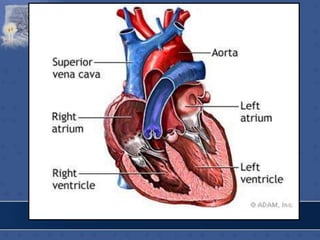
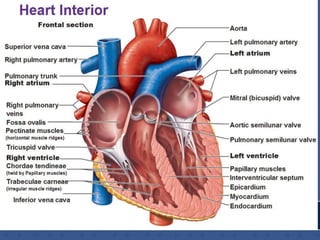
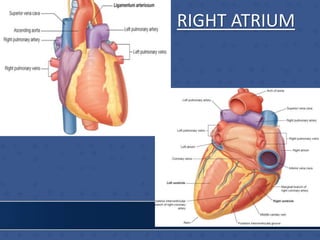
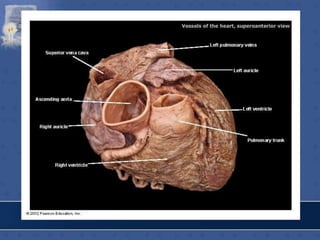
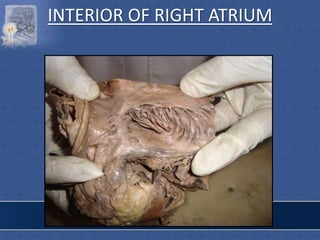
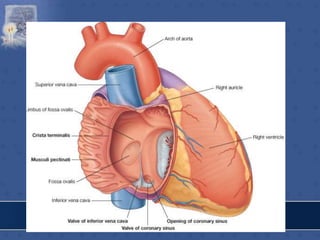
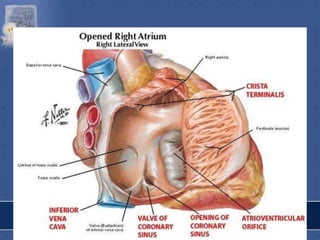
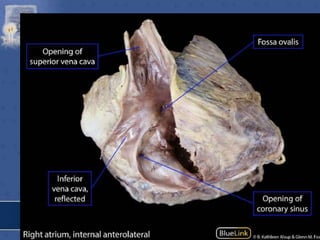
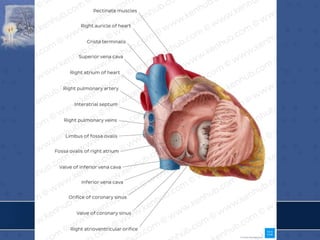
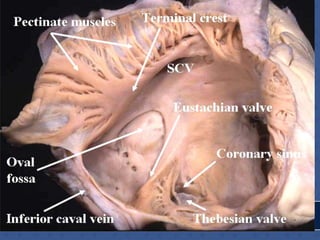
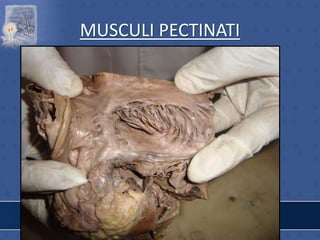
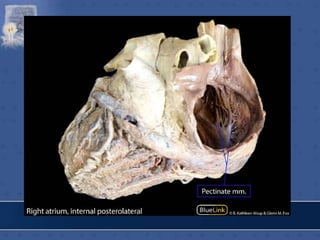
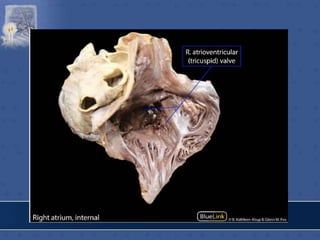
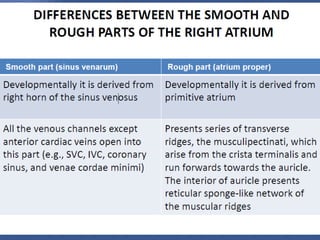
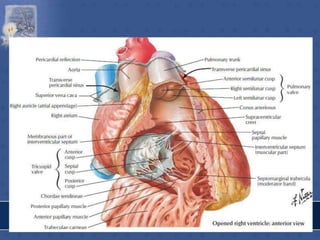
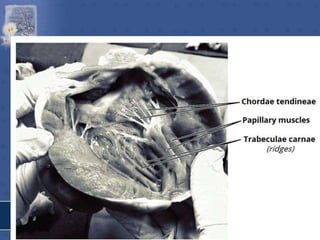
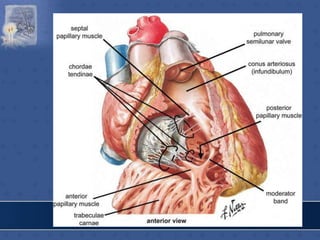
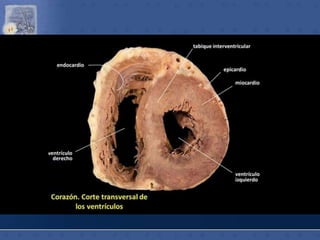
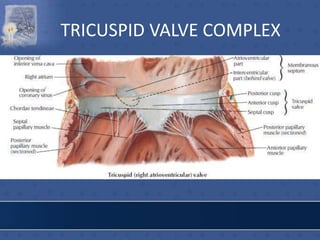
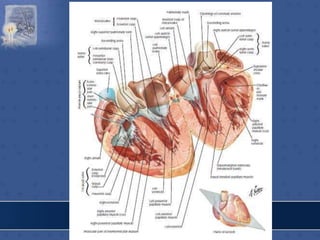
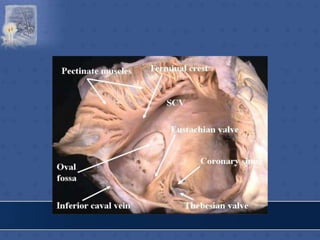
1. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, and coronary sinus. It has a smooth posterior wall called the sinus venarum and a rough anterior wall.
