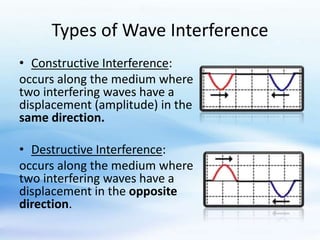
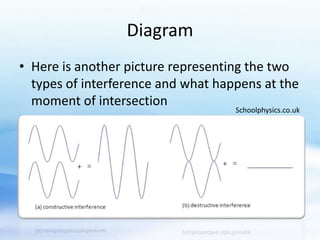
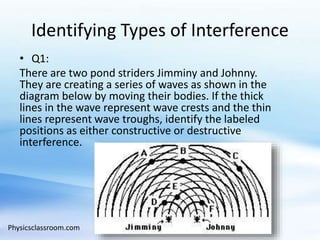
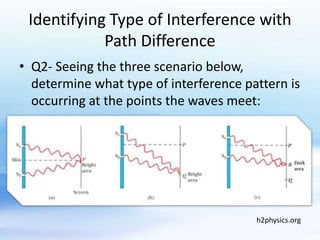
Wave interference occurs when two waves interact along the same medium. There are two types of interference: constructive and destructive. Constructive interference happens when wave displacements are in the same direction, while destructive interference occurs when they are in opposite directions. The type of interference can be determined by whether the path difference between waves is an integer or half-integer multiple of the wavelength.