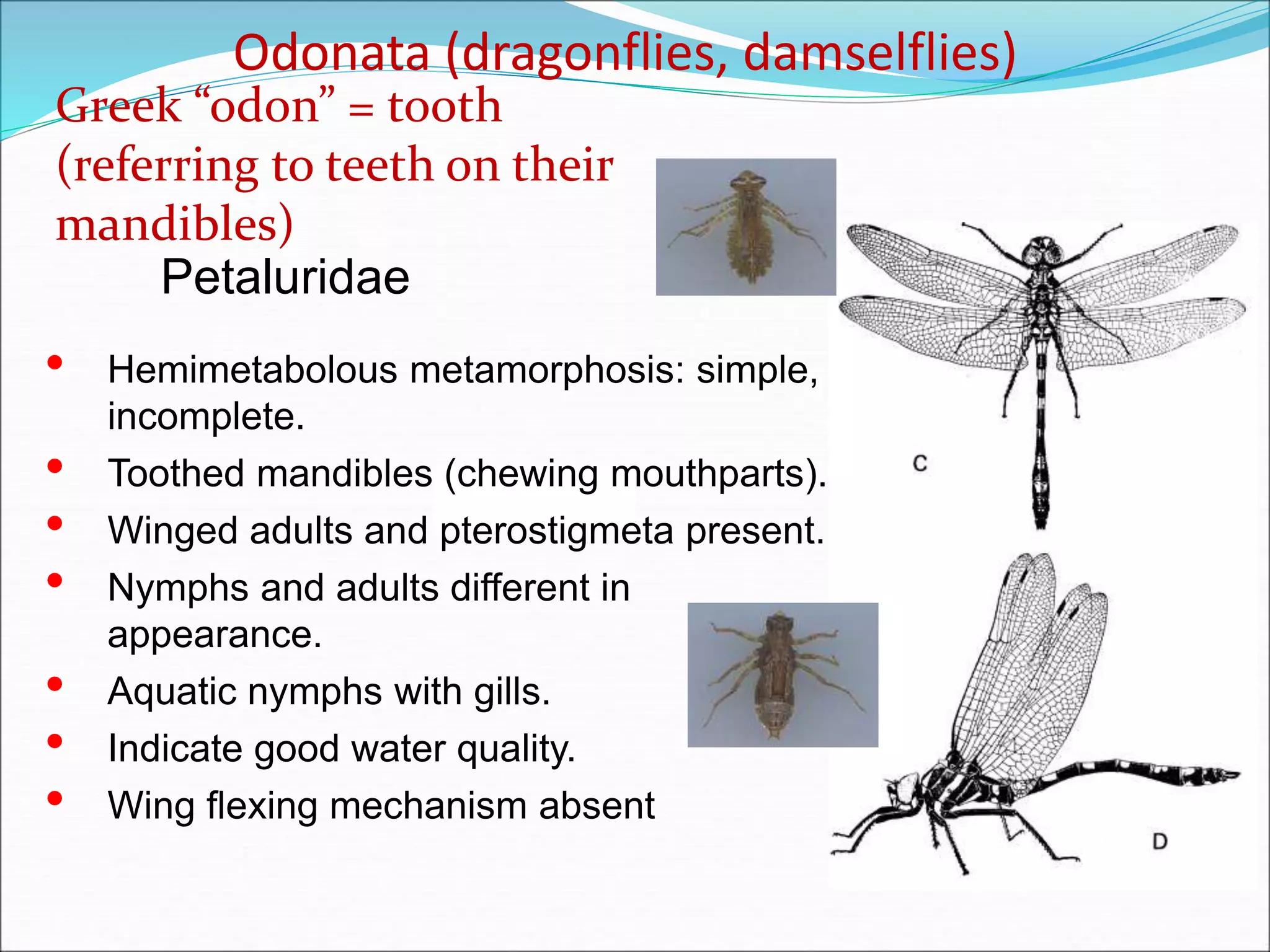
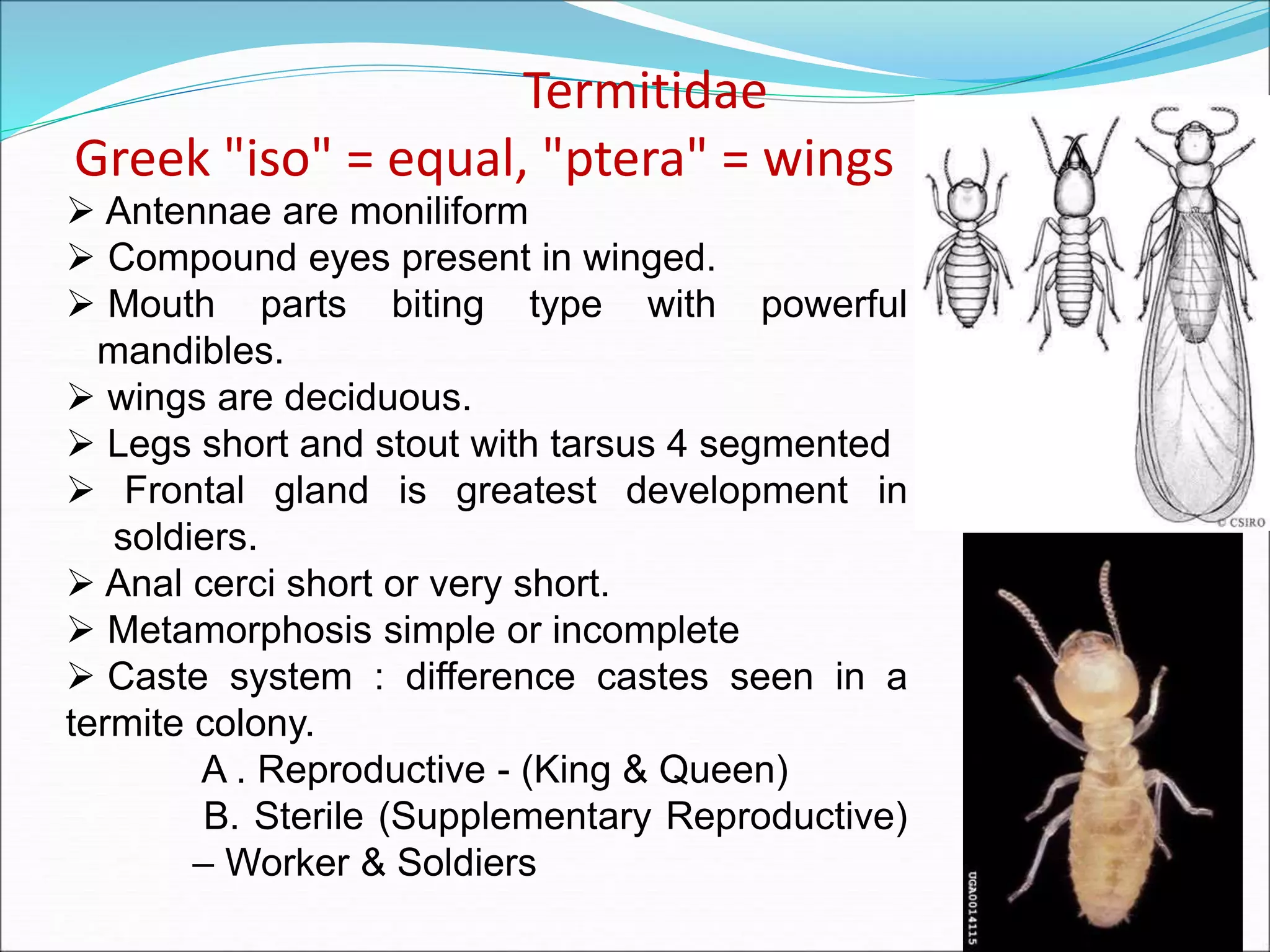
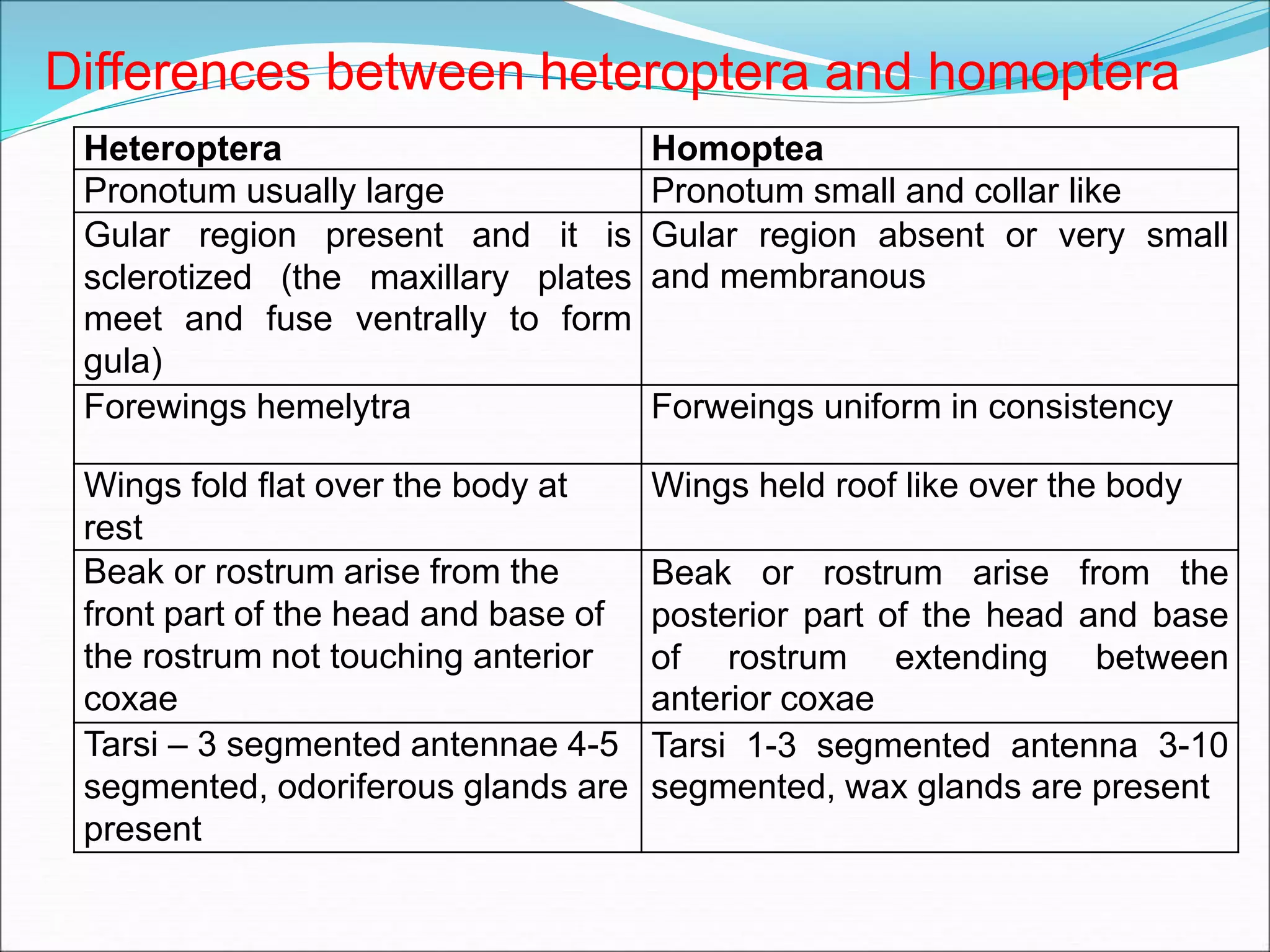
