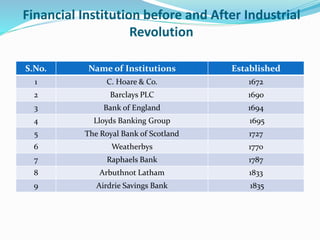
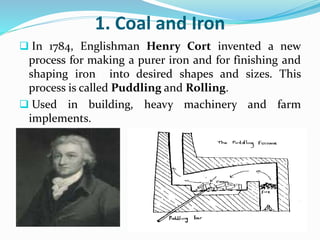
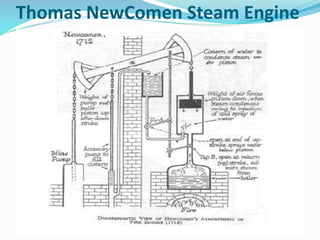
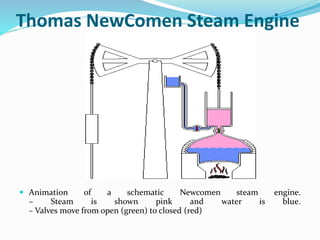
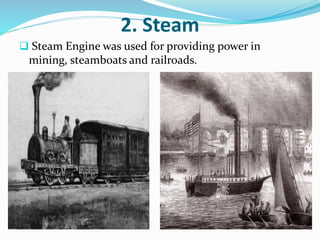
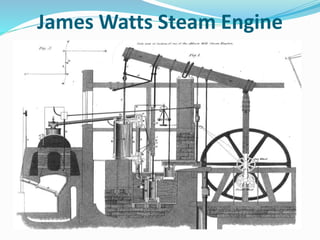
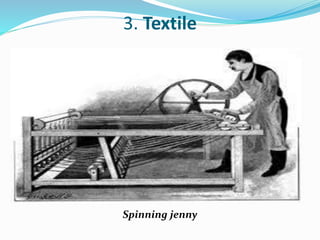
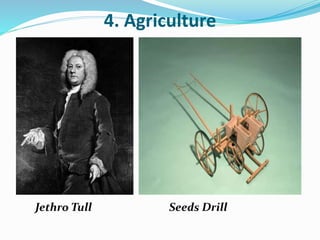
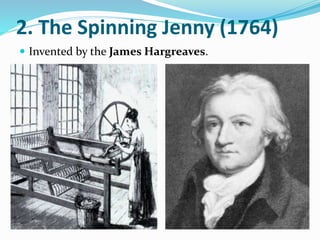
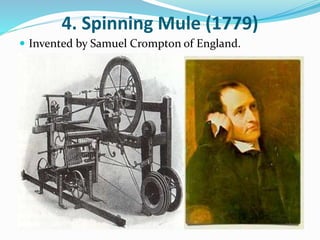
The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain in the late 18th century and led to rapid industrialization and major social changes. New machines were invented to increase production in textiles, iron manufacturing, and other industries. Steam power was also developed to help power factories. As a result, there was a mass movement of people from rural areas to cities to work in the new factories. The Industrial Revolution transformed economies and had widespread effects on social, cultural, and economic conditions.