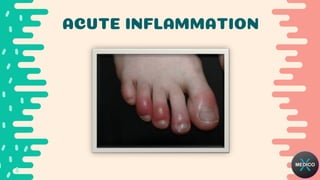
Acute inflammation is the body's initial response to harmful stimuli and involves both vascular and cellular events. The vascular events include increased blood flow, vascular permeability and blood vessel dilation. The cellular events include the recruitment of leukocytes from the bloodstream to the site of injury and their migration into tissues. This is followed by phagocytosis of pathogens and damaged cells by macrophages and neutrophils. Mediators of acute inflammation such as histamine, cytokines and complement proteins are released from cells to promote the inflammatory response. The response and its outcomes can vary depending on factors related to the host and the causative agent.








































![Nitric oxide [NO];
L- arginine NO
Guanylate cyclase Inhibits Calcium channel
cGMP
Smooth muscle relaxation
vasodilation
NOS
eNOS iNOS nNOS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acuteinflammationdated20thfeb21-210228074053/85/Acute-inflammation-Pathology-X_patho-42-320.jpg)























