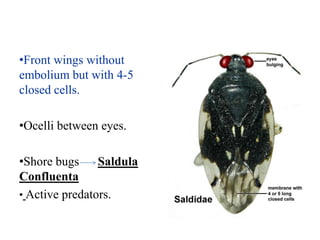
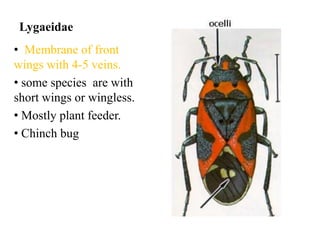
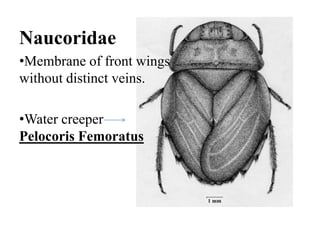
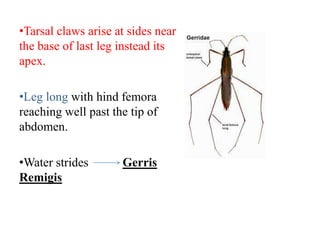
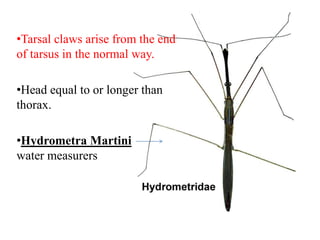
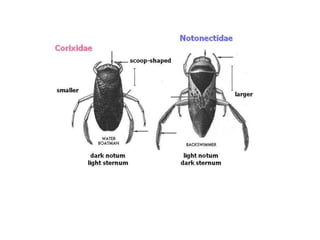
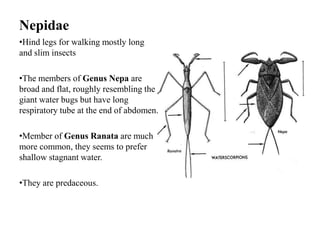
Hemiptera, commonly known as true bugs, have front wings that are leathery at the base and membranous at the tips. They undergo incomplete metamorphosis and have piercing and sucking mouthparts. Hemiptera are classified into two suborders - Cryptocerata which are mostly aquatic bugs like water boatmen and backswimmers, and Gymnocerata which include terrestrial bugs like plant bugs, assassin bugs, and stink bugs. Examples mentioned include the giant water bug Belostoma grandis, avocado lace bug Corythuca ciliata, and assassin bug Reduvius personatus.