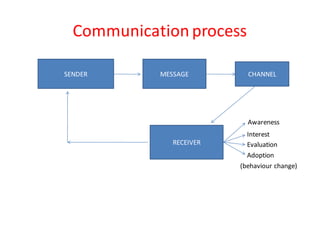
This document discusses communication for health education. It defines communication as a two-way process of sharing ideas, feelings, and information between a sender and receiver. It identifies the key parts of the communication system as the sender, receiver, message, channel, and feedback. The document then discusses various types of communication channels, barriers to effective health communication, and the goals of health communication, including providing information, education, motivation, persuasion, counseling, and supporting health development and organization.