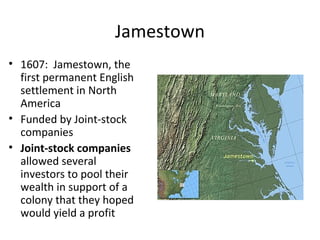
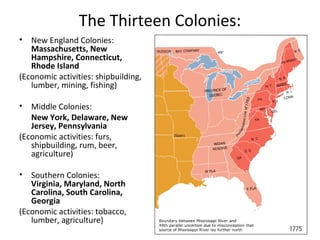
The early British colonies were established for economic reasons, with the first being Jamestown in 1607. Tobacco became a profitable crop in Virginia while indentured servitude provided labor. Self-governance emerged through entities like the Virginia House of Burgesses and Mayflower Compact. Puritans founded colonies like Plymouth and Massachusetts Bay to escape religious persecution in England. The 13 original colonies developed diverse economies while remaining tied to England through the Navigation Acts; however, they gained a growing spirit of self-determination.