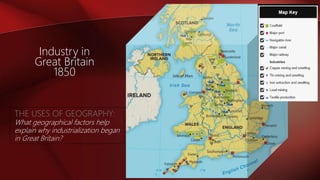
The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain in the late 18th century due to several key factors: abundant natural resources like coal and iron ore, a growing population and food supply that created a labor force, and entrepreneurs willing to invest in new technologies. The cotton industry was transformed by inventions like the spinning jenny and powered loom that increased production. This led to a shift from cottage industries to factory work, bringing difficult conditions for many workers. The Industrial Revolution then spread across Europe and to the United States in the 19th century, fundamentally changing economies and societies.