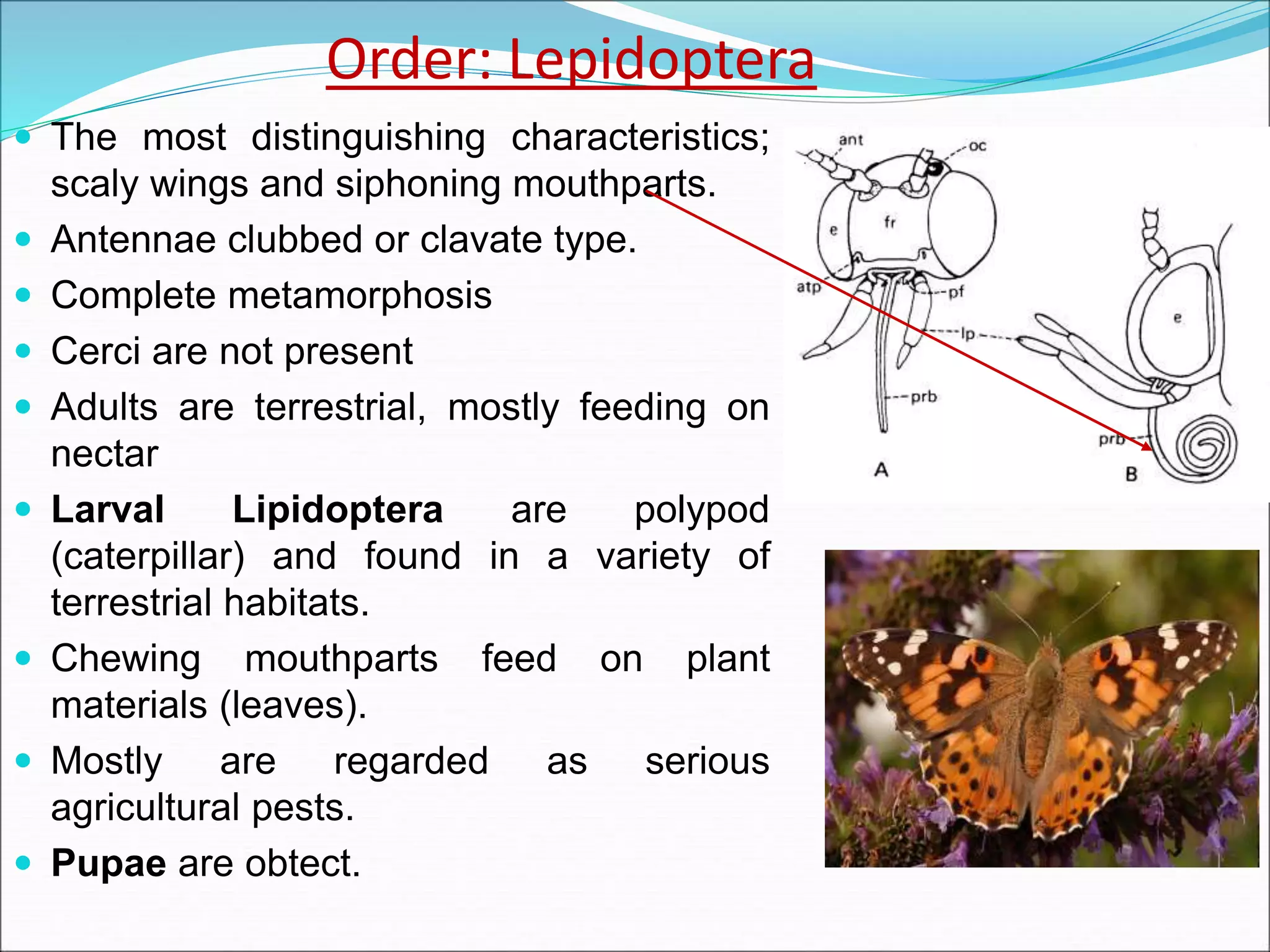
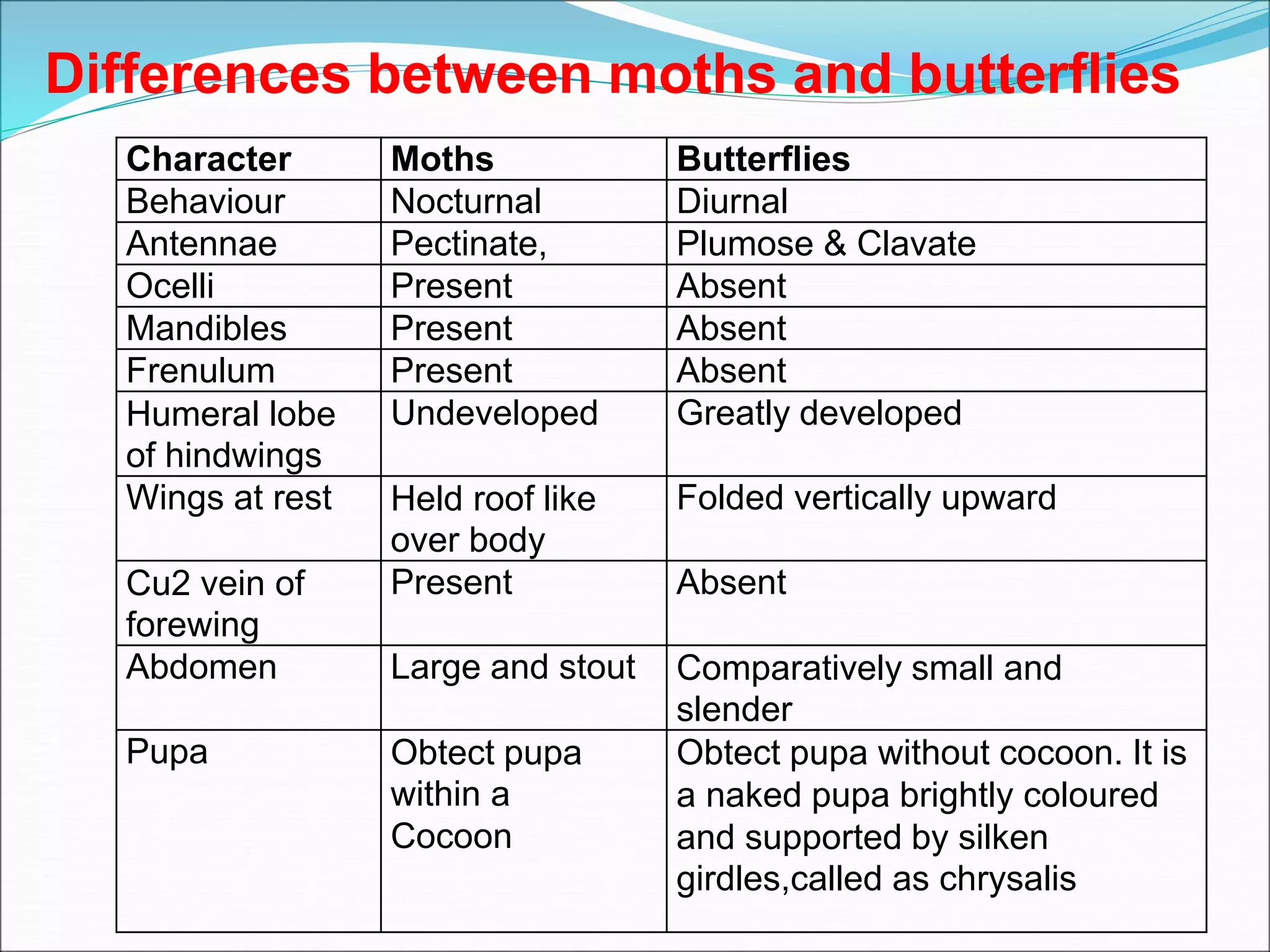
