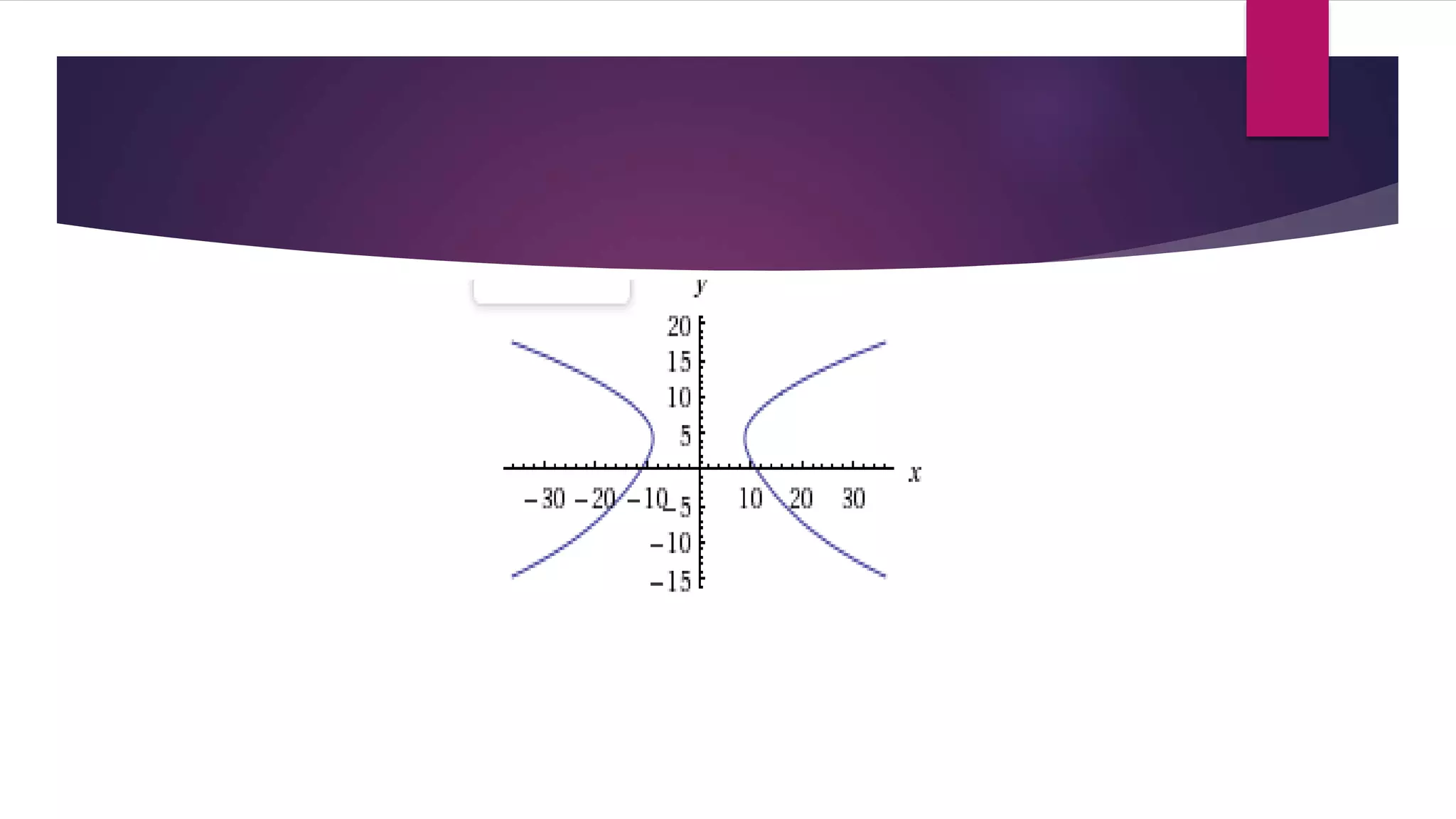
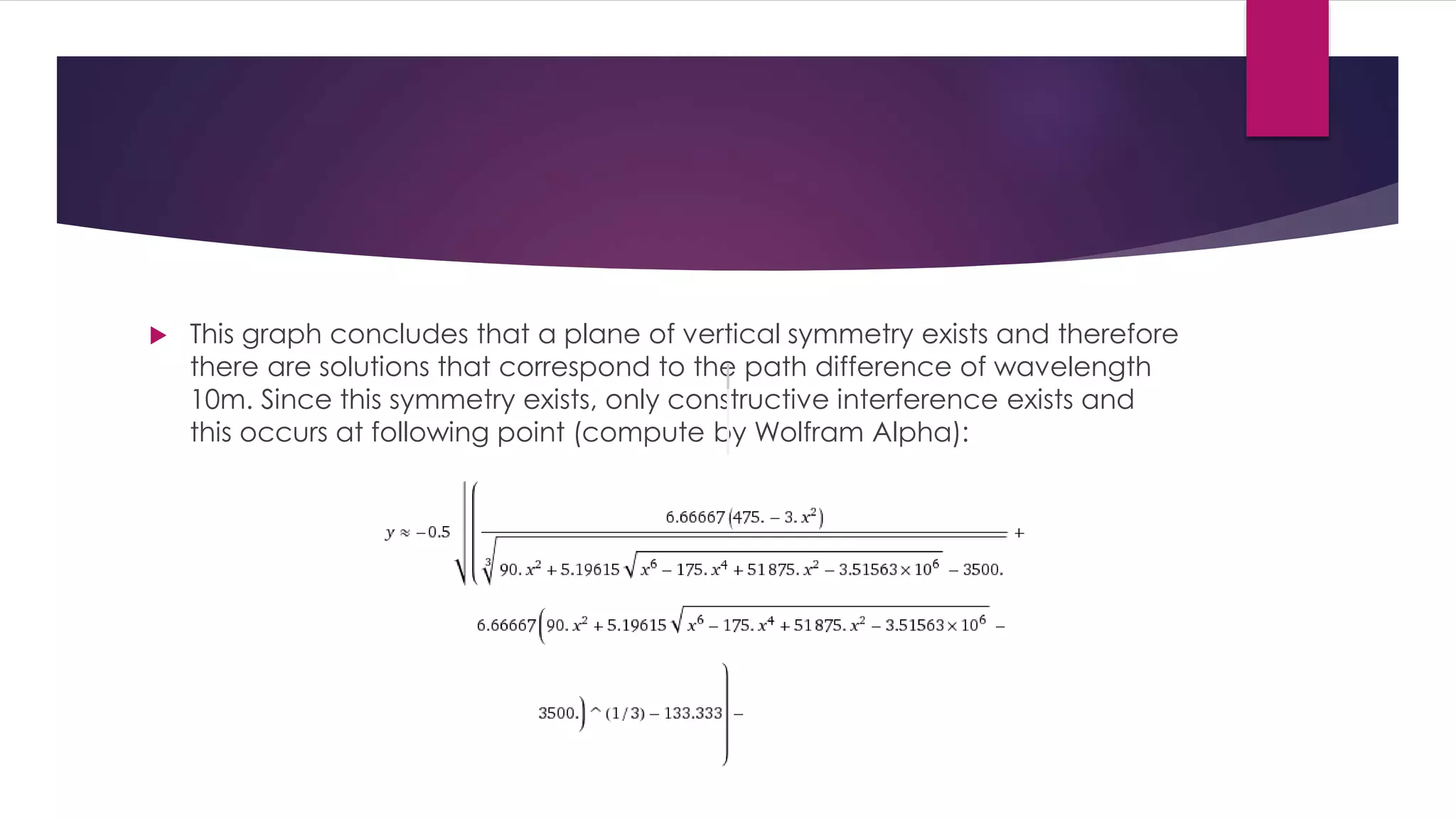
This document discusses wave interference patterns produced by two point sources of waves. It explains that when two waves are perfectly in phase, constructive interference occurs, shown as circular wave fronts. The points of constructive and destructive interference can be determined mathematically based on the path difference between the sources being equal to integer multiples of the wavelength. As an example, it analyzes the interference pattern between two boats emitting waves 80m apart, finding the point of constructive interference occurs at x = -8.90995 due to the symmetry of the setup.