Embed presentation
Downloaded 225 times








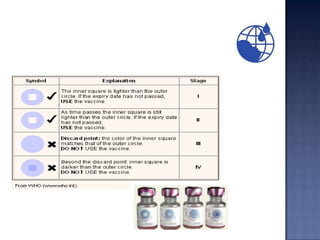
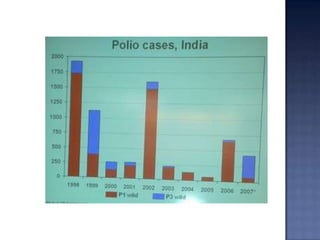





The document summarizes the history of polio vaccination efforts including the development of the inactivated Salk vaccine in 1955 and the live oral Sabin vaccine in 1961. It describes the World Health Organization's goal in 1988 to eradicate polio globally by 2000 through vaccination campaigns. It provides details about India's Intensified Pulse Polio Immunization program launched in 1995 and national immunization days, highlighting challenges in reaching all children.














