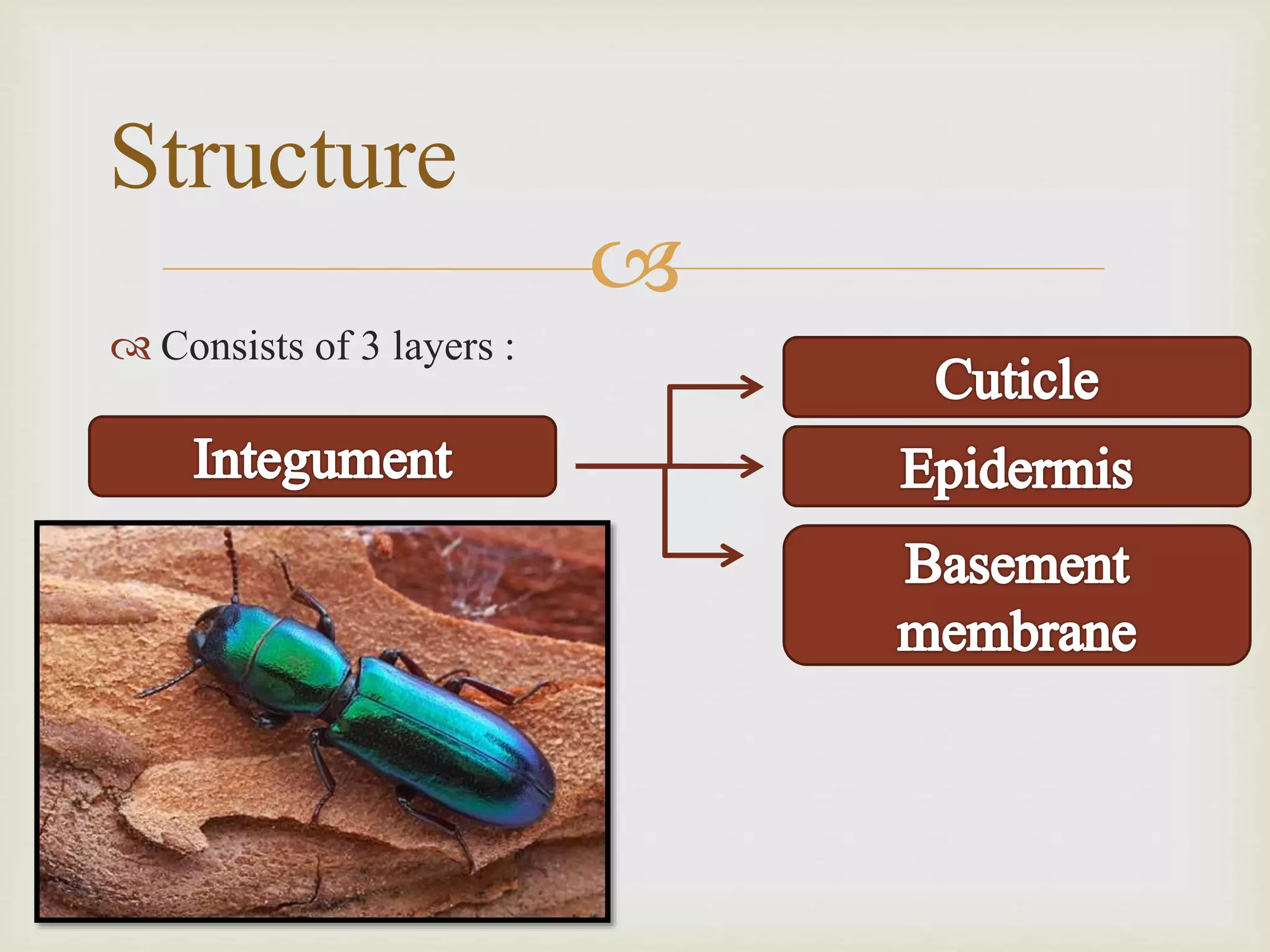
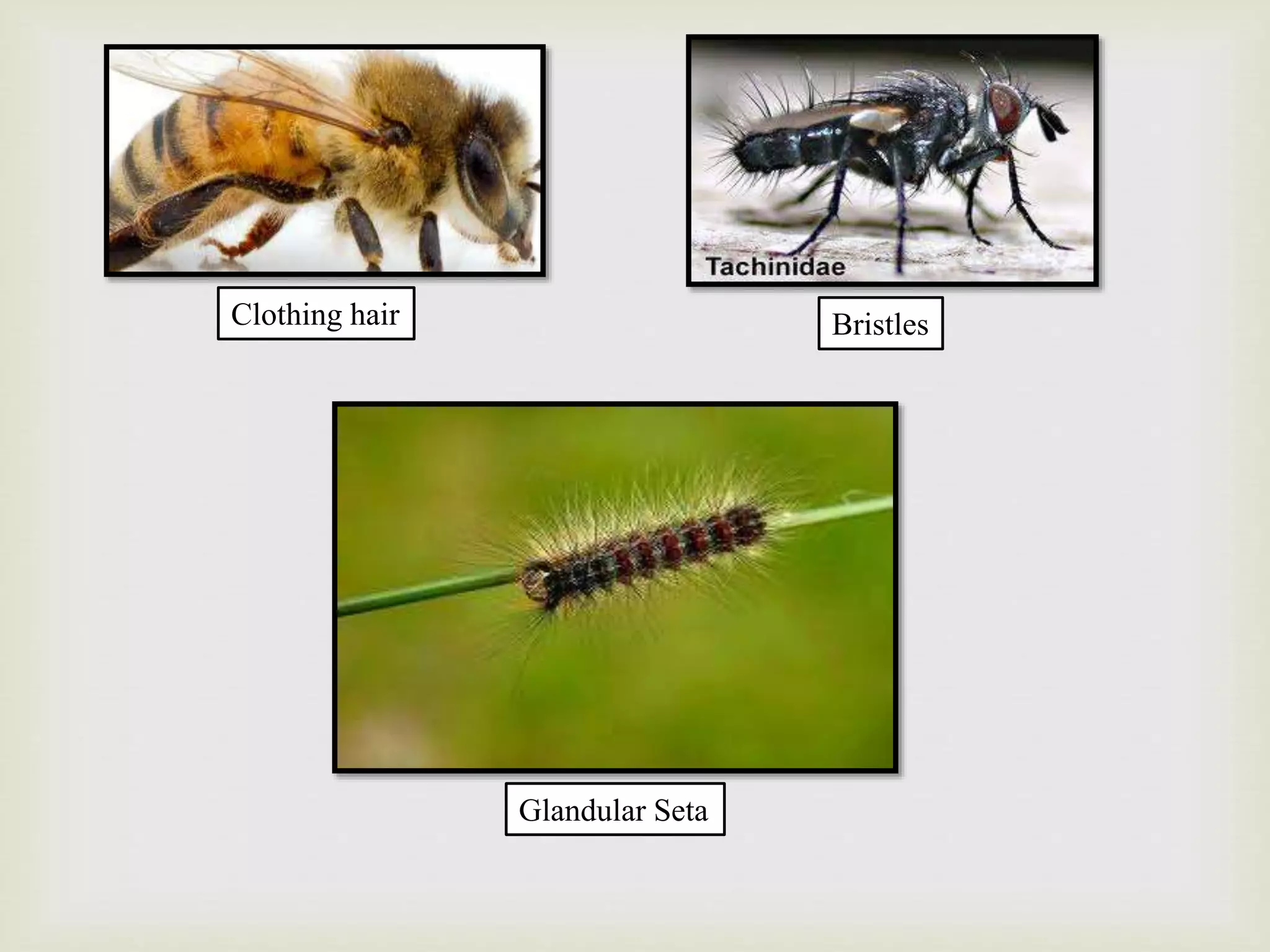
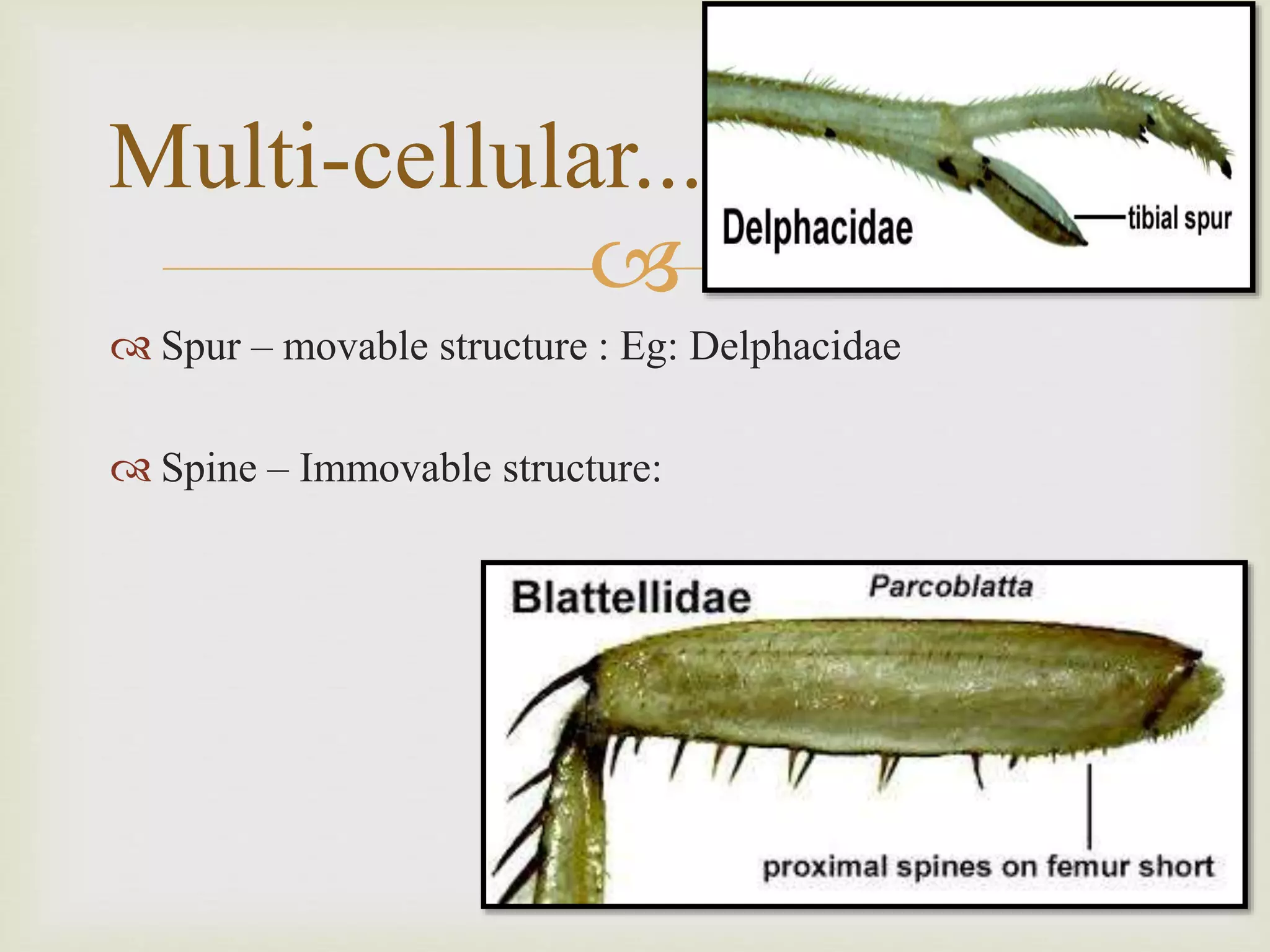
The document summarizes the structure and functions of the insect integument or exoskeleton. It consists of three layers - the outer non-cellular epicuticle layer with wax and cement layers, the thicker procuticle layer divided into outer exocuticle and inner endocuticle layers composed of chitin and proteins, and the inner epidermis layer. The integument provides protection, prevents water loss, allows for muscle attachment, and gives the insect its shape. It can have various appendages like hairs, scales, spines, and glands. The integument acts as an external armor and strengthens the insect while protecting internal organs.