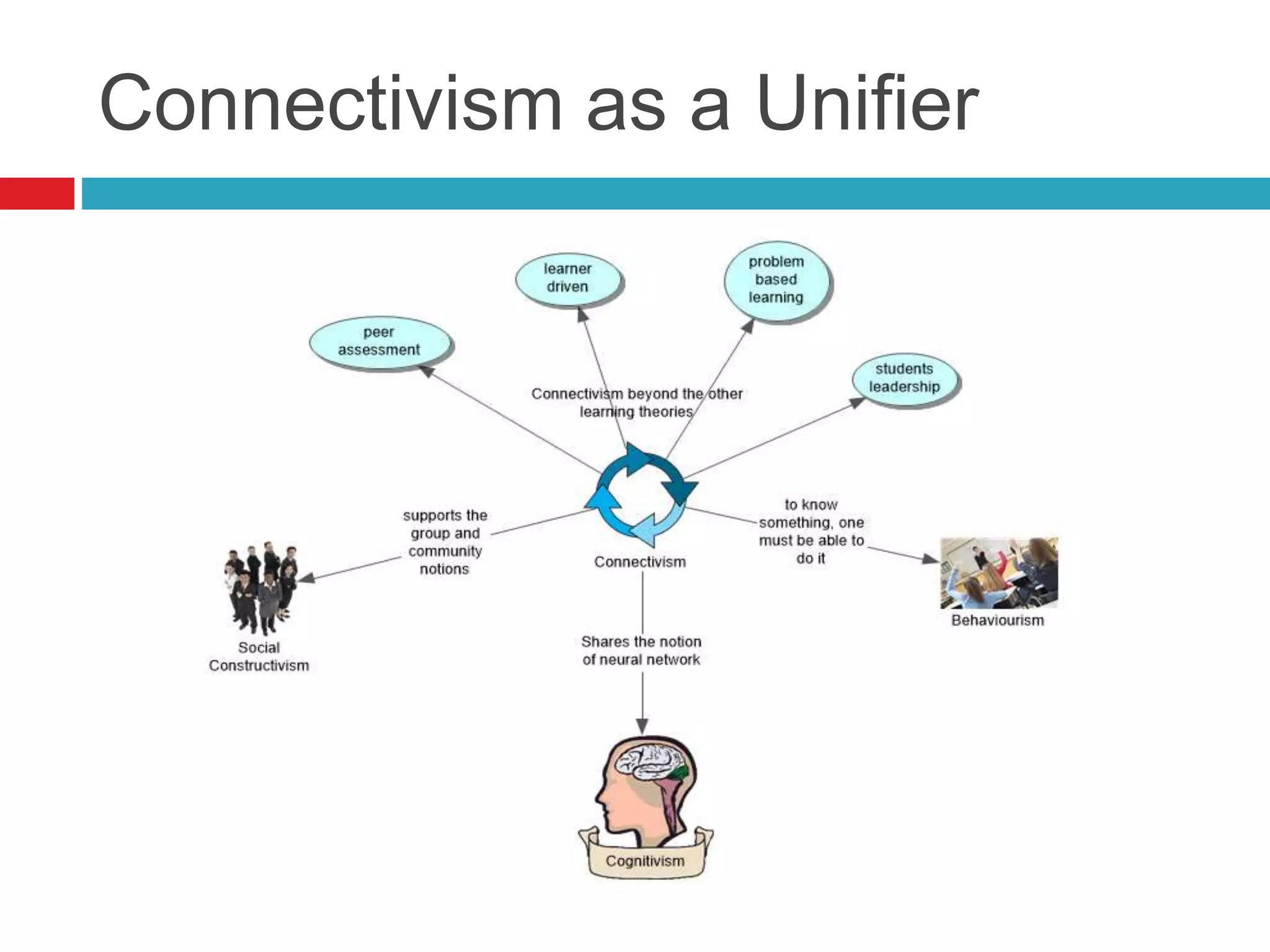
Connectivism is a learning theory developed by George Siemens and Stephen Downes that argues knowledge exists throughout a network and learning occurs as connections are formed within that network. The theory was proposed in response to limitations of existing learning theories in the digital age where knowledge and information grow exponentially. According to connectivism, learning is a process of connecting specialized information sources, and the ability to construct and evaluate the relevance of connections is important. Technology plays an integral role by facilitating networked learning and sharing of experiences.