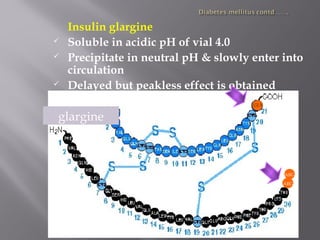
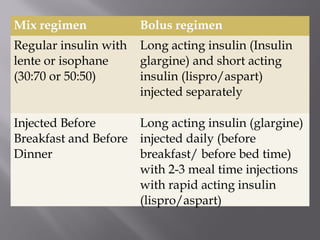
This document discusses diabetes mellitus, including its signs, symptoms, types, and complications. It also covers the physiology of insulin production and secretion by the pancreas, as well as the mechanisms and effects of insulin. Different insulin preparations are described based on source, onset and duration of action. Guidelines for insulin administration and considerations for special cases and drug interactions are provided.















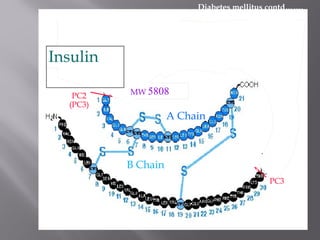







![Rapid acting: insulin lispro
lysine [B28], proline [B29]
Given immediately before or after meal
LYS
PROLYS
PRO
InsulinlisproInsulin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insulin-180729003444/85/Insulin-29-320.jpg)