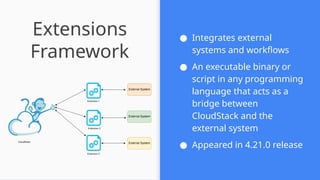
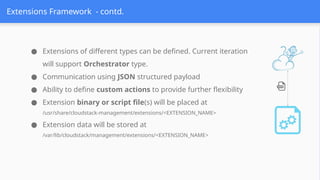
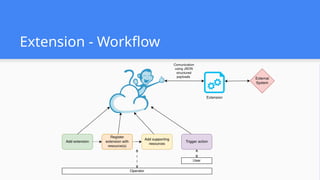
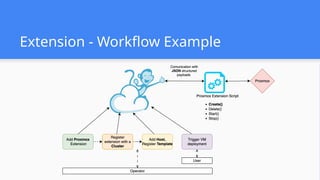
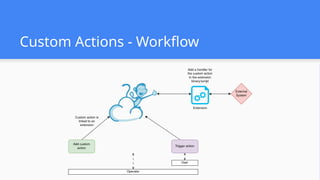
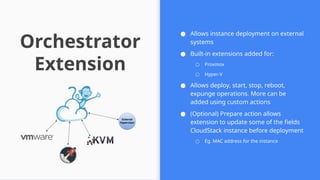
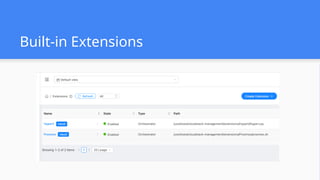
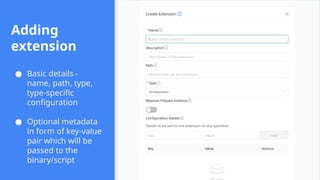
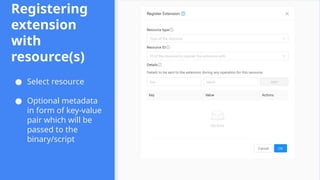
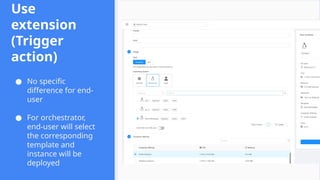
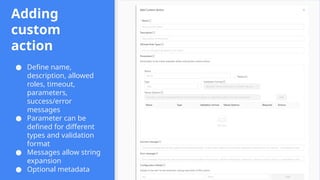
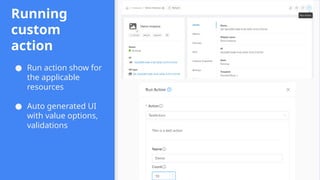
This session demonstrates the flexibility of the new Extensions Framework, allowing cloud builders to integrate custom services, orchestrators, and even third-party hypervisors directly into CloudStack’s lifecycle. A game-changer for extensibility and vendor-neutral operations.