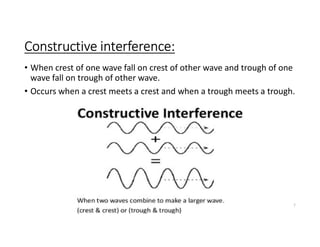
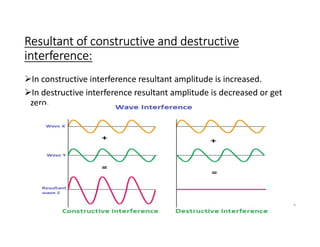
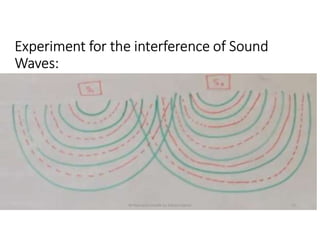
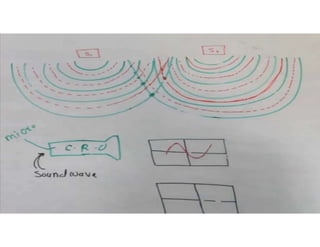
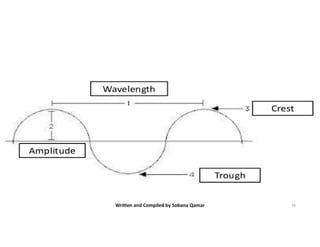
Interference occurs when two waves overlap in the same space and time. There are two types of interference: constructive and destructive. Constructive interference occurs when crest meets crest or trough meets trough, increasing amplitude. Destructive interference occurs when crest meets trough, decreasing or eliminating amplitude. Interference can be observed more easily with water waves and is demonstrated by the principle of superposition, where the resultant displacement is the vector sum of individual wave displacements.