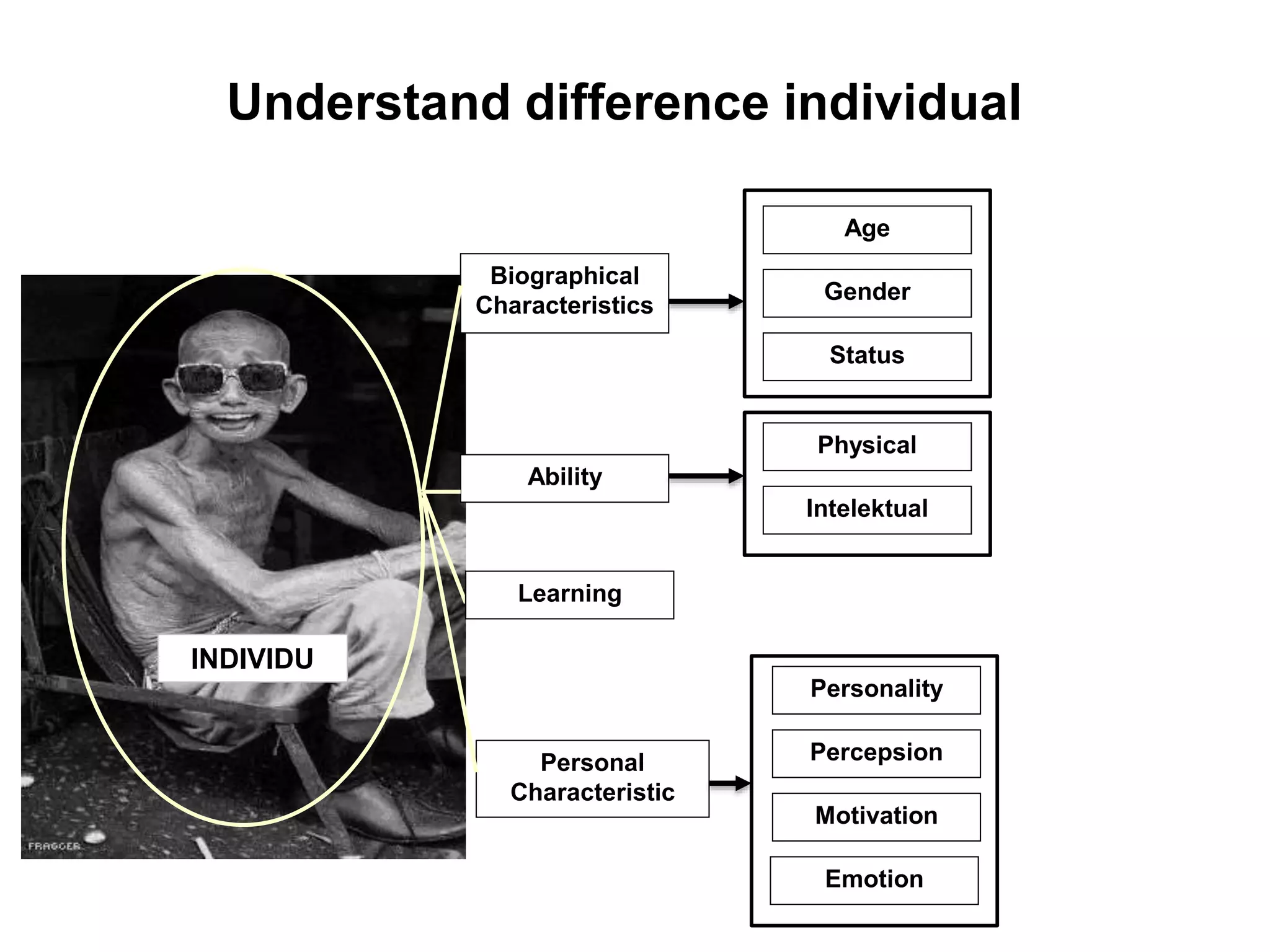
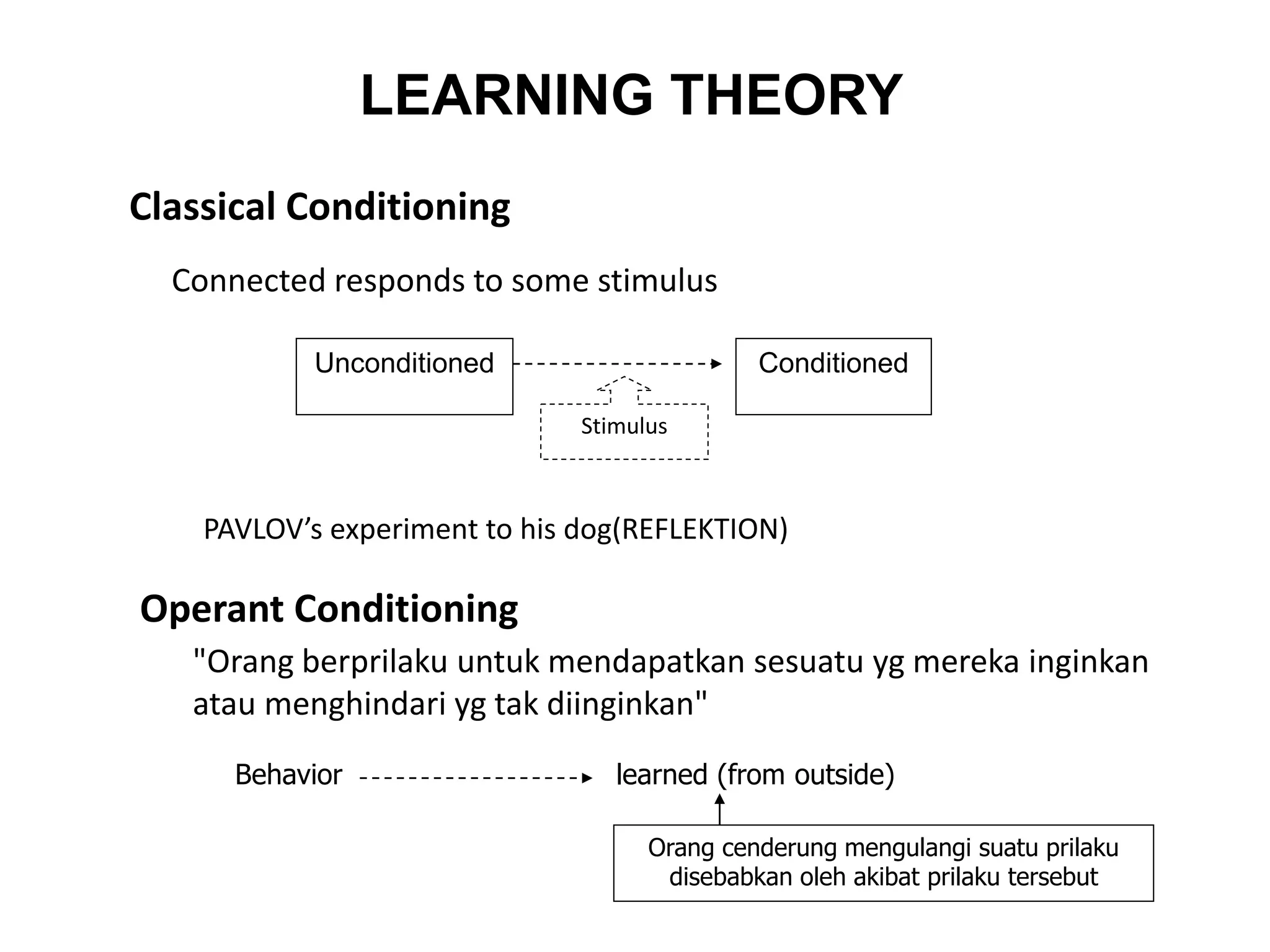
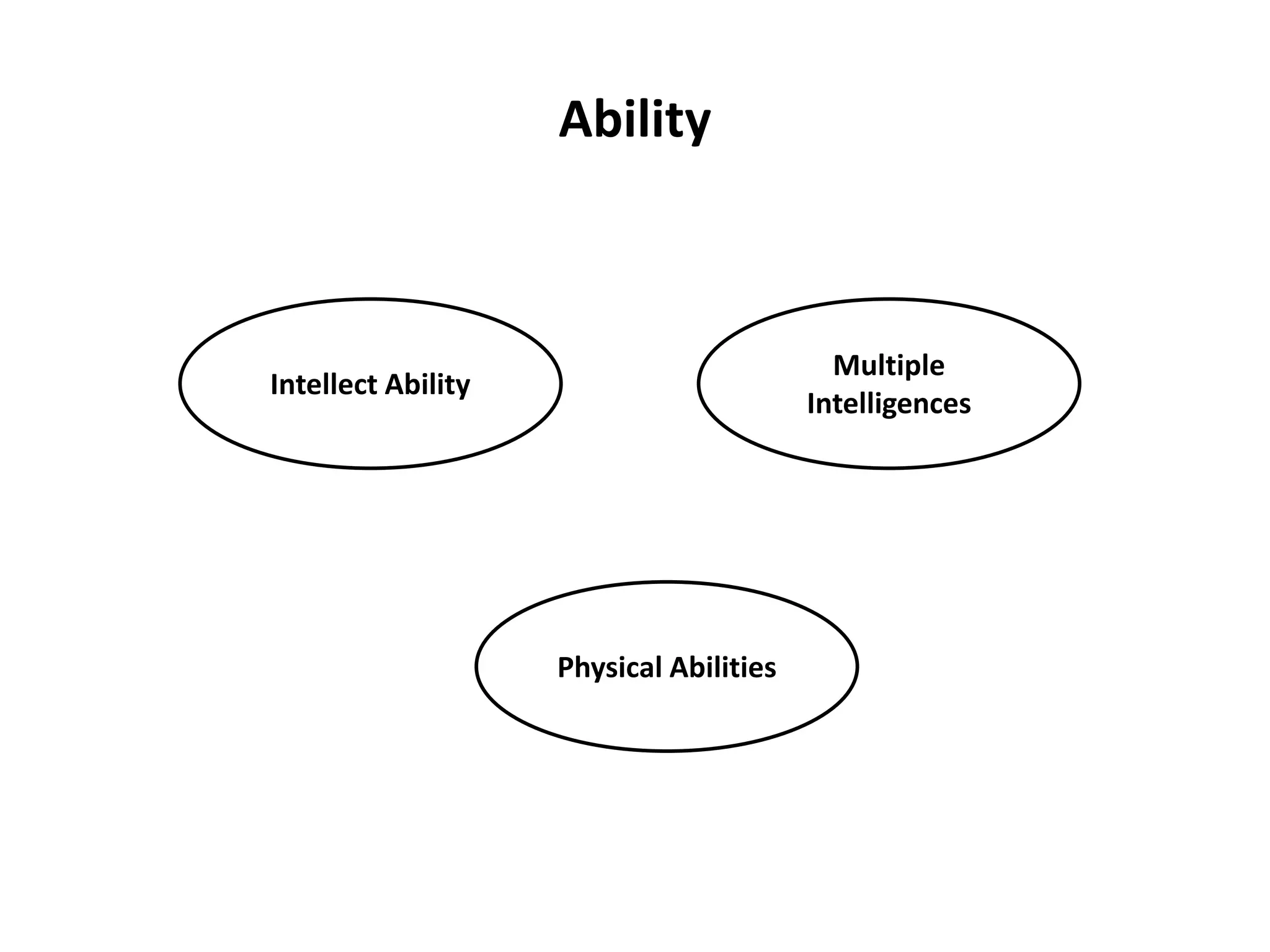
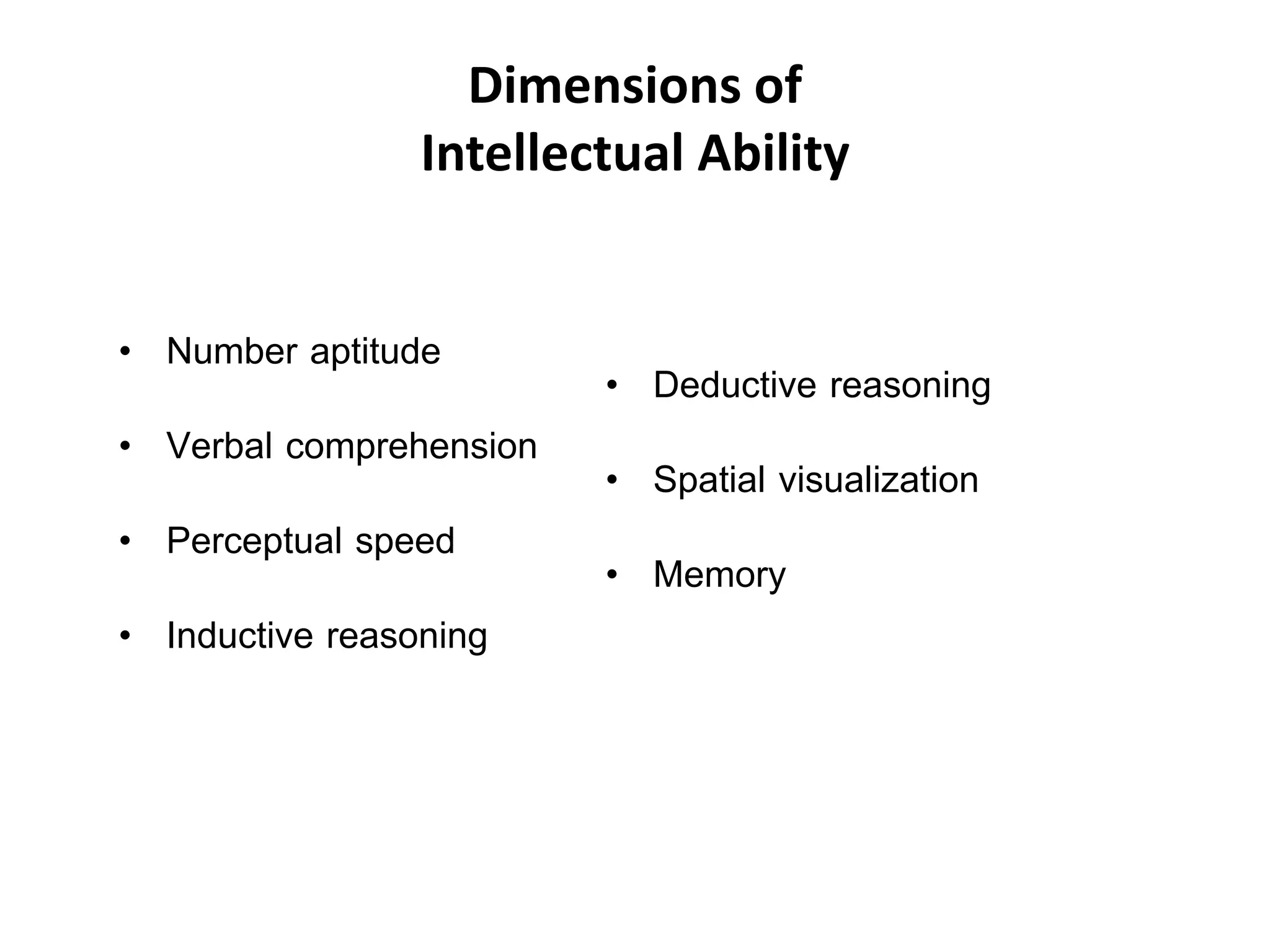
