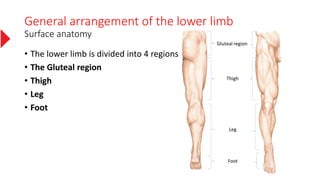
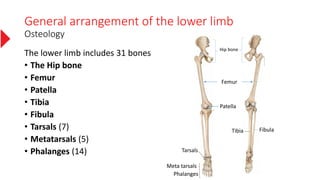
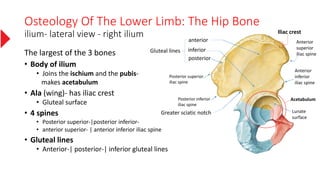
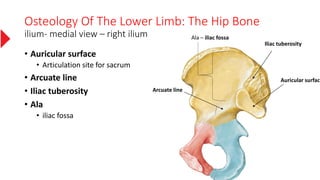
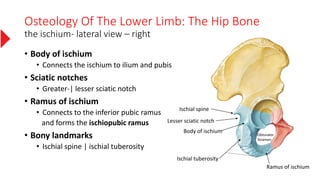
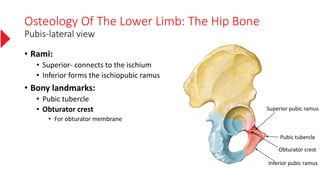
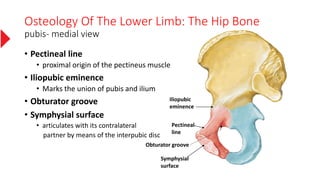
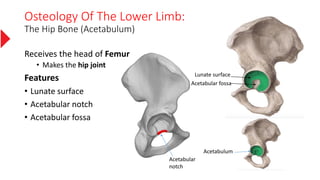
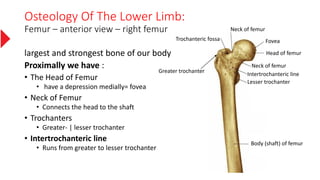
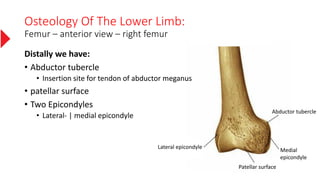
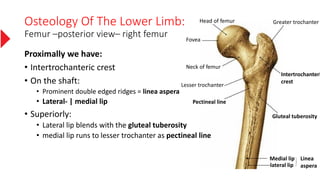
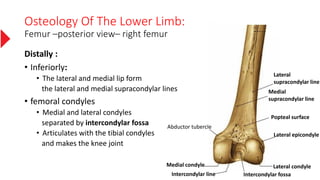
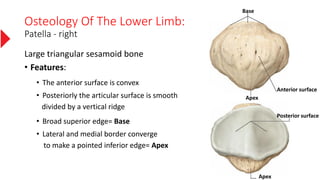
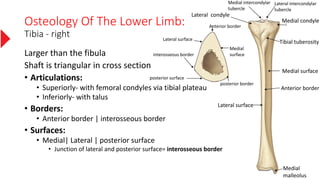
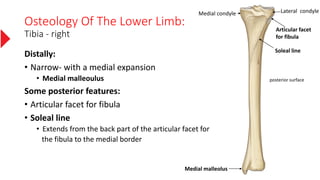
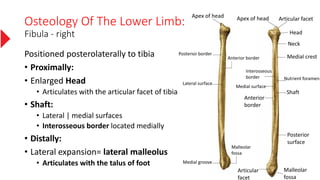
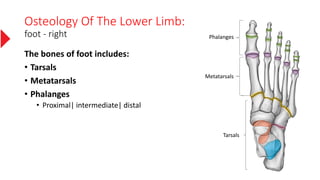
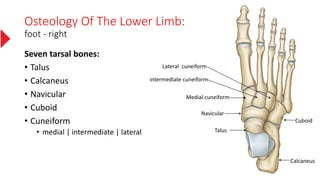
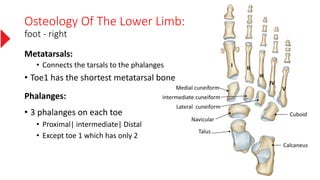
The document provides a detailed overview of the lower limb's anatomy, organized into four regions: gluteal region, thigh, leg, and foot. It describes the osteology of the lower limb, including the 31 bones such as the hip bone, femur, patella, tibia, fibula, and various bones in the foot. Key anatomical features such as the acetabulum, femoral condyles, and tarsals are highlighted with their respective functions and articulations.