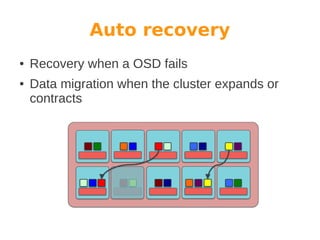
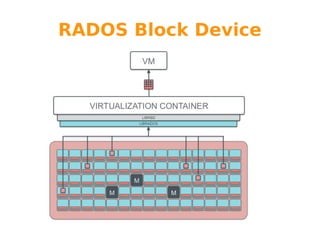
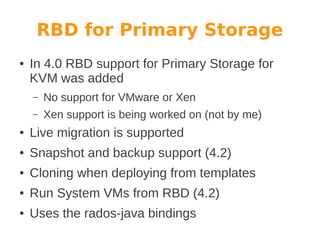
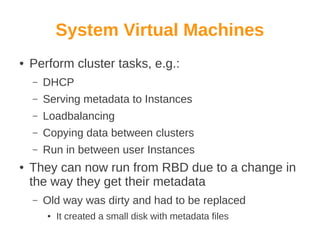
Wido den Hollander is a Ceph and CloudStack consultant who has contributed code to integrate Ceph storage with CloudStack. Ceph is an open source distributed object store that provides features like auto recovery from hardware failures and scaling capacity by adding new nodes. It uses commodity hardware and RADOS block devices to provide reliable primary storage for virtual machines in CloudStack. Future plans include adding RBD write caching and using Ceph for secondary storage. Help from the community is welcome to improve integration between Ceph, libvirt, and CloudStack.