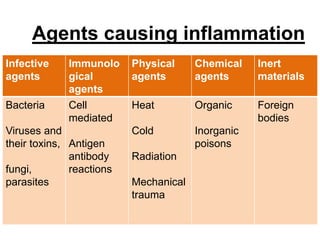
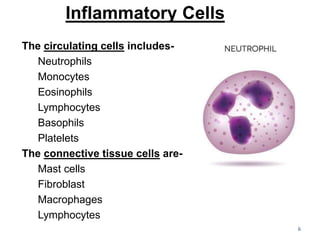
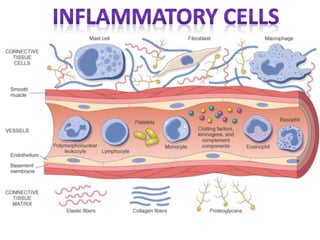
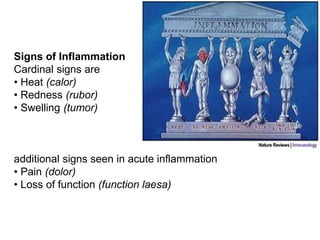
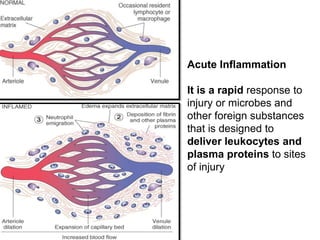
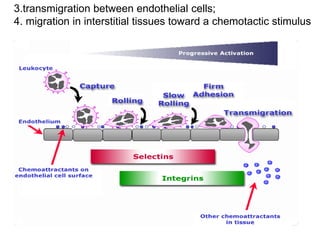
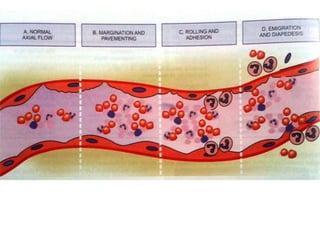
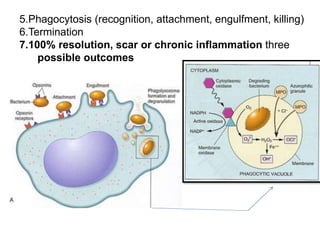
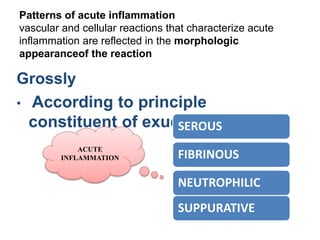
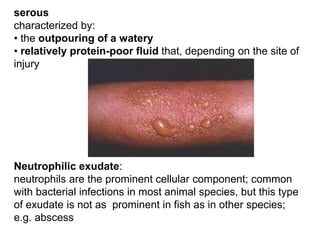
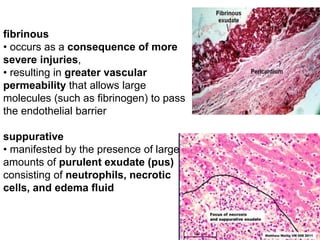
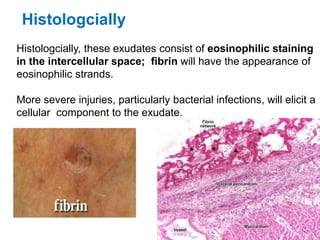
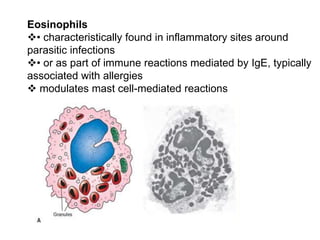
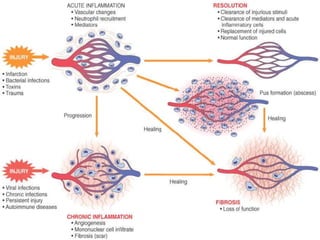
1. Inflammation is the body's protective response to injury or infection that involves blood vessels, immune cells, and chemical mediators.
