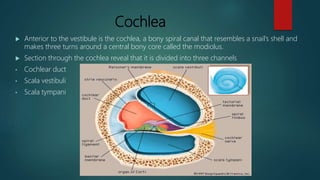
The internal ear, also called the labyrinth, has a bony and membranous portion. The bony labyrinth contains the semicircular canals for balance and the cochlea for hearing. The membranous labyrinth sits inside the bony labyrinth and contains the vestibule, semicircular ducts, and cochlear duct. The cochlea is coiled like a snail shell and contains the organ of Corti with hair cells that detect sound vibrations.