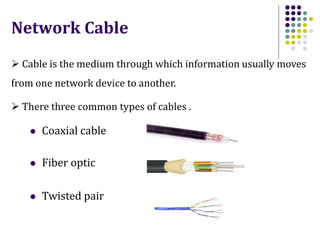
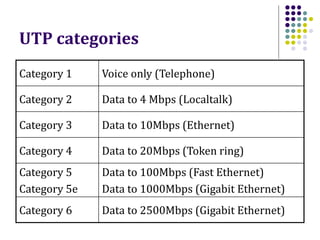
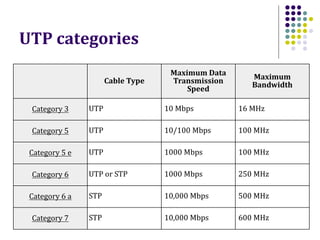
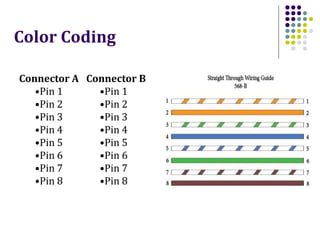
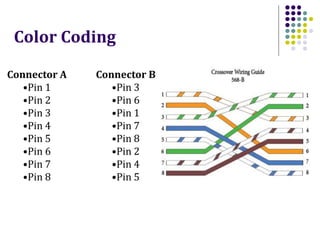
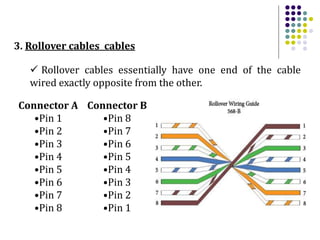
This document discusses different types of network cabling. It describes the three main types as twisted pair, coaxial, and fiber optic cables. Twisted pair cable, especially unshielded twisted pair (UTP), is most commonly used for local area networks. UTP cables are categorized based on their bandwidth and transmission speed capabilities. The document also covers topics such as cable connectors, color coding, straight-through and crossover cables, and guidelines for installing network cabling.