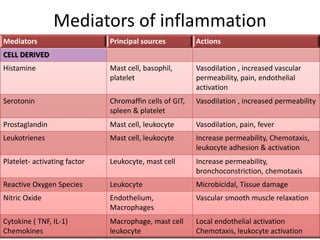
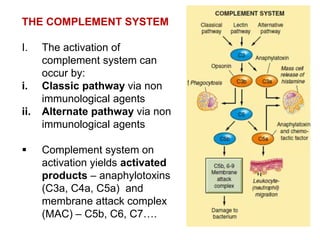
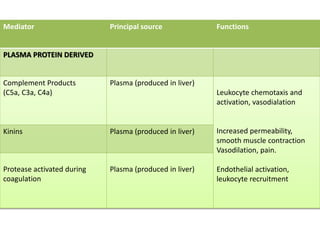
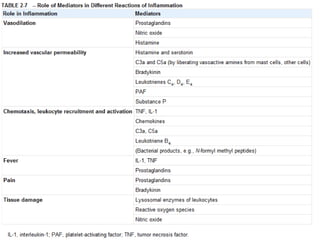
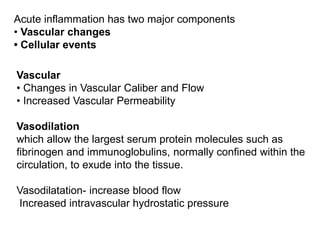
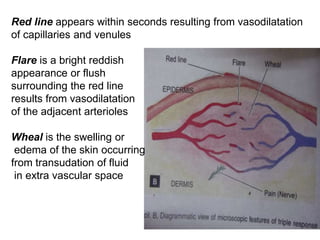
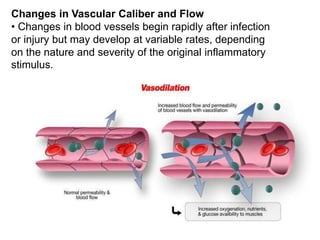
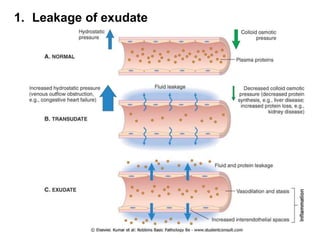
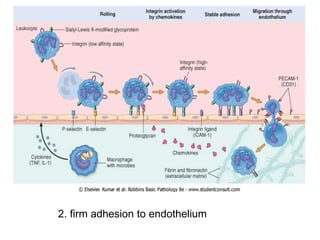
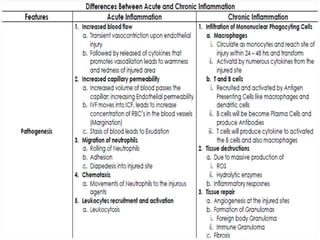
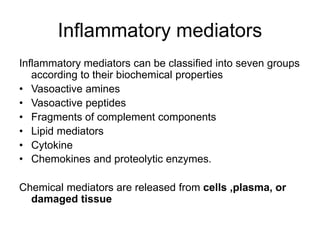
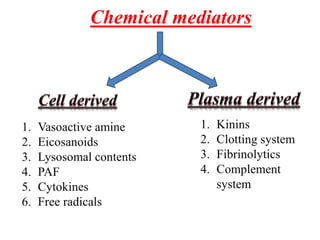
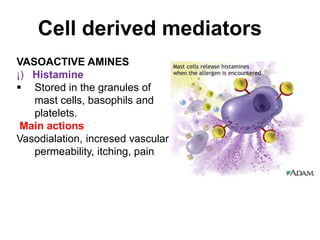
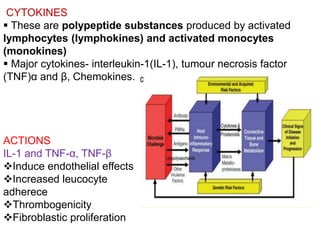
2. Chemical mediators of inflammation include vasoactive amines, peptides, lipid mediators, cytokines, and enzymes that are released from immune cells and damaged tissues. These mediators cause changes like increased blood flow and vascular permeability.
