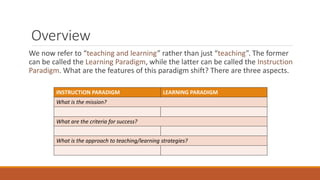
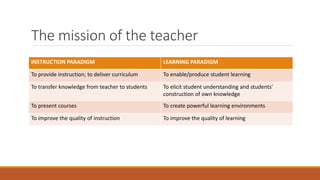
The document discusses the paradigm shift from an instruction-focused approach to a learning-centered approach in teaching. It highlights the roles, criteria for success, and strategies involved in both paradigms, emphasizing the importance of facilitating student learning. The conclusion reinforces that while instruction is necessary, teachers must also prioritize enabling students to construct their own knowledge.