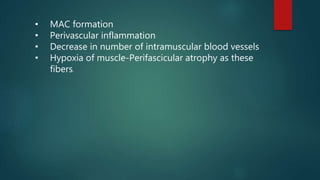
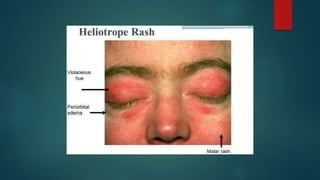
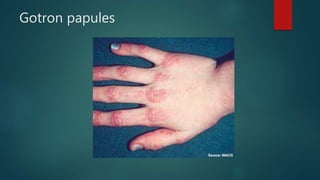
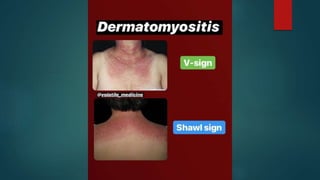
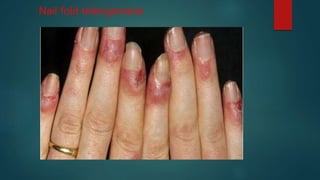
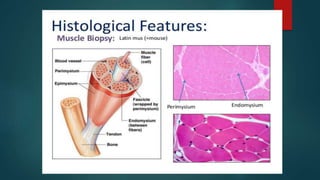
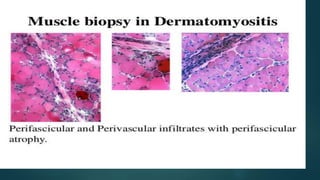
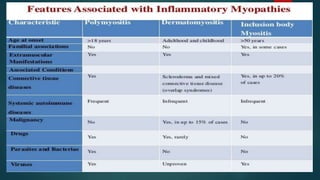
Inflammatory myopathies include dermatomyositis, polymyositis, and inclusion body myositis, primarily affecting muscle strength and causing fatigue and inflammatory symptoms, with a potential autoimmune origin. Clinical features include distinctive dermatologic manifestations such as heliotrope rash and Gottron's papules, with a significant risk of malignancy and interstitial lung disease. Diagnosis involves identifying immunoglobulin and complement deposits in muscle tissue, and elevated creatine kinase levels are common.