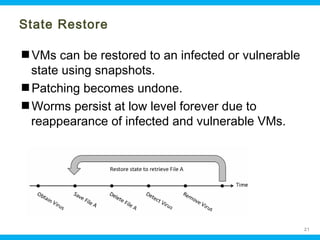
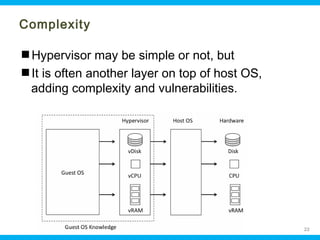
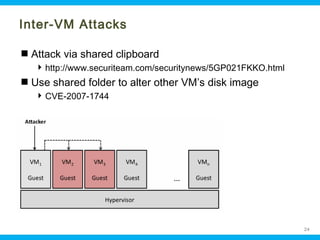
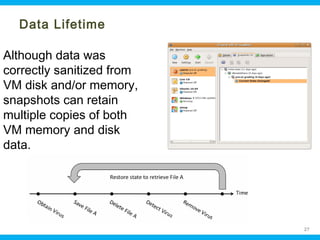
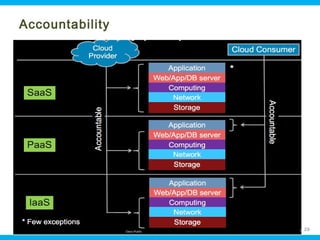
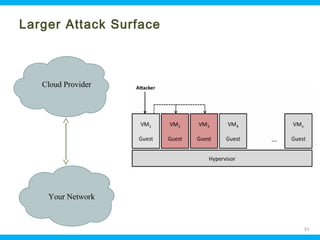
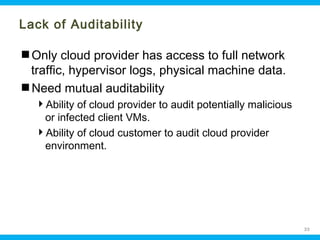
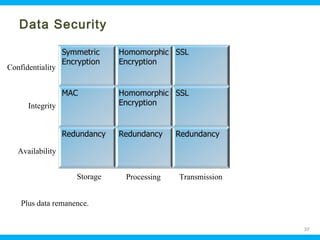
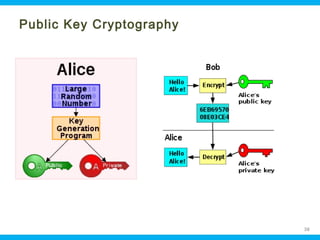
This document discusses security issues related to cloud computing. It begins by defining cloud computing and describing common cloud service and deployment models. It then outlines traditional security problems like data loss, downtime, and malware that still apply in cloud environments. New issues introduced by cloud characteristics like virtualization, multi-tenancy, and elastic scaling are also examined, such as virtualization vulnerabilities and lack of network perimeter control. The document concludes by focusing on data security challenges involving confidentiality, integrity and availability of data in transit, at rest, and in use within cloud platforms. Homomorphic encryption is presented as a potential solution for securely outsourcing computation on encrypted data.



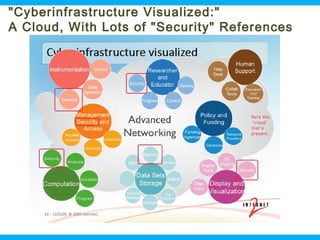
![Why Is "Security" Everywhere on That Slide?
Security is generally perceived as a huge issue for the cloud:
During a keynote speech to the Brookings Institution
policy forum, “Cloud Computing for Business and Society,”
[Microsoft General Counsel Brad] Smith also highlighted data
from a survey commissioned by Microsoft measuring
attitudes on cloud computing among business leaders and
the general population.
The survey found that while 58 percent of the general
population and 86 percent of senior business leaders are
excited about the potential of cloud computing, more than
90 percent of these same people are concerned
about the security, access and privacy of their own
data in
the cloud.
5
Ohio Information Security Forum
http://www.microsoft.com/presspass/press/2010/jan10/1-20BrookingsPR.mspx
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloud-security-131220185727-phpapp02/85/Cloud-Security-5-320.jpg)