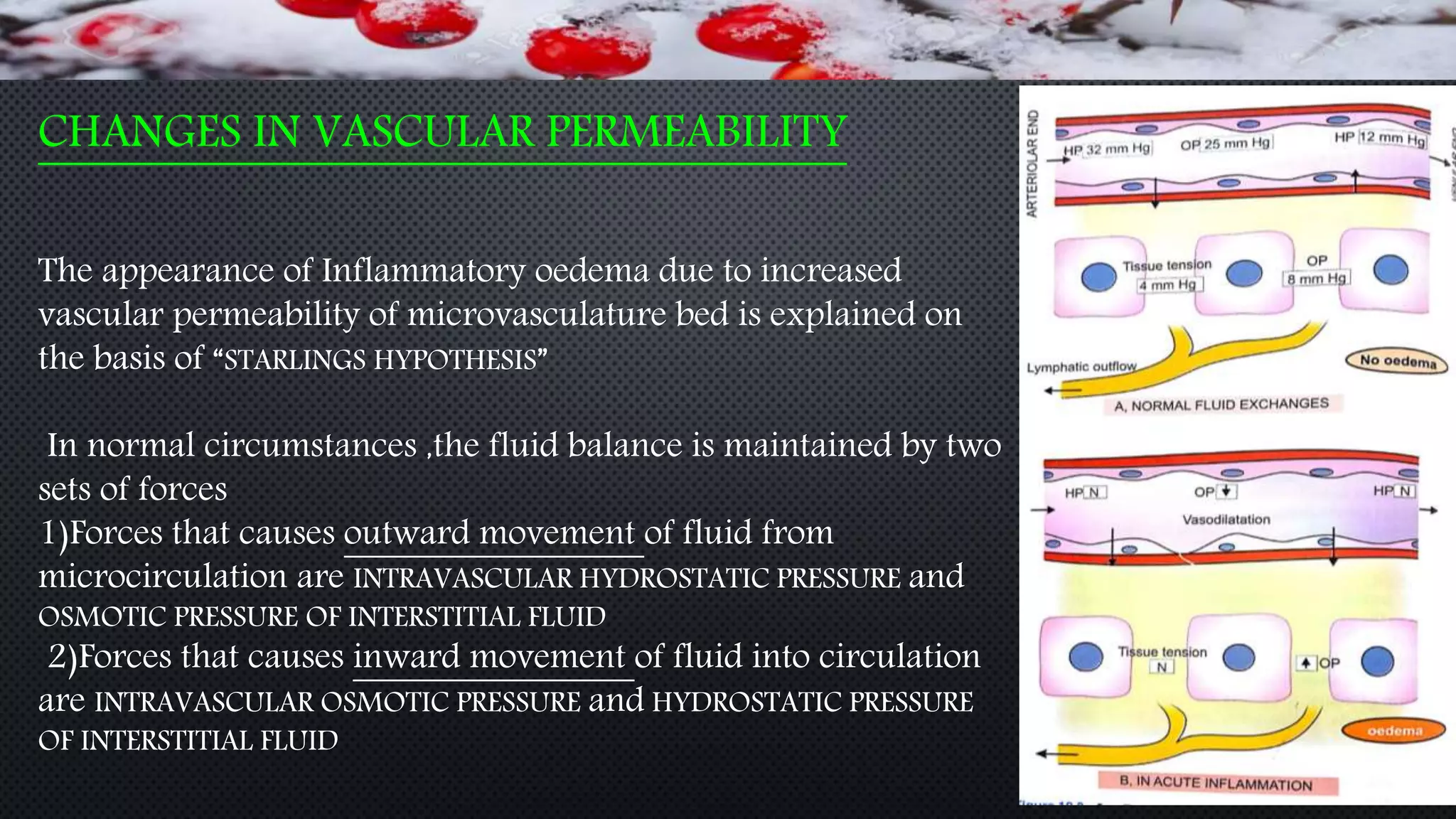
The document provides an extensive overview of inflammation and wound healing, defining inflammation as a protective response to tissue injury and outlining its causes, types, and cellular events. It details the mechanisms of acute inflammation, including chemical mediators, and describes the processes of healing through repair and regeneration, emphasizing the differences between healing by first and second intention. Additionally, it discusses factors influencing wound healing and the phases involved in the healing process from initial injury through recovery.