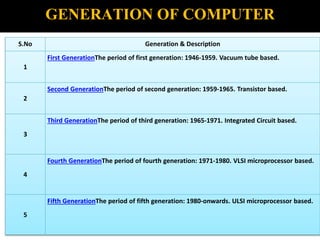
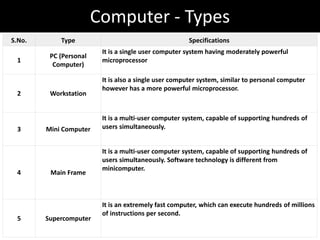
1. The document discusses the history and components of computers from first to fifth generations, including vacuum tube, transistor, integrated circuit, and microprocessor technologies.
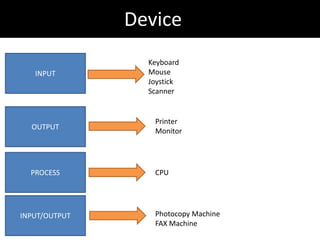
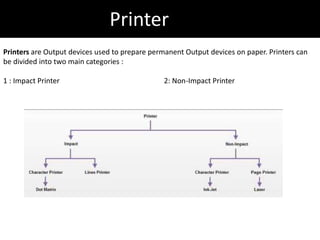
2. It describes the basic parts of a computer including input devices like the keyboard and mouse, output devices like monitors, and central processing units.
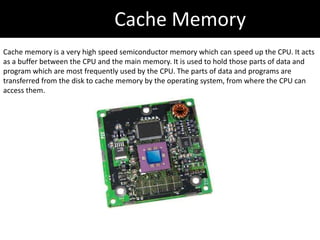
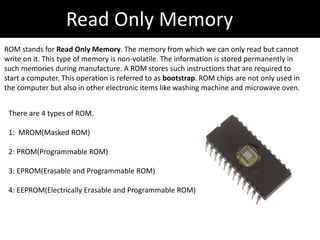
3. Memory types are explained including cache, primary, and secondary memory. RAM and ROM are also summarized.