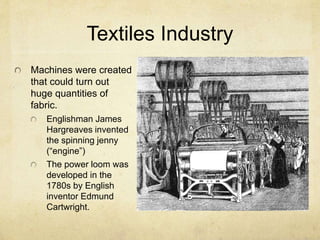
The Industrial Revolution began in Britain and caused widespread economic, technological, and social changes. Britain was able to industrialize first due to its coal resources, iron production, intellectual climate allowing innovation, and global colonial trade networks. Key developments included the steam engine, which improved transportation by land and sea, and new textile machines that vastly increased fabric production. The factories created many new jobs and ultimately led to a more prosperous, educated, and socially mobile society.