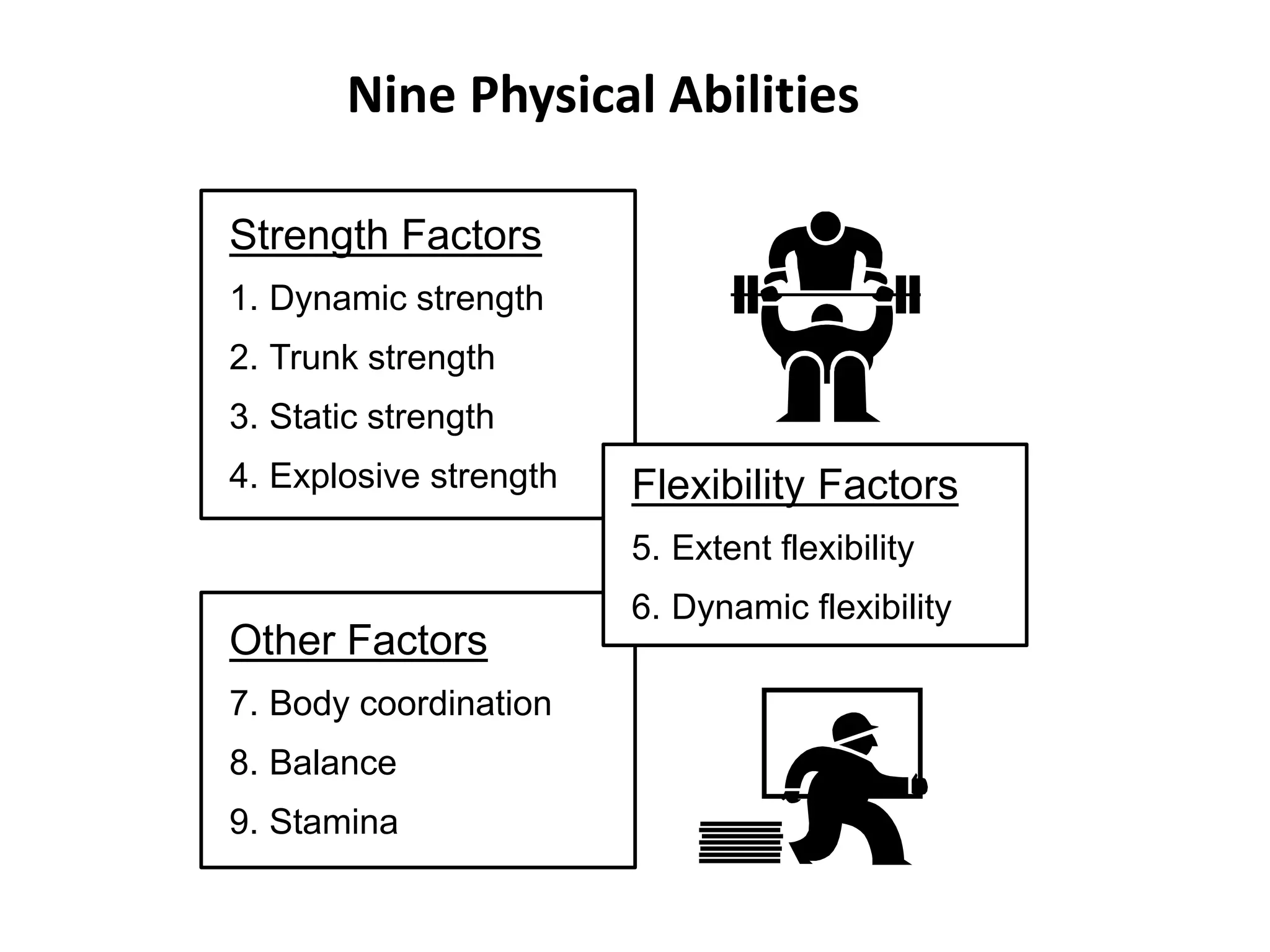
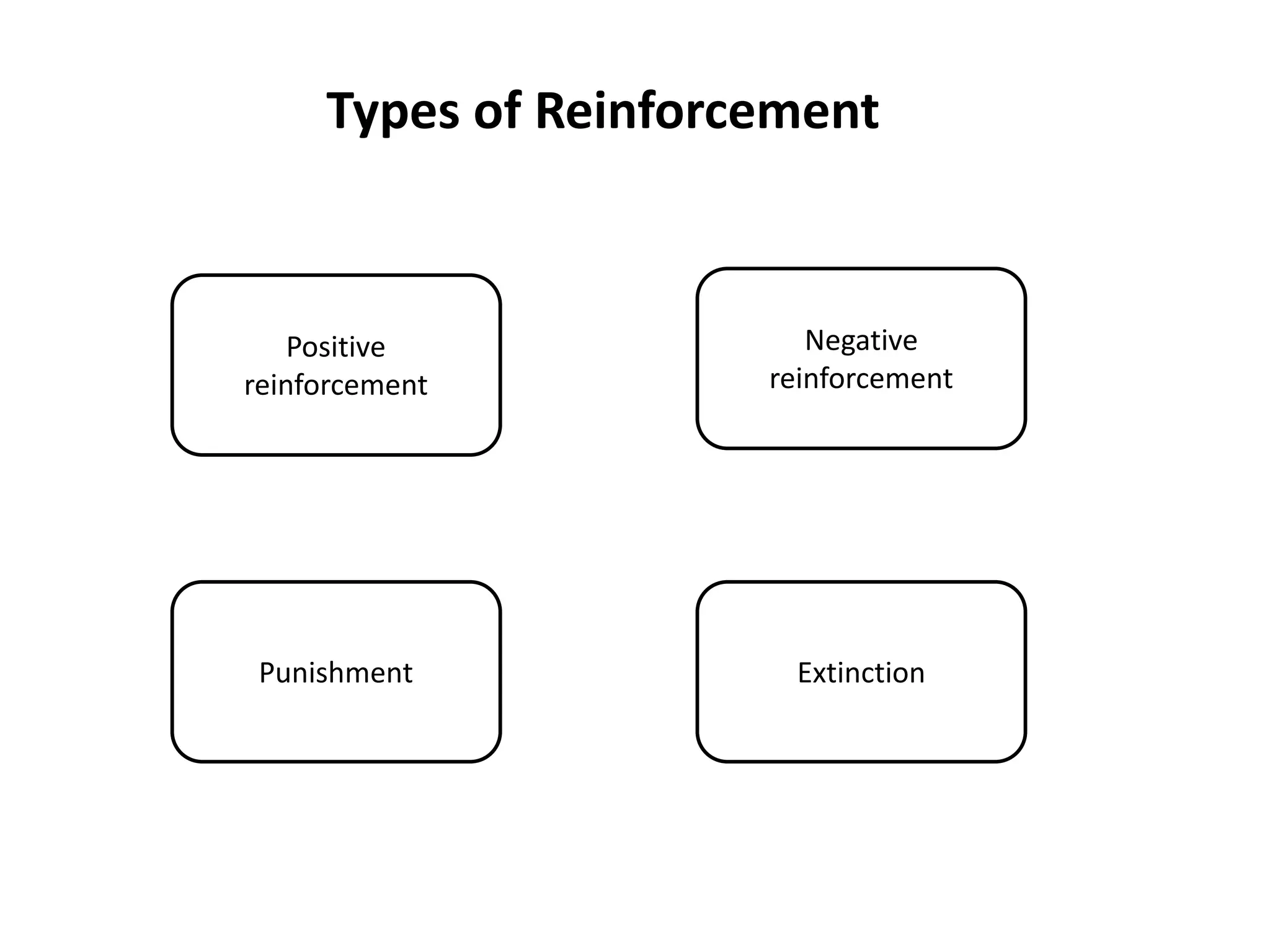
This document discusses individual learning and defines key related concepts. It begins by defining learning as a relatively permanent change in behavior resulting from experience. It then defines individuals as the smallest units that make up society and notes that while individuals have shared characteristics as members of a group, they also have unique attributes. The document goes on to describe individual learning as the capacity to build knowledge through personal reflection and experience, mediated by interactions with others and the environment. It asserts that while social context provides support, learning itself is an individual process. The document then discusses various factors that influence individual learning, such as biographical characteristics, abilities, personality and learning theories.