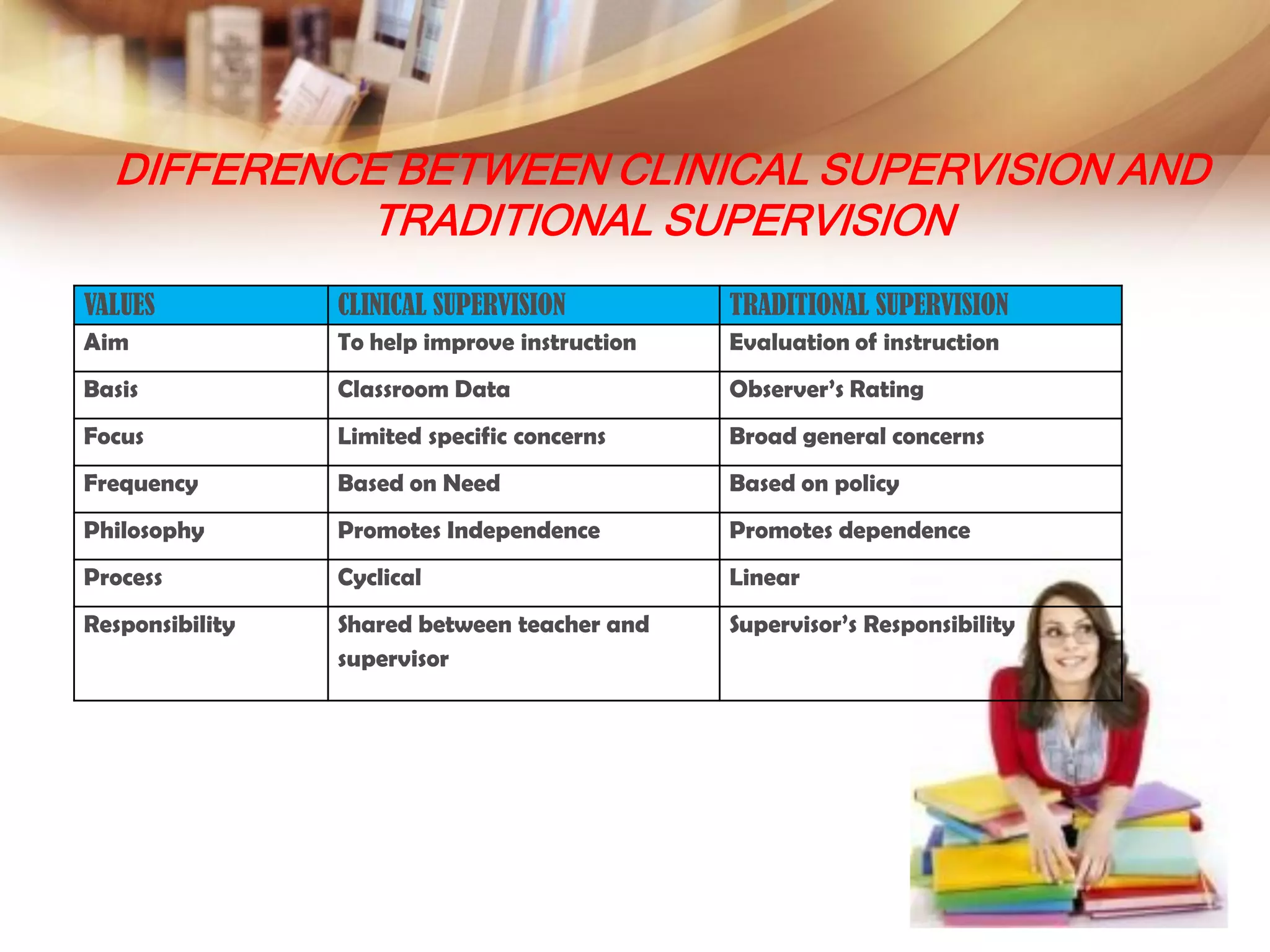
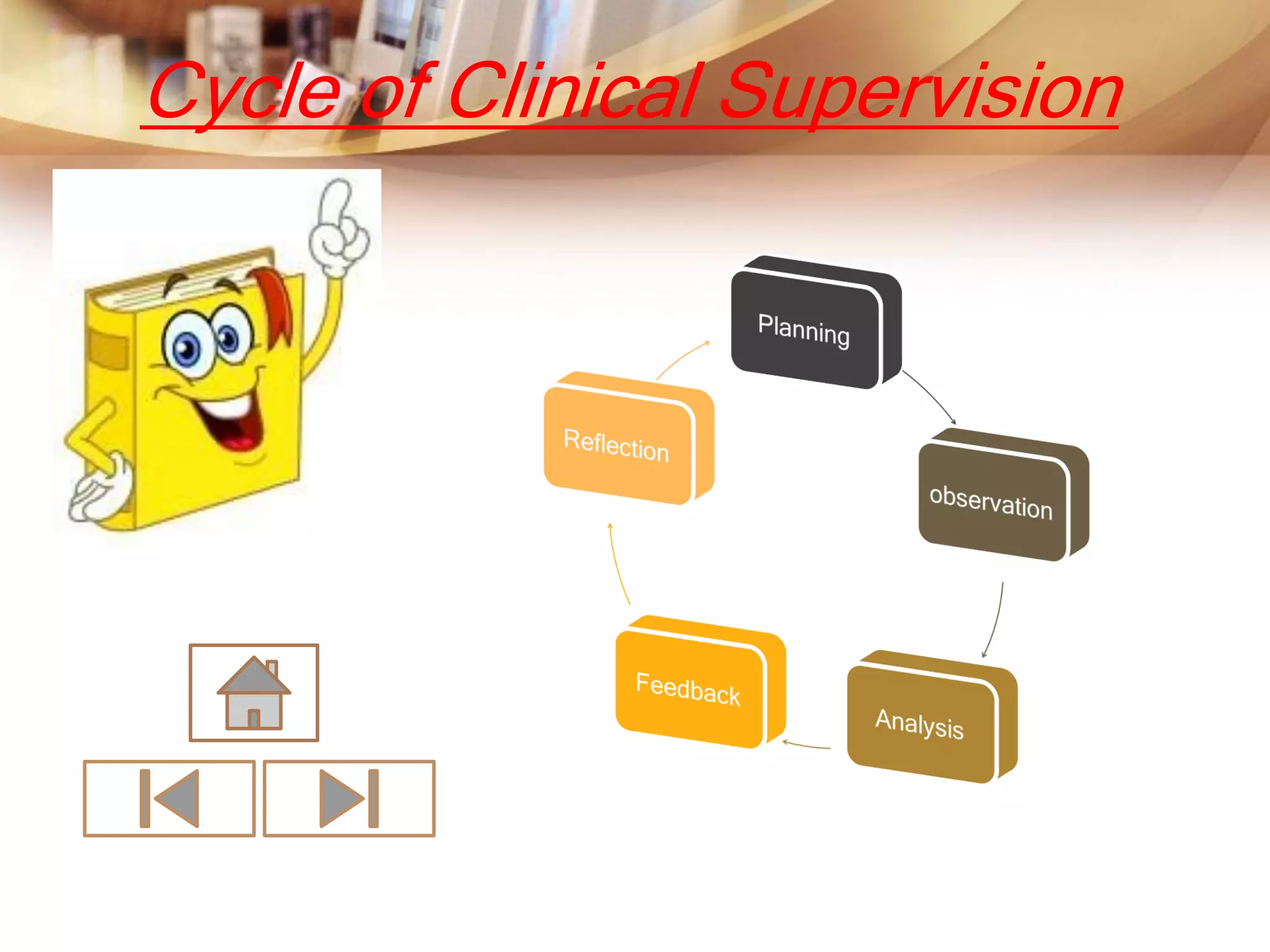
This document discusses various methods of supervision and evaluation of teachers. It describes elements common to observational systems, types of classroom visits and supervision in the Philippines. It then focuses on clinical supervision, outlining its characteristics, model, and differences from traditional supervision. Other methods discussed include cognitive coaching, mentoring, peer assessment, portfolio assessment, and action research. Clinical supervision aims to help teachers improve instruction through self-analysis and reflection.