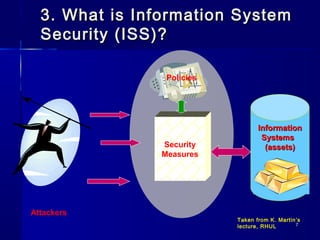
This document provides an introduction to information system security. It discusses key concepts like security, information security, vulnerabilities, threats, attacks, security policies, and security measures. The document outlines common security risks like interruption, interception, modification, masquerading, and repudiation. It explains that security policies provide guidelines for implementing security controls to protect information system assets from such risks according to the security principles of confidentiality, integrity, and availability.