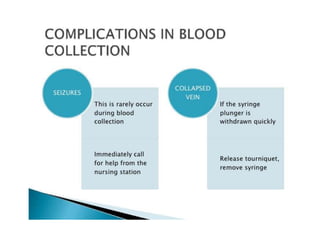
This document discusses blood collection for laboratory tests using anticoagulated vacutainers and sources of preanalytical errors. It describes the appropriate vacutainers and additives used for different tests like CBC, coagulation studies, chemistry etc. The sequence of filling different vacutainer tubes is explained. Common causes of preanalytical errors like hemolysis, lipemia, patient misidentification, and not following guidelines for mixing blood with additives are summarized. The importance of following standard operating procedures for collection, transport, and processing of specimens is highlighted to reduce preanalytical errors.














![SEQUENCE OF FILLING OF TUBES
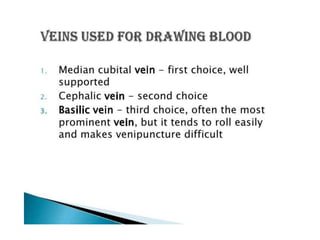
• First Container : blood culture
• First tube : Plain tube [serum]
• Second tube : Tube containing anticoagulant
citrate for PT.
• Third tube : anticoagulant like EDTA or Heparin
• Fourth tube : Tube containing additional
stablilizing agent like fluoride.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathoseminar-160826074802/85/collection-of-blood-sample-and-preanalytical-errors-24-320.jpg)
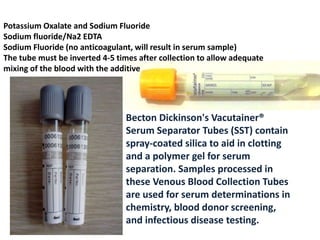
![ANTICOAGULANT VACUTAINERS
• Anticoagulants used for hematological investigations
are EDTA [ Ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid ],
heparin, double oxalate, and trisodium citrate.
• EDTA [1.5mg/ml], dried: also called SEQUESTRENE or
VERSENE. This is the recommended anticoagulant for
routine hematological investigations. EDTA is used for
CBC, blood smear, Hb electrophoresis, sickling test.
However it cannot be used for coagulation studies.
EDTA can cause pseudothrombocytopenia on
hematology analyser. Its mechanism of action is by
chelation of Calcium. Erythrocytes, leukocytes (white
blood cells) and thrombocytes (platelets) are stable
in EDTA anticoagulated blood for up to 24 hours.
Preparation of blood smears should be done within 3
hours after blood collection.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathoseminar-160826074802/85/collection-of-blood-sample-and-preanalytical-errors-25-320.jpg)
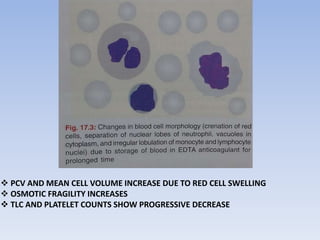

![• DOUBLE OXALATE [WINTROBE MIXTURE]
CONTAINS AMMONIUM OXALATE AND
POTASSIUM OXALATE IN 3:2 PROPORTION.ACTS
BY REMOVING CALCIUM.
IT IS USED FOR ROUTINE HEMATOLOGICAL
TESTS AND FOR ESTIMATION OF ESR BY
WINTROBE METHOD. IT CAUSES CRENATION OF
RED CELLS AND MORPHOLOGIC ALTERATIONS IN
WBC ,IT CANNOT BE USED FOR MAKING BLOOD
FILMS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathoseminar-160826074802/85/collection-of-blood-sample-and-preanalytical-errors-28-320.jpg)
![TRISODIUM CITRATE [3.2 %]
• ANTICOAGULANT OF CHOICE FOR
COAGULATION STUDIES AND FOR
ESTIMATION OF ESR BY WESTERGREN
METHOD
• 1:9 [ANTICOAGULANT TO BLOOD ] IS
RECOMMENDED FOR COAGULATION
STUDIES, AND FOR ESR 1:4
PROPORTION IS RECOMMENDED.
• ESR SHOULD BE MEASURED WITHIN 4
HOURS AND COAGULATION STUDIES
SHOULD BE PERFORMED WITHIN 2
HOURS OF COLLECTION OF BLOOD.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathoseminar-160826074802/85/collection-of-blood-sample-and-preanalytical-errors-29-320.jpg)


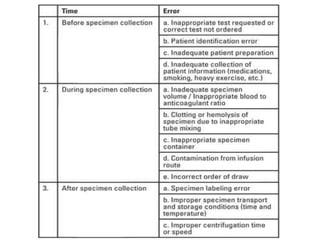
![Types of preanalytical errors
• Patient misidentification [ incorrectly labelled tubes or
incorrectly filled forms ] .
Most common causes are :
1] inadequate data on test requisition form
2] missing patient identifiers
3] labelling specimen container away from bedside
Possible consequences include wrong blood transfusion
leading to acute hemolytic reaction.
Specimen collection from wrong patient leading to
delayed diagnosis or misdiagnosis
To minimize such errors, atleast 2 patient identifiers
should be used, specimen should be labelled immediately
after specimen collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pathoseminar-160826074802/85/collection-of-blood-sample-and-preanalytical-errors-34-320.jpg)




