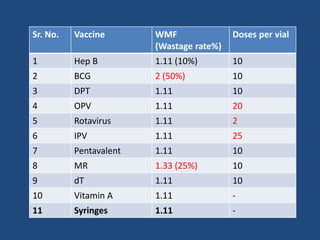
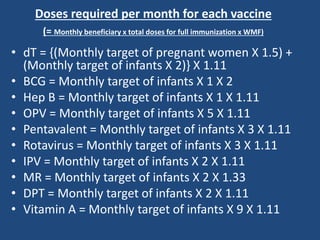
The document discusses vaccine logistics, covering concepts such as vaccine dropout rates, efficacy, usage, and wastage rates while detailing calculations and examples related to these metrics. It explains how to calculate dropout rates, vaccine efficacy, and the necessary logistics like monthly vaccine requirements and wastage factors for immunization sessions. Additionally, it provides examples for practical understanding, showcasing the calculations needed to ensure proper vaccine administration and allocation in healthcare settings.








![Usage Rate for a vaccine (%)
= (Doses Administeredx100)/Doses issued
Wastage Rate for a vaccine (%)
= 100 – Usage Rate
= 100 – [(Doses Administeredx100)/Doses issued]
Definition :
Wastage rate(%) is the proportion of vaccine
(and other injection items) that is wasted due to
variety of reasons to that which was appropriately
used (i.e. number of infants vaccinated).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vaccineslogistics-191128131659/85/Vaccine-Logistics-10-320.jpg)