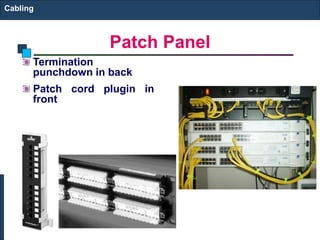
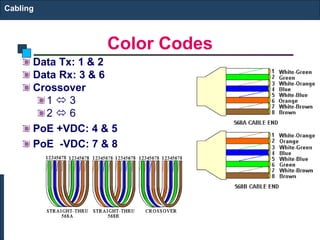
This document discusses different types of cabling used in structured cabling infrastructures. It covers components for both UTP and fiber optic cabling including information outlets, patch panels, cables, patch cords, connectors and tools. It provides guidelines for properly installing, terminating and testing cabling.