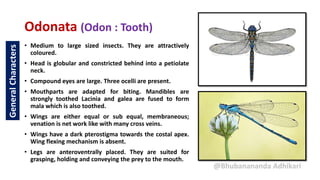
The document describes various exopterygote insect orders including Odonata (dragonflies and damselflies), Orthoptera (grasshoppers, locusts, crickets), Dictyoptera (cockroaches and mantids), Thysanoptera (thrips), and Hemiptera. For Odonata, it discusses their morphology, life stages, suborders of Anisoptera and Zygoptera. For Orthoptera, it covers suborders of Caelifera and Ensifera and families including Acrididae, Tettigonidae, Gryllidae, and Gryllotalpidae. It also provides details on Dictyoptera sub



















![Dictyoptera
@Bhubanananda Adhikari
Basic Difference between 2 Suborders (Blattaria,
Mantodea)
Blattaria
[Family: Blattidae]
Cockroach
Mantodea
[Family: Mantidae]
Preying mantids
Head is not mobile in all
direction as it is hidden by
shield like pronotum
Head is mobile in all
direction as it is not covered
by pronotum (elongated)
2 fenestrae (degenerated
ocelli)
3 ocelli
All legs cursorial Foreleg raptorial, other are
ambulatorial](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect13exopterygoteorders-210717102738/85/Exopterygote-21-320.jpg)
![Dictyoptera
@Bhubanananda Adhikari
Basic Difference between 2 Suborders (Blattaria,
Mantodea)
Blattaria
[Family: Blattidae]
Cockroach
Mantodea
[Family: Mantidae]
Preying mantids
Gizzard with chitinous teeth No chitinous teeth in gizzard
Female does not devour
male
Female often devours the
male during mating
Eggs inside ootheca Eggs in egg case
Nymps are not cannibalistic Cannibalistic nymph
No mimicry Mimicry
Omnivorous Carnivorous](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect13exopterygoteorders-210717102738/85/Exopterygote-22-320.jpg)
























![@Bhubanananda Adhikari
S.O : Heteroptera
(C: Corium, CL: Clavus,
CU: Cuneus, E: embolium)
[I: Lygaeidae, II: Miridae,
III: Anthocoridae]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect13exopterygoteorders-210717102738/85/Exopterygote-47-320.jpg)










