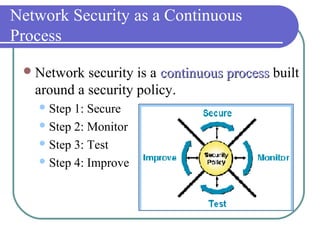
Information security involves protecting information and systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. It includes measures to ensure information availability, accuracy, authenticity, confidentiality and integrity. Network security aims to secure network components, connections and contents through authentication, encryption, firewalls and vulnerability patching in a continuous process of securing, monitoring, testing and improving security. Key related terms include assets, threats, vulnerabilities, risks, attacks, and countermeasures.