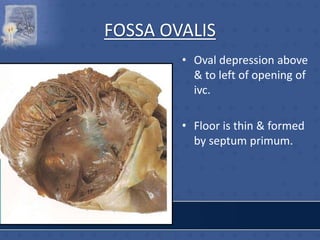
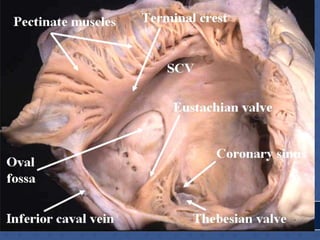
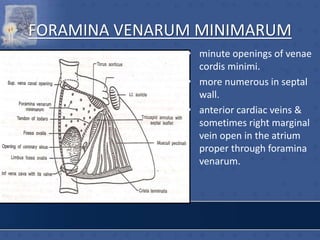
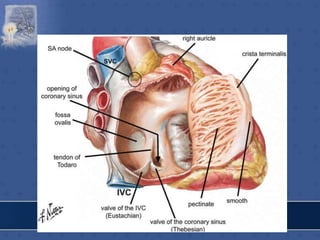
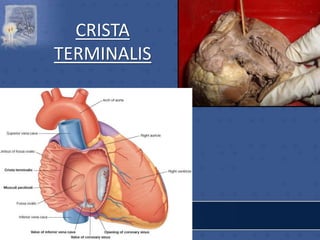
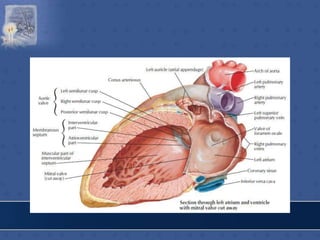
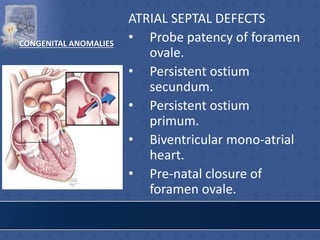
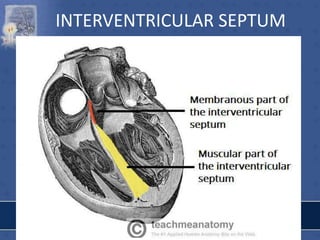
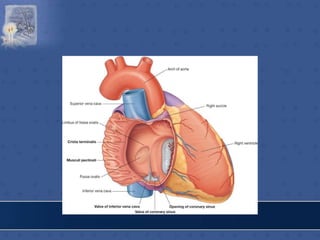
2. The interatrial septum separates the right and left atria. It contains the fossa ovalis, limbus fossa ovalis, and openings for the coronary sinus and venae cordis minimae.
