Embed presentation
Downloaded 41 times


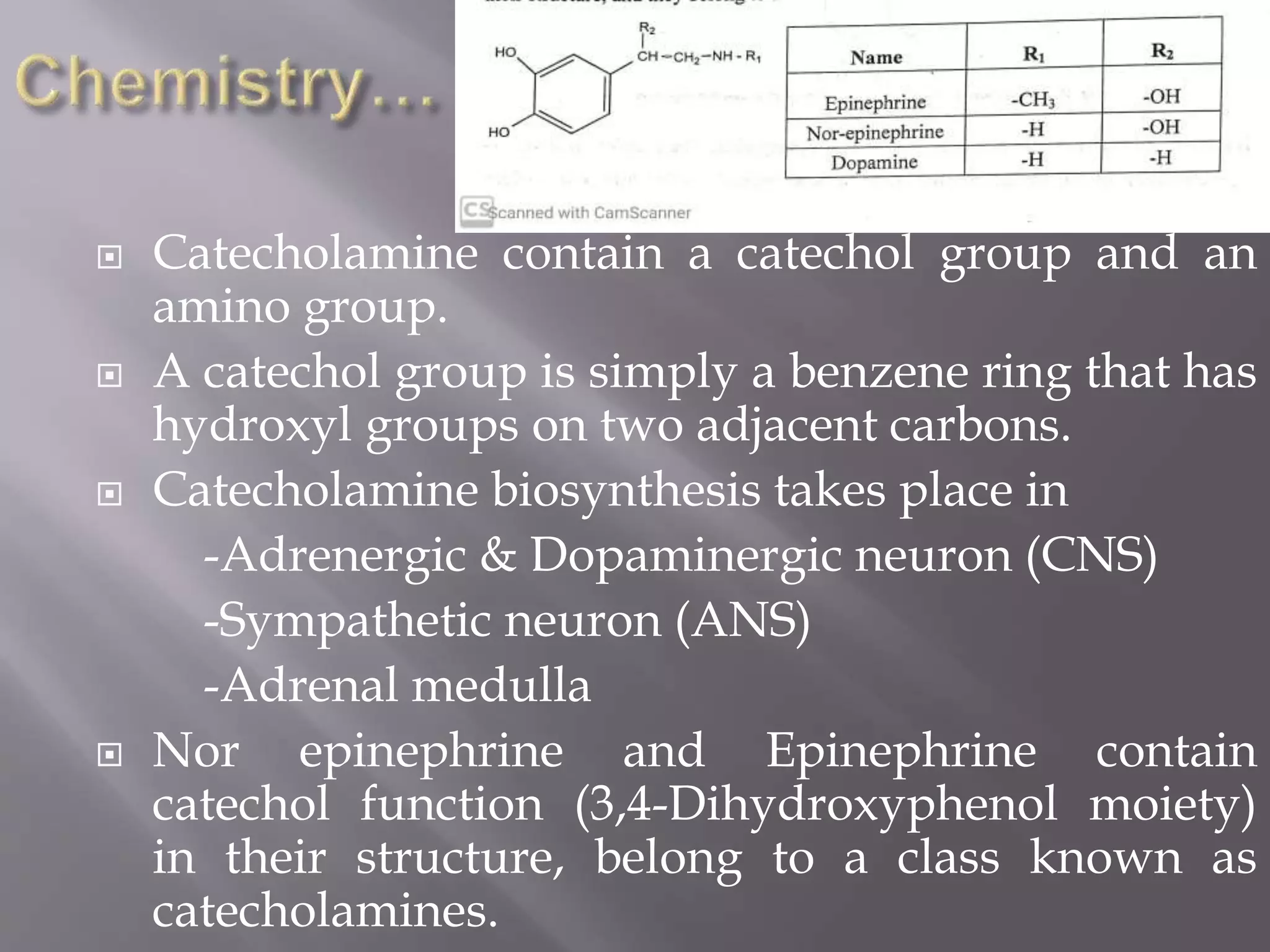



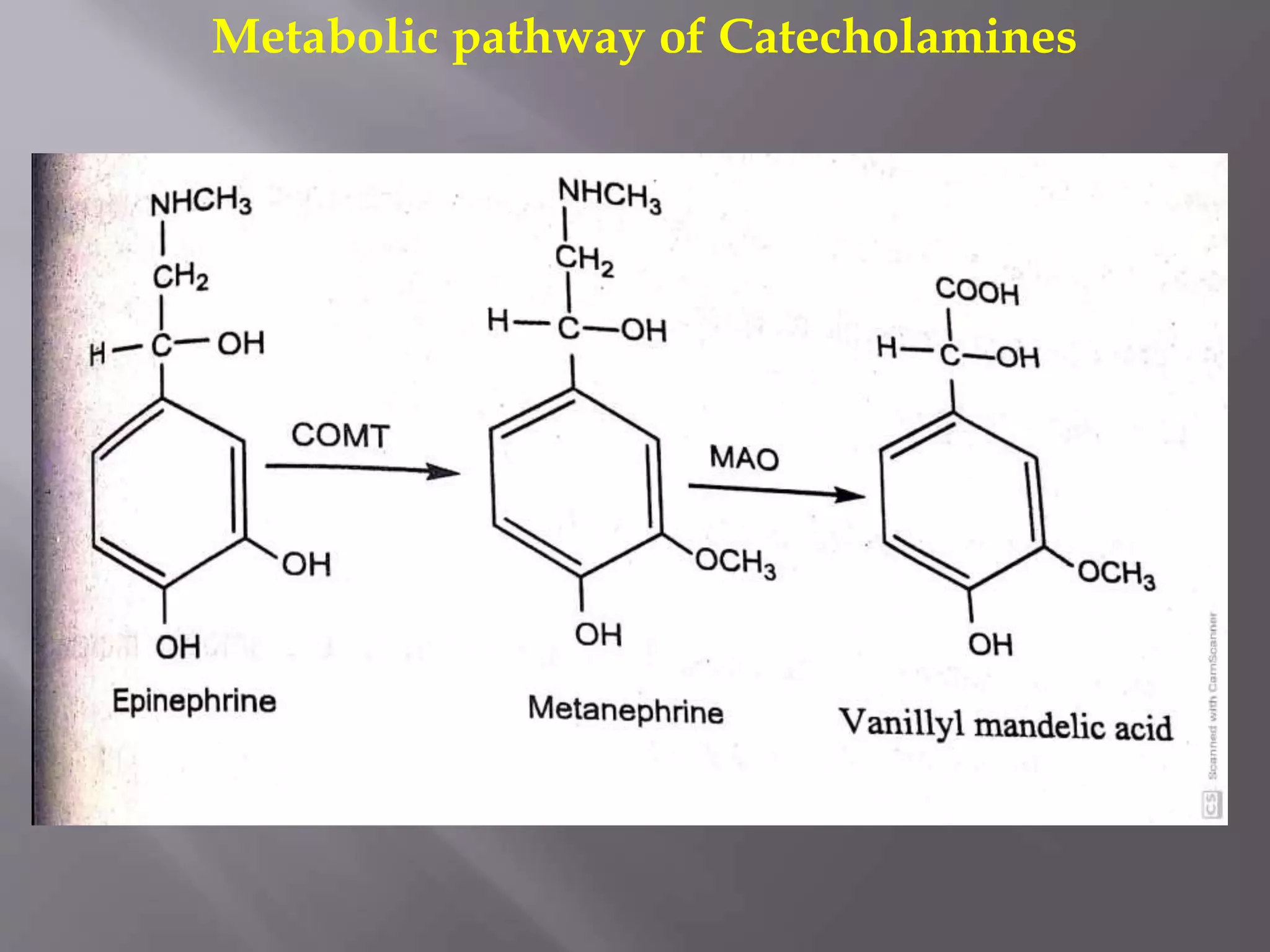

Catecholamines, hormones produced by the adrenal glands, include dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, and are released during physical or emotional stress. Their biosynthesis occurs in various neurons, and their actions are terminated through re-uptake, diffusion, and metabolic transformations. The structure of norepinephrine and epinephrine features a catechol group, classifying them as catecholamines.







