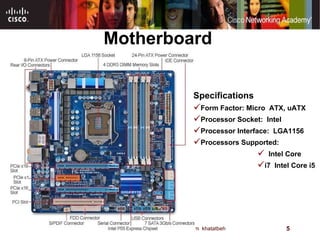
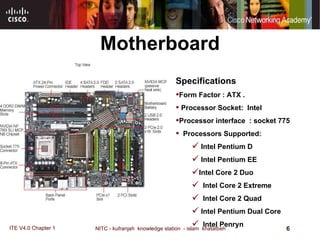
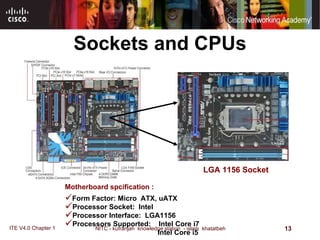
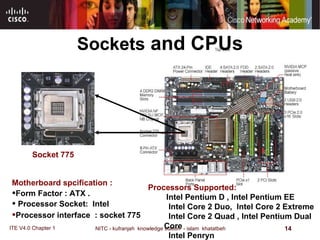
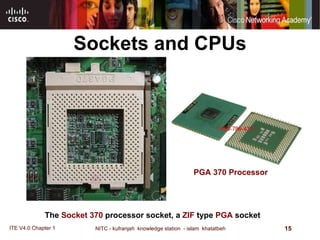
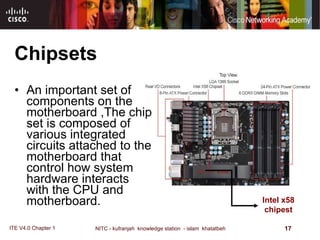
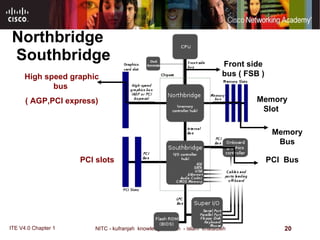
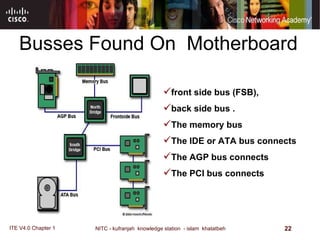
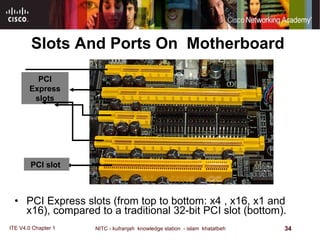
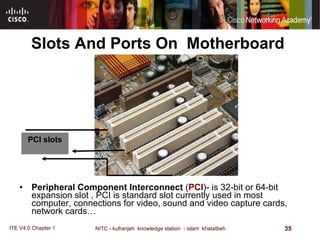
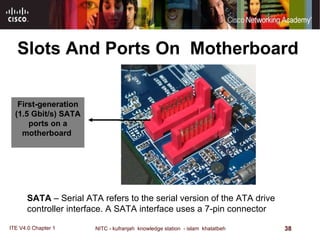
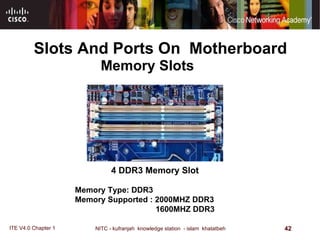
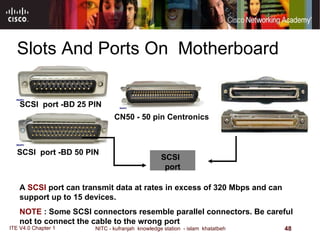
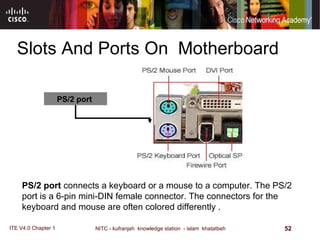
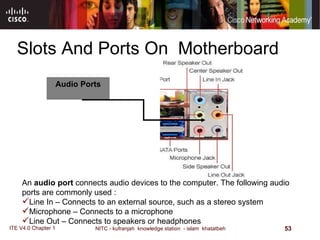
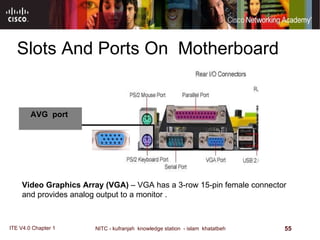
The motherboard is the main circuit board that connects the central components of a computer system. It accommodates the CPU, RAM, expansion slots, and connectors. Motherboards come in various form factors that determine component layout and case compatibility. The CPU socket and chipset standards on the motherboard must match the CPU for proper functioning. The chipset includes a northbridge that connects to RAM and graphics and a southbridge that connects to storage and ports.