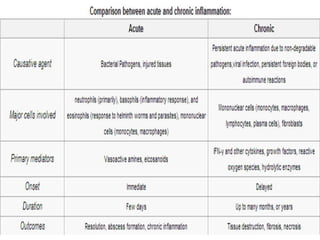
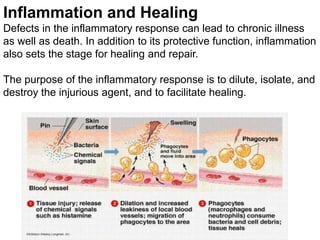
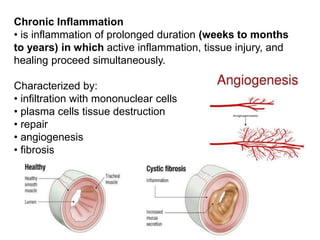
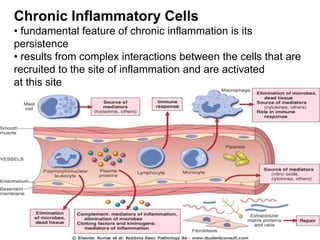
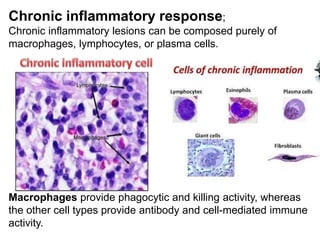
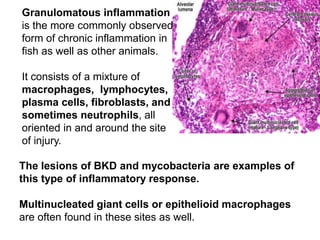
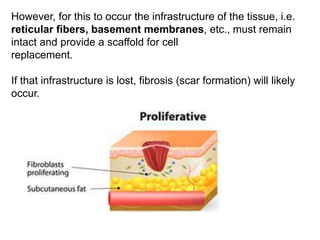
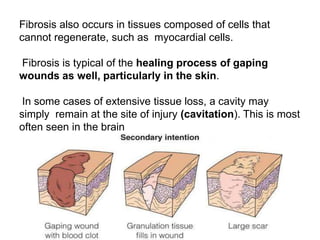
3. The inflammatory response aims to destroy and isolate the injurious agent while facilitating tissue repair. Prolonged inflammation can lead to chronic disease if the trigger persists.





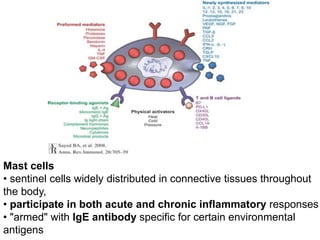

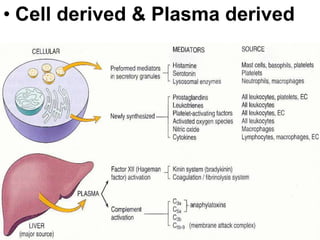
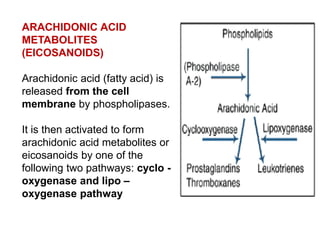
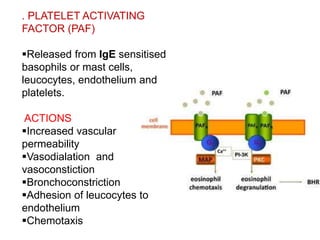
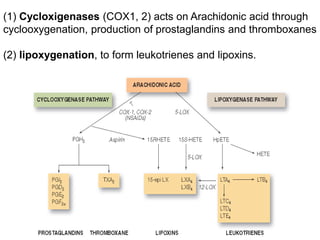
![(1)derived from metabolism of phospholipids and arachidonic acid
(e.g., prostaglandins, thromboxanes, leukotrienes, lipoxins,
platelet-activating factor [PAF])
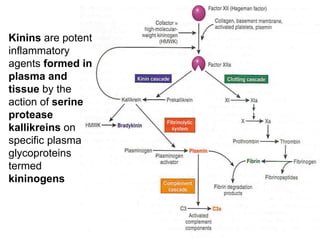
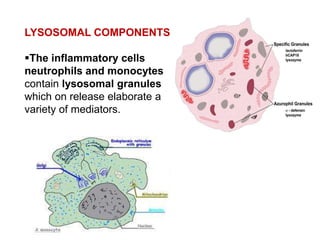
(2) preformed and stored in cytoplasmic granules (e.g.,histamine,
serotonin, lysosomal hydrolases),
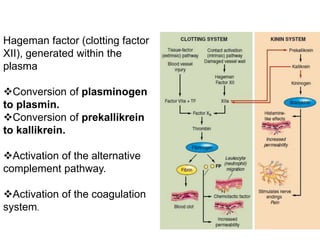
(3) derived from altered production of normal regulators of vascular
function (e.g., nitric oxide and neurokinins).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inflammation-161203134322/85/Inflammation-in-skin-49-320.jpg)