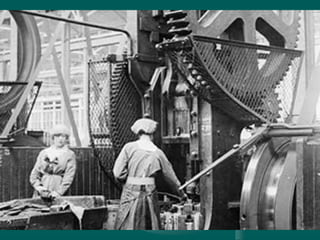
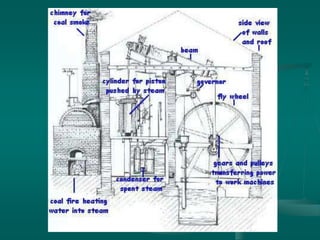
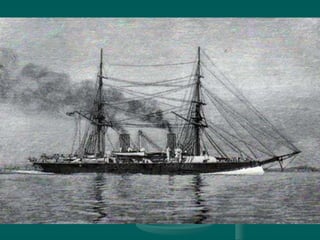
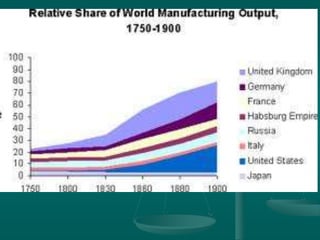
The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain in the late 18th century and spread to other Western European countries, the United States, Russia, and Japan in the 19th century. It involved a transition from manual labor and animal or water power to machine production using steam power in factories. This led to increased production, specialization of labor, and a shift from rural home production to urban factory work. The Industrial Revolution brought both benefits like improved production but also social problems such as child labor and poor working conditions.