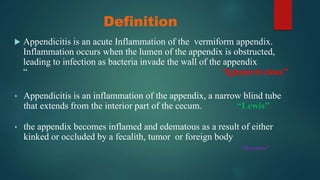
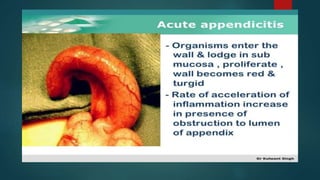
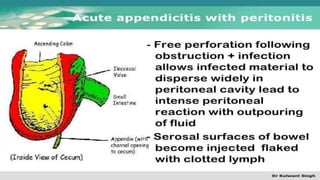
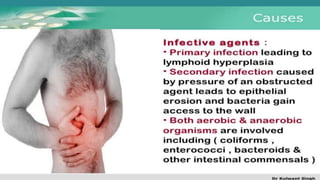
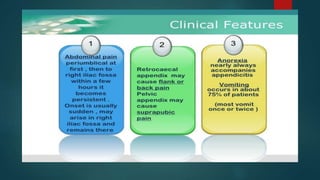
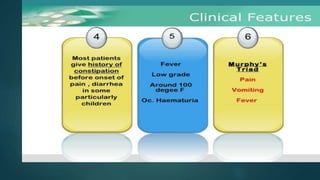
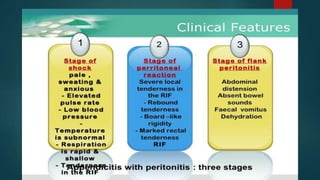
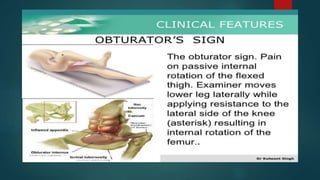
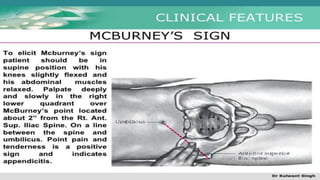
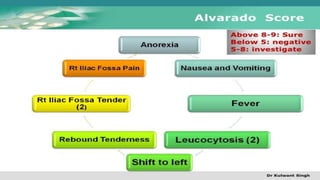
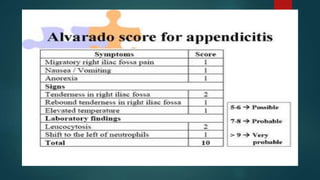
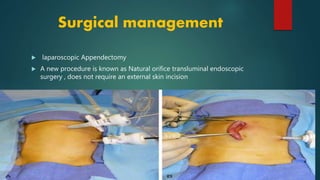
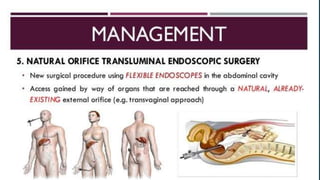
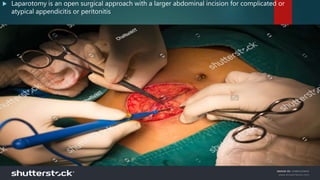
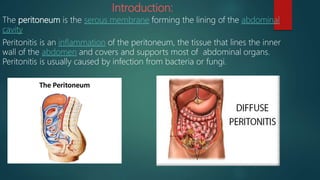
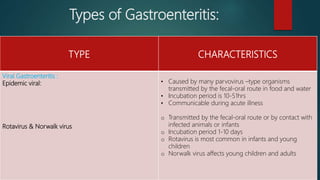
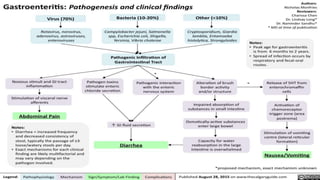
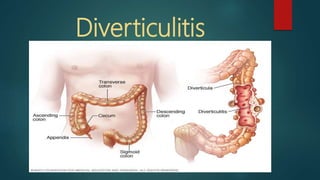
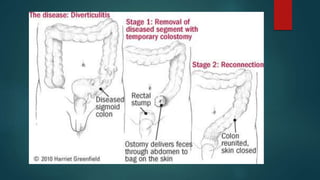
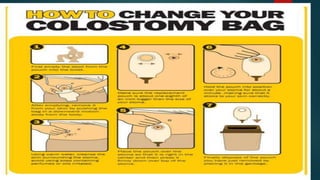
The document discusses inflammatory intestinal disorders, particularly focusing on appendicitis, peritonitis, gastroenteritis, and diverticulitis. It details the causes, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluations, and management approaches for each condition. Appendicitis is characterized by obstruction and inflammation of the appendix, peritonitis involves inflammation of the peritoneum due to infection, gastroenteritis is inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract leading to diarrhea and vomiting, and diverticulitis results from inflammation of diverticula in the colon.