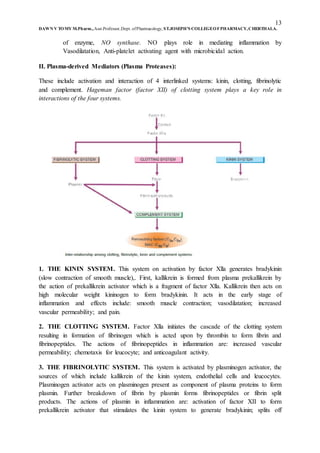
Inflammation is the body's response to eliminate injurious agents and damaged tissue. The four cardinal signs of inflammation are redness, swelling, heat, and pain. Inflammation can be classified as acute, chronic, or subacute based on its duration and the host's defense capacity. Acute inflammation involves fluid accumulation, platelet activation, and neutrophil infiltration within 2 weeks to repair tissue. Chronic inflammation lasts a long time and involves lymphocytes, plasma cells, and macrophages with granulation tissue formation. The inflammatory response involves vascular changes like vasodilation, increased permeability and leukocyte migration, as well as cellular events like phagocytosis to remove pathogens and debris.