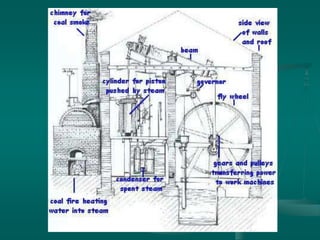
The Industrial Revolution transformed societies through industrialization in Western Europe, the United States, and later Japan during the 19th century. It introduced factories powered by new technologies like steam engines, which replaced human and animal labor. This led to massive social changes like urbanization, new divisions of social class, and changes in family structures. While industrialization provided economic growth and technological progress, it also had negative consequences for workers and the environment, including dangerous working conditions, pollution, low wages, and lack of regulations. Responses to these issues included government reforms and the rise of labor unions and radical groups advocating for workers' rights.