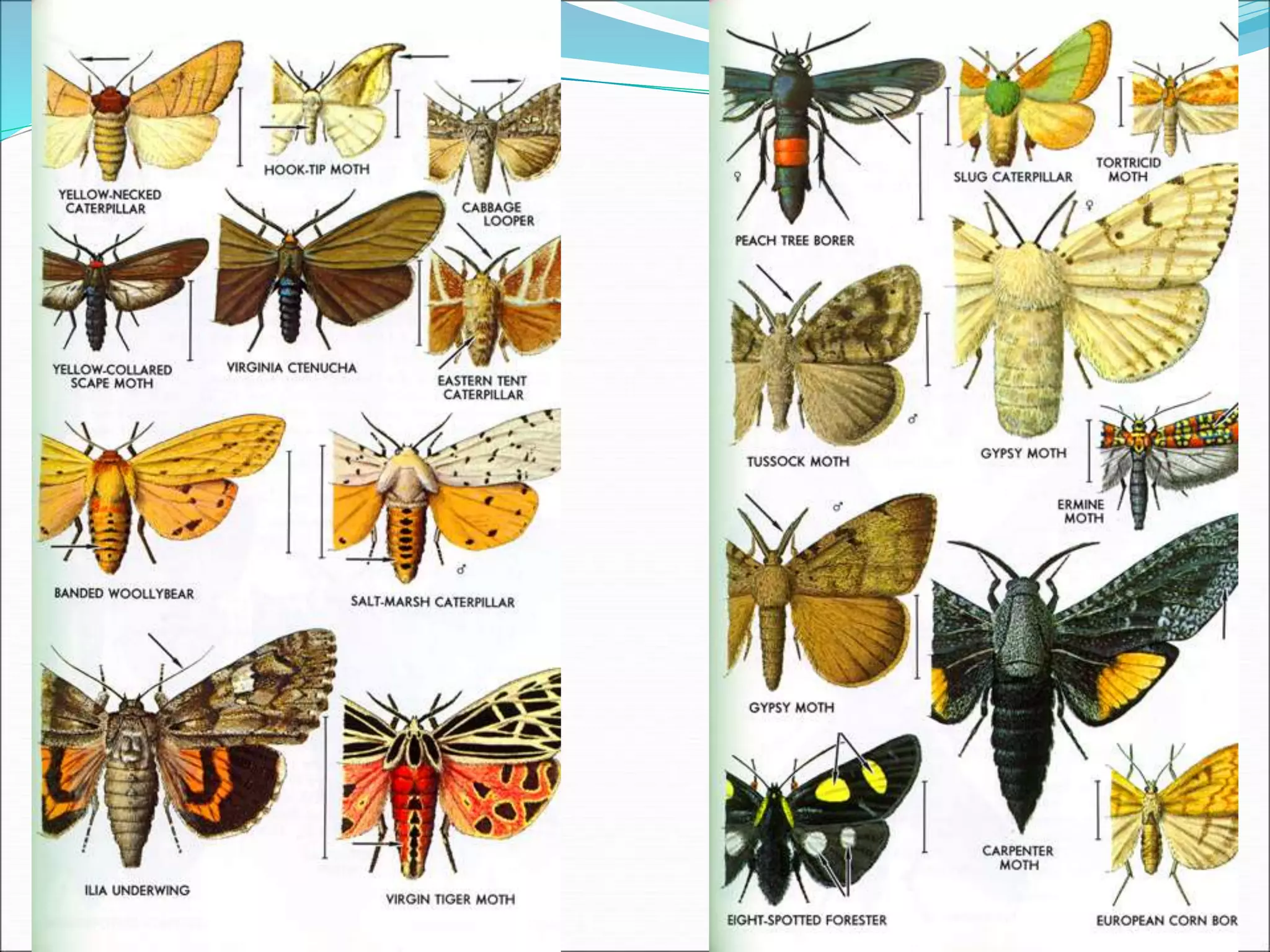
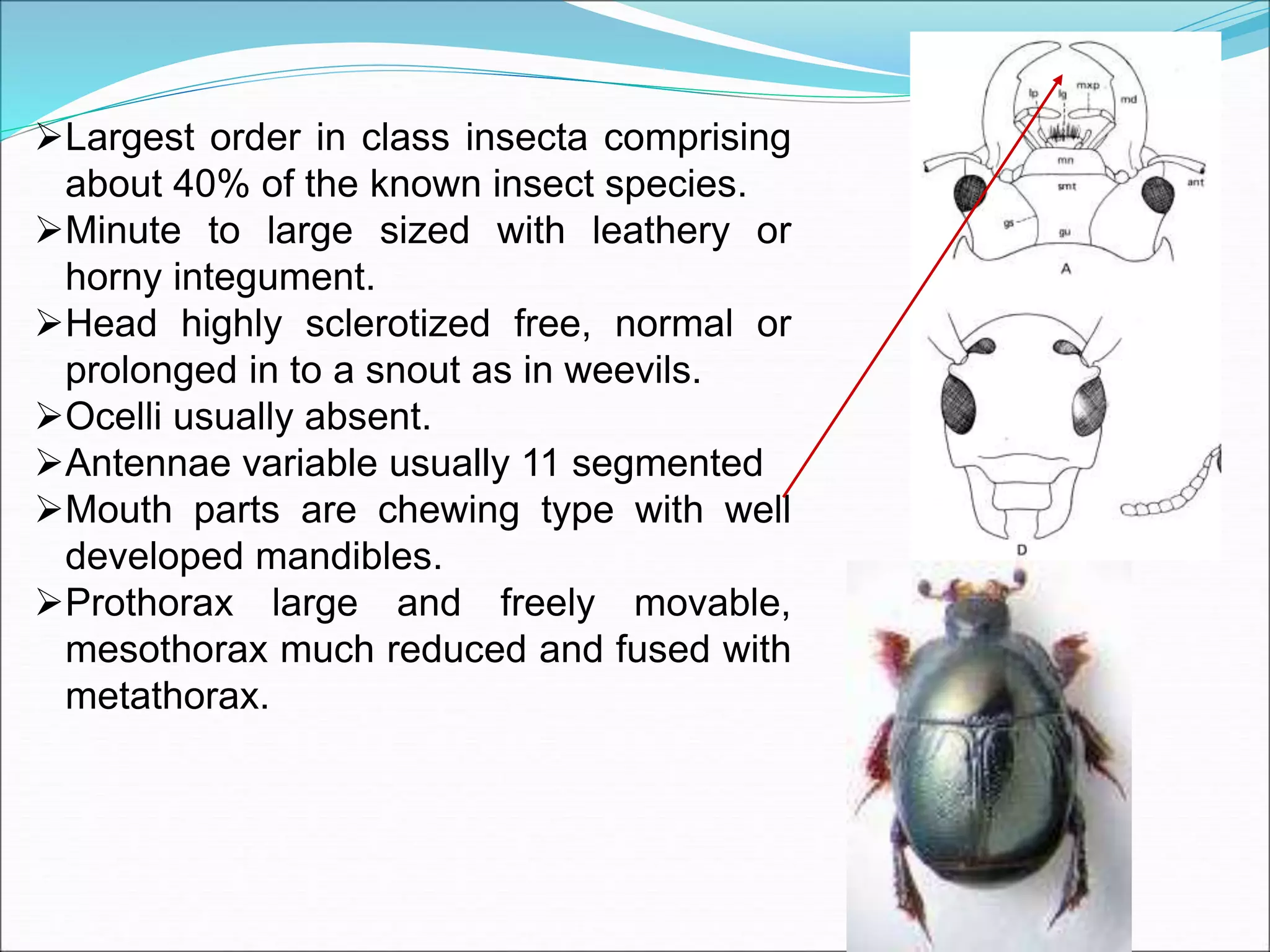
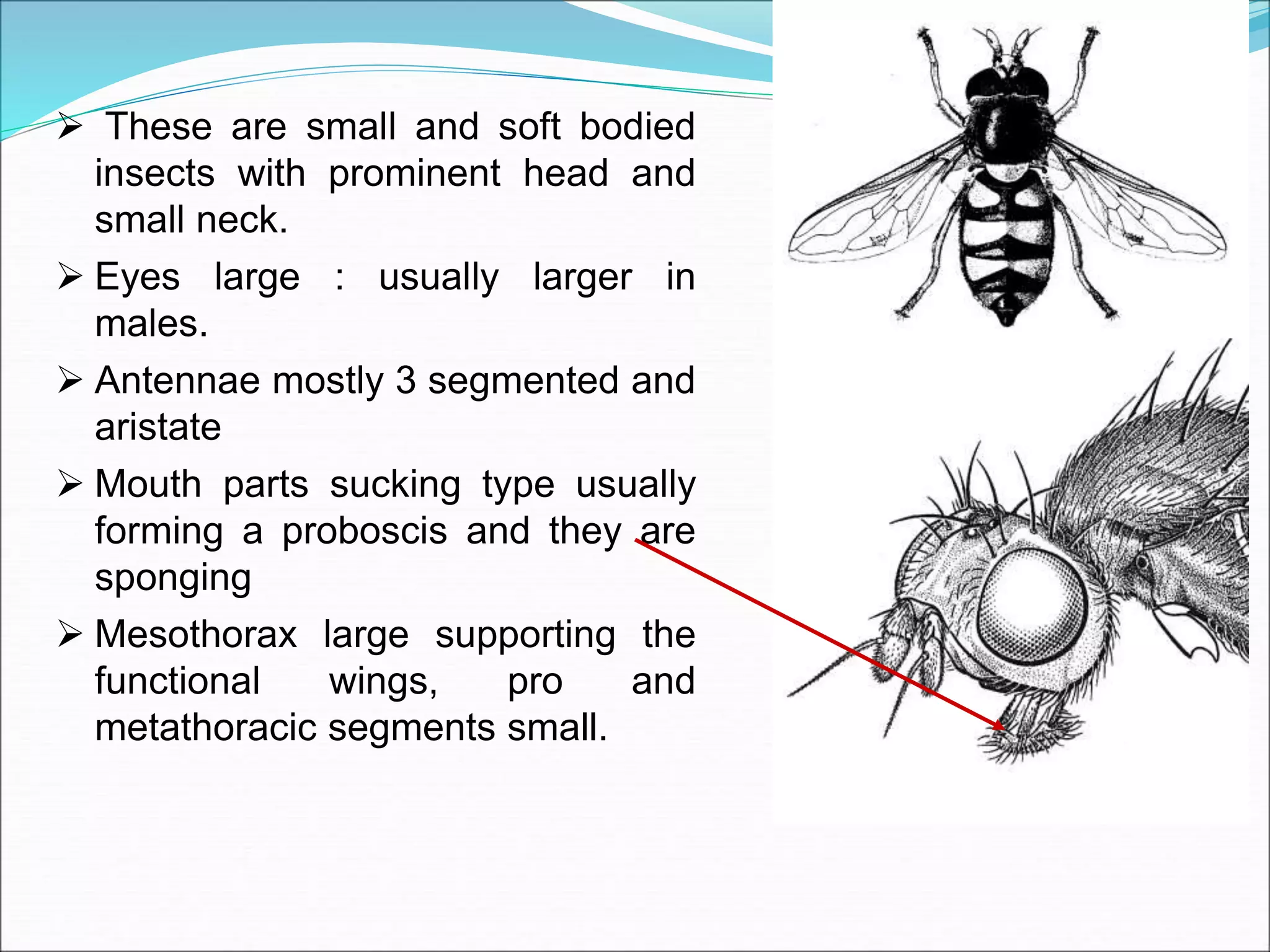
This document provides information on various orders of insects through descriptions of key characteristics. It covers orders such as Orthoptera (grasshoppers), Dictyoptera (mantids), Blattodea (cockroaches), Odonata (dragonflies and damselflies), Neuroptera (lacewings and antlions), Isoptera (termites), Thysanoptera (thrips), Hemiptera (true bugs), Lepidoptera (butterflies and moths), Coleoptera (beetles), Hymenoptera (sawflies, wasps, bees and ants), Diptera (flies) and provides comparisons between different groups such as moths and butter