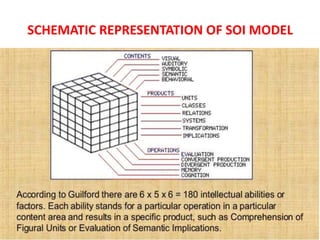
J.P. Guilford proposed the Structure of Intellect (SOI) model to describe 180 different types of intellectual abilities. The SOI model categorizes abilities into three dimensions: operations (6 types of thinking processes), content (5 types of information), and products (6 types of outcomes). Each combination of one operation, one content, and one product defines a specific intellectual ability. The model suggests intelligence involves distinct skills that can be improved through training. It also implies curriculum should incorporate different combinations of operations, content, and products to develop students' intellects based on their individual differences.