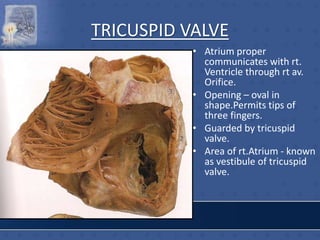
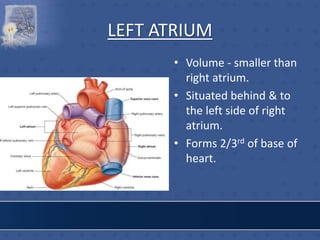
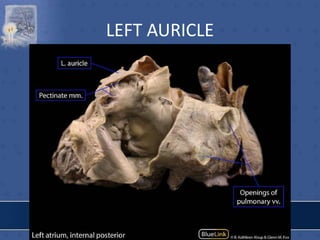
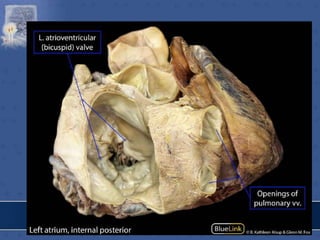
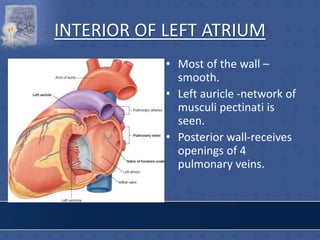
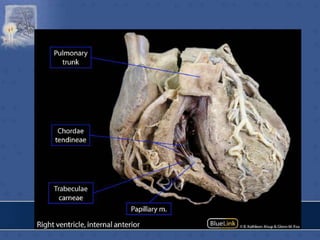
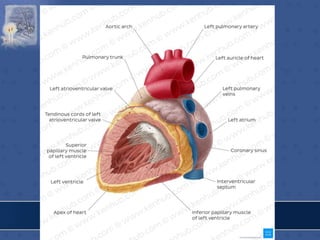
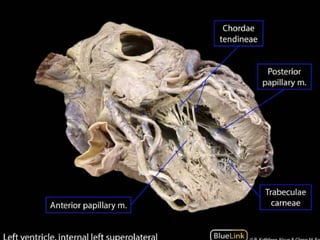
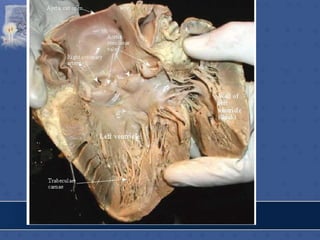
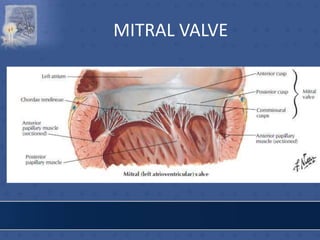
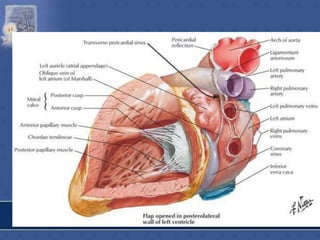
3. The interior of the left atrium is mostly smooth walled and receives the four pulmonary veins. Both atria pump blood into the ventricles through the atrioventricular valves.


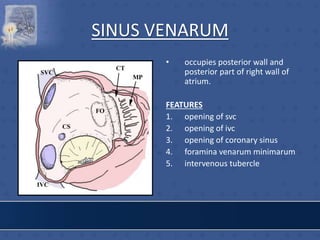
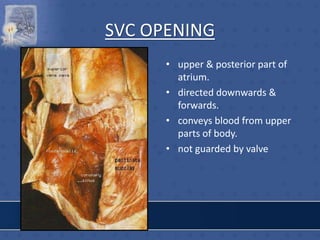
![IVC OPENING
• lower & posterior part of
atrium close to septum.
• conveys blood from lower
part of body.
• opening guarded by a
rudimentary semilunar
valve [eustachian valve] -
formed by duplication of
endocardium containing a
few muscle fibres.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interiorofheart-220824135019-e1b4cd4e/85/INTERIOR-OF-HEART-ppt-17-320.jpg)
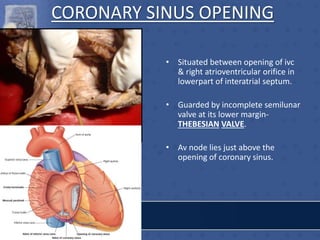




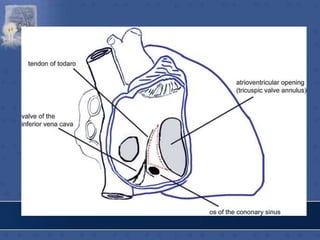
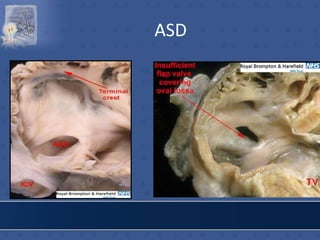
![RT.SIDE OF INTERATRIAL SEPTUM
• FOSSA OVALIS
• LIMBUS FOSSA OVALIS
• TRIANGLE OF KOCH
[Triangular area bounded
in front by base of septal
leaflet of tricuspid
valve,behind by antero-
median margin of opening
of coronary sinus,above by
tendon of todaro-av node
lodges in the triangle]
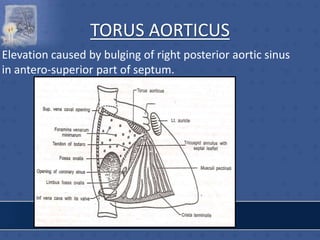
• TORUS AORTICUS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interiorofheart-220824135019-e1b4cd4e/85/INTERIOR-OF-HEART-ppt-31-320.jpg)




![FEATURES
RIGHT SIDE
1. FOSSA OVALIS
2. LIMBUS FOSSA OVALIS
3. FORAMINA VENARUM
MINIMARUM
4. ATRIO VENTRICULAR
NODE[AV NODE].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interiorofheart-220824135019-e1b4cd4e/85/INTERIOR-OF-HEART-ppt-75-320.jpg)