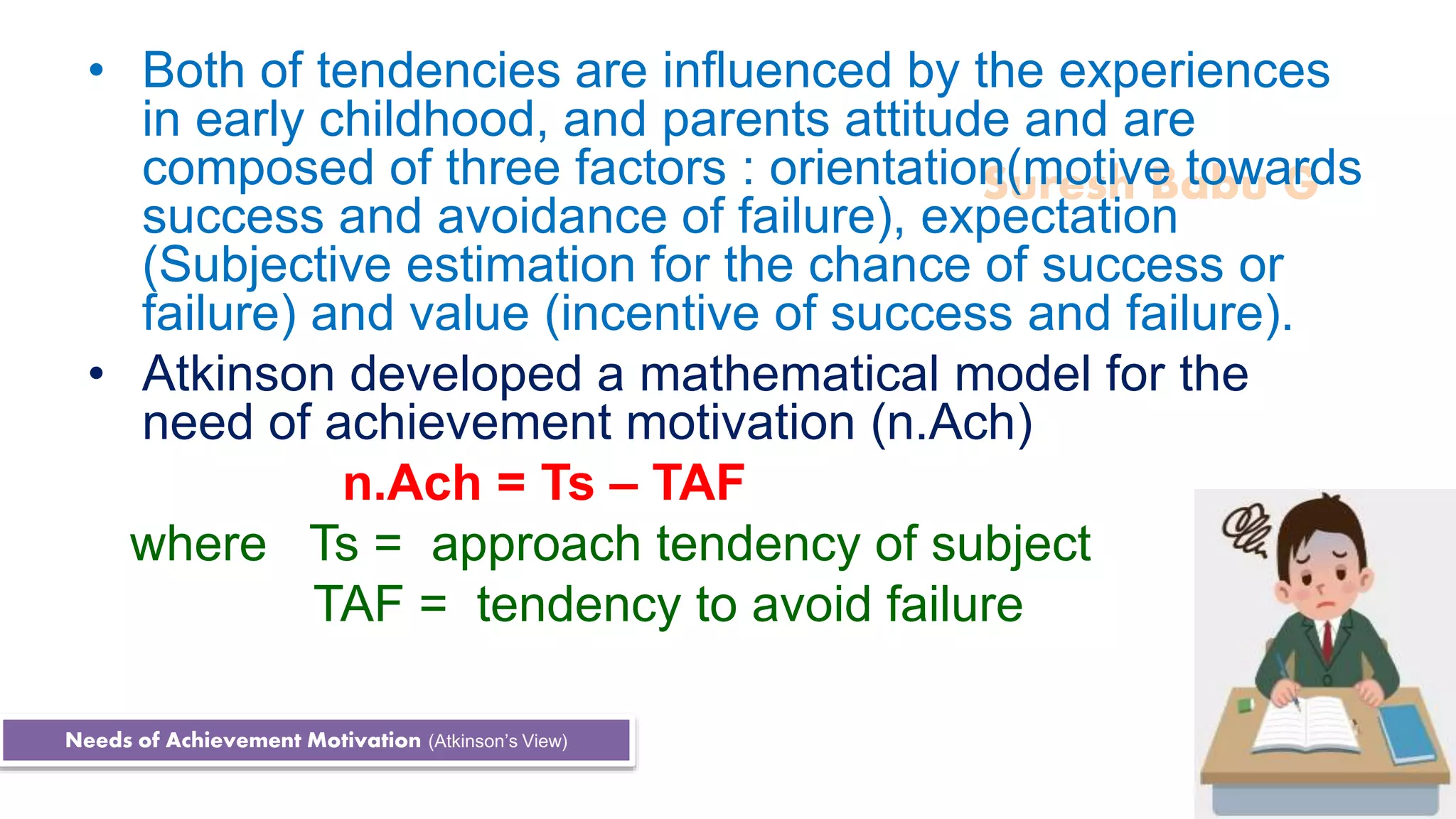
The document discusses motivation, defining it as a process that initiates and directs behavior towards achieving specific goals, citing various definitions and types of motivation such as intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. It explores achievement motivation, emphasizing its characteristics, needs, and the influence of early experiences on an individual's drive to succeed. Additionally, the document outlines strategies for teachers to foster motivation in learners and the roles of reward and punishment in the learning process.