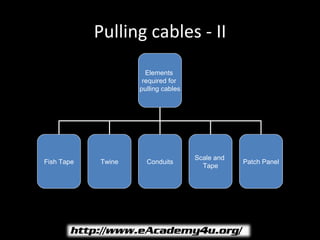
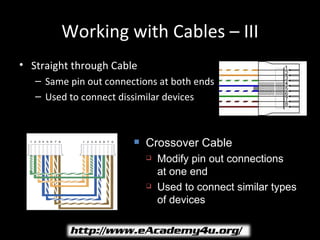
This document provides information on installing and designing a structured cabling network. It discusses the components of structured cabling including cables, patch panels, outlets, and cross-connect devices. It also covers design considerations for installing cable runs, closets, racks, and ensuring proper grounding. The goal is to provide an organized and consistent wiring system to transmit data throughout a building or site.