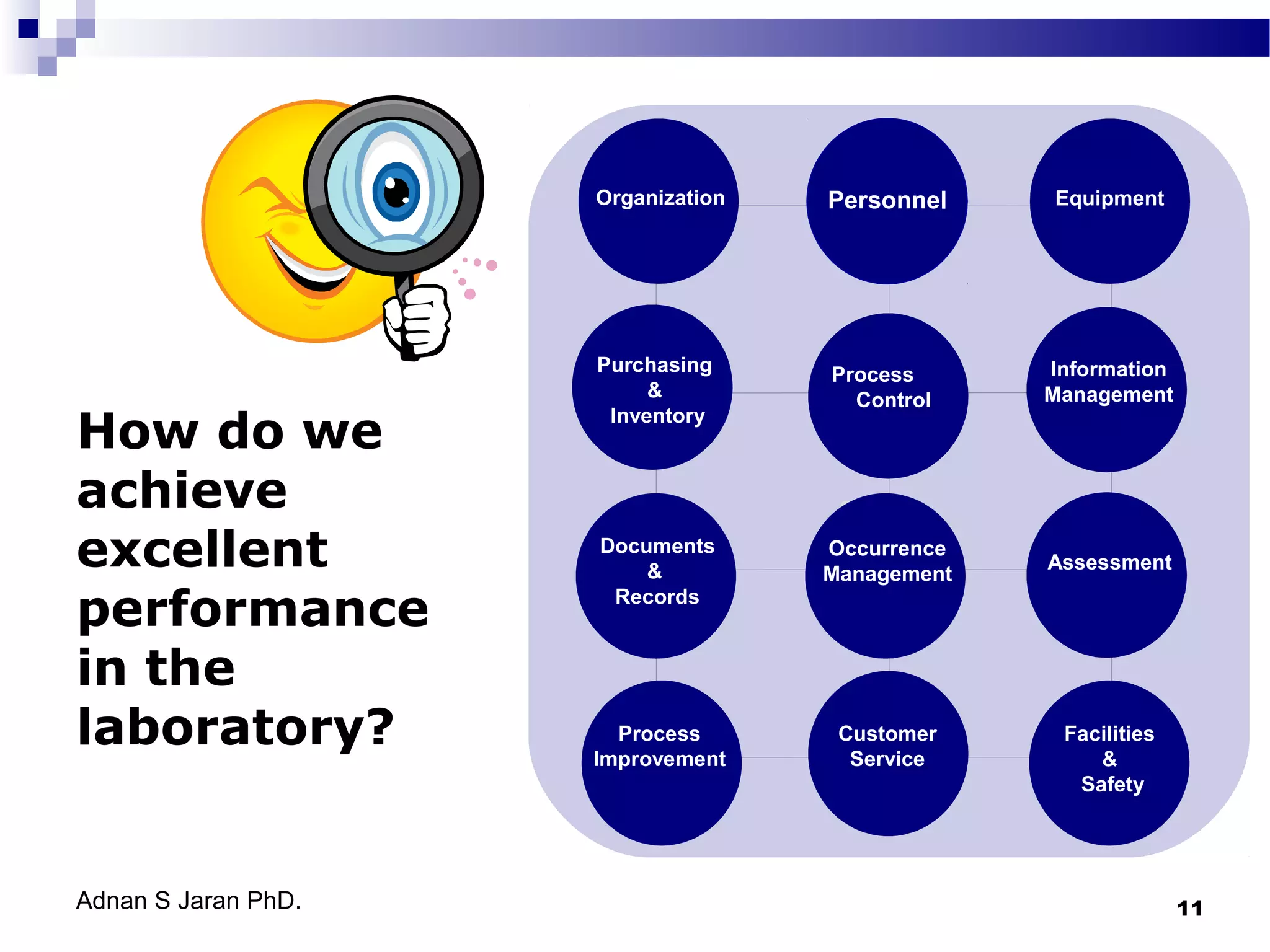
This document discusses quality control in medical laboratories. It emphasizes that quality is achieved through determining customer requirements, ensuring necessary resources are available, planning management procedures, training staff, undertaking tasks correctly, taking corrective action when errors occur, conducting regular reviews and audits, and total management commitment. The quality assurance cycle involves various steps from patient preparation to reporting. Achieving high quality requires addressing all aspects of the laboratory, including organization, personnel, equipment, purchasing, process control, information management, documents, occurrence management, assessment, process improvement, customer service, and facilities/safety. The goal is to detect and prevent errors through a quality management system.



![QUALITY is ACHIEVED BY:[cont]
Ensuring that all activities are
undertaken correctly
Ensuring that when things go wrong,
effective corrective action is taken to
avoid repetition of errors
Undertaking regular reviews and audits
of all processes
Total and organised commitment from
management
Adnan S Jaran PhD.
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qualitycontrolinmedicallab3-131116042305-phpapp02/75/Quality-control-in-the-medical-laboratory-4-